Archive:Development/Tutorials/Using KXmlGuiWindow (zh TW)
Development/Tutorials/Using_KXmlGuiWindow
Languages: عربي | Asturianu | Català | Česky | Kaszëbsczi | Dansk | Deutsch | English | Esperanto | Español | Eesti | فارسی | Suomi | Français | Galego | Italiano | 日本語 | 한국어 | Norwegian | Polski | Português Brasileiro | Română | Русский | Svenska | Slovenčina | Slovenščina | српски | Türkçe | Tiếng Việt | Українська | 简体中文 | 繁體中文
Template:TutorialBrowser (zh TW)
摘要
本教學承接上一講第一個程式教學,進一步介紹 KXmlGuiWindow 類別的使用。
在上一講中,程式只是彈出了一個對話框。在本講中,我們要讓我們的程式具備更加實際功能。
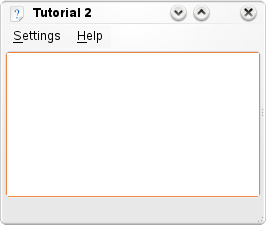
KXmlGuiWindow
KXmlGuiWindow 提供完整的主視窗檢視包含選單列、工具列、狀態列和中央的主區域。大多數KDE應用程式會衍生此類別,因為它提供了一個簡單的方法,透過XML檔案定義選單和工具列的排版(這種技術稱為XMLGUI)。雖然我們不會使用 XMLGUI 在本教學中,但下一課我們會用到它。
為了使用 KXmlGuiWindow,我們必須對它子類別化。因此,我們創建兩個檔案, mainwindow.cpp 和 mainwindow.h 放置我們的程式碼。
mainwindow.h
- ifndef MAINWINDOW_H
- define MAINWINDOW_H
- include <KXmlGuiWindow>
- include <KTextEdit>
class MainWindow : public KXmlGuiWindow
{
public:
MainWindow(QWidget *parent=0);
private:
KTextEdit* textArea;
};
- endif
首先,我們在第7行宣告 KXmlGuiWindow 的子類別:class MainWindow : public KXmlGuiWindow。
接下來我們宣告一個建構子 MainWindow(QWidget *parent=0); 。
最後我們宣告了一個指標,它指向構成我們程式主體的物件。KTextEdit 是一個通用的文字編輯器,並具有很多 KDE 特有的優點,如游標自動隱藏等。
mainwindow.cpp
- include "mainwindow.h"
MainWindow::MainWindow(QWidget *parent) : KXmlGuiWindow(parent)
{
textArea = new KTextEdit();
setCentralWidget(textArea);
setupGUI();
}
首先,很自然的,我們在第一行含入(include)有類別宣告的標頭檔(header file)。
在第五行,我們初始化了文字編輯器物件。接下來在第6行,我們使用 KXmlGuiWindow 內建的 setCentralWidget() 函數,它告訴 KXmlGuiWindow 什麼東西應該顯示在視窗的中央。
最後,呼叫 KXmlGuiWindow::setupGUI(),它會替我們完成很多底層的工作,並創建一個預設的選單列(包含 Settings 和 Help)。
回到 main.cpp
為了能夠實際運行前面定義的視窗,我們還需要在 main.cpp 中增加幾行:
main.cpp
- include <KApplication>
- include <KAboutData>
- include <KCmdLineArgs>
- include <KLocale>
- include "mainwindow.h"
int main (int argc, char *argv[])
{
KAboutData aboutData( "tutorial2", 0,
ki18n("Tutorial 2"), "1.0",
ki18n("A simple text area"),
KAboutData::License_GPL,
ki18n("Copyright (c) 2007 Developer") );
KCmdLineArgs::init( argc, argv, &aboutData );
KApplication app;
MainWindow* window = new MainWindow();
window->show();
return app.exec();
}
與教學1相比,唯一新增的就是第6、18和19行。在第18行,我們生成了一個 MainWindow 物件實例,然後在第19行顯示它。
CMake
The best way to build the program is to use CMake. All that's changed since tutorial 1 is that mainwindow.cpp has been added to the sources list and any tutorial1 has become tutorial2.
CMakeLists.txt
project (tutorial2)
find_package(KDE4 REQUIRED)
include_directories(${KDE4_INCLUDES})
set(tutorial2_SRCS
main.cpp
mainwindow.cpp
)
kde4_add_executable(tutorial2 ${tutorial2_SRCS})
target_link_libraries(tutorial2 ${KDE4_KDEUI_LIBS})
Compile it
To compile, link and run it, use:
mkdir build && cd build cmake .. make ./tutorial2
繼續前進
現在你可以開始學習下一課:使用 KActions。
