Development/Tutorials/First program (csb)
Development/Tutorials/First_program
Languages: عربي | Asturianu | Català | Česky | Kaszëbsczi | Dansk | Deutsch | English | Esperanto | Español | Eesti | فارسی | Suomi | Français | Galego | Italiano | 日本語 | 한국어 | Norwegian | Polski | Português Brasileiro | Română | Русский | Svenska | Slovenčina | Slovenščina | српски | Türkçe | Tiếng Việt | Українська | 简体中文 | 繁體中文
| Tutorial Series | Tutorial dlô zaczinającëch |
| Previous | C++, Qt, KDE4 development environment |
| What's Next | Tutorial 2 - KXmlGuiWindow |
| Further Reading | CMake |
Abstract
Twòjô pierszô programa mô witac swiat drësznym "Witôj Swiece". Do tegò ùżëjemë KMessageBox ë dodómë swòje nôdpisë do knąpów.


Przeczëtôj nen tutorial abë ùstawic dobrze KDevelop dlô nech dzejaniów. Nôpierwi chcesz sprôwdzëc, czë ùstôwë robią co do nich słëchô òtmëkającë bëtną aplikacëjã KDE 4 w KDevelop.
Równak bãdzesz wcyg mùszôł editowac CMake rãczno..
Kòd
Wszëtczé kòdë jaczich je nót to le jeden lopk: main.cpp. Ùsôdzë gò z kòdã pòdónym niżi:
- include <KApplication>
- include <KAboutData>
- include <KCmdLineArgs>
- include <KMessageBox>
int main (int argc, char *argv[])
{
KAboutData aboutData(
// Miono programë brëkòwóné bùtën.
"tutorial1",
// Miono katalogù wiadła
// Jeżlë ni ma, miono programù mdze brëkòwóné.
0,
// Miono jaczé sã wëskrzeni.
ki18n("Tutorial 1"),
// Wersëjô programë.
"1.0",
// Krótczi òpisrnk co robi aplikacëjô.
ki18n("Displays a KMessageBox popup"),
// Licencëjô kòdu
KAboutData::License_GPL,
// Aùtorsczi prawa
ki18n("(c) 2007"),
// Òptacëjny tekst wëskrzeniony w òknie Ò programie.
// Mòże tam bëc co le chcesz...
ki18n("Some text..."),
// Domôcô starna programë.
"http://tutorial.com/",
// Adresa e-mail dlô repòrtowaniô felów.
"[email protected]");
KCmdLineArgs::init( argc, argv, &aboutData );
KApplication app;
KGuiItem yesButton( i18n( "Hello" ), QString(),
i18n( "This is a tooltip" ),
i18n( "This is a WhatsThis help text." ) );
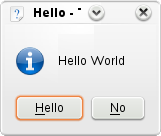
KMessageBox::questionYesNo( 0, i18n( "Hello World" ),
i18n( "Hello" ), yesButton );
return 0;
}
The first KDE specific code we come across in this program is KAboutData. This is the class used to store information about the program such as a short description, authors or license information. Pretty much every KDE application should use this class.
Then we come to KCmdLineArgs. This is the class one would use to specify command line switches to, for example, open the program with a specific file. However, in this tutorial, we simply initialise it with the KAboutData object we created so we can use the --version or --author switches.
Then we create a KApplication object. This needs to be done exactly once in each program since it is needed for things such as i18n.
Now we've done all the necessary KDE setup, we can move on to doing interesting things with our application. We're going to create a popup box but we're going to customise one of the buttons. To do this customisation, we need to use a KGuiItem object. The first argument in the KGuiItem constructor is the text that will appear on the item (in our case, a button). Then we have an option of setting an icon for the button but we don't want one so we just give it QString(). We then set the tooltip (what appears when you hover over an item) and finally the "What's This?" (accessed through right-clicking or Shift-F1) text.
Now we have our item, we can create our popup. We call the KMessageBox::questionYesNo() function which, by default, creates a message box with a "Yes" and a "No" button. The second argument is the text that will appear in the message box above the buttons. The third is the caption the window will have and finally we set the KGuiItem for (what would normally be) the "Yes" button to the KGuiItem guiItem we created.
Note that all user-visible text is passed through the i18n() function; this is necessary for the UI to be translatable. More information on localization can be found in the localization tutorial.
We're all done as far as the code is concerned. Now to build it and try it out.
Bùdowanié
You want to use CMake for your build environment. You provide a file CMakeLists.txt, cmake uses this file to generate all Makefiles out of it.
CMakeLists.txt
Create a file named CMakeLists.txt in the same directory as main.cpp with this content:
project (tutorial1)
find_package(KDE4 REQUIRED)
include (KDE4Defaults)
include_directories(${KDE4_INCLUDES})
set(tutorial1_SRCS main.cpp)
kde4_add_executable(tutorial1 ${tutorial1_SRCS})
target_link_libraries(tutorial1 ${KDE4_KDEUI_LIBS})
install(TARGETS tutorial1 ${INSTALL_TARGETS_DEFAULT_ARGS})
The find_package() function locates the package that you ask it for (in this case KDE4) and sets some variables describing the location of the package's headers and libraries. In this case we will use the KDE4_INCLUDES variable which contains the path to the KDE4 header files.
In order to allow the compiler to find these files, we pass that variable to the include_directories() function which adds the KDE4 headers to the header search path.
Next we create a variable called tutorial1_SRCS using the set() function. In this case we simply set it to the name of our only source file.
Then we use kde4_add_executable() to create an executable called tutorial1 from the source files listed in our tutorial1_SRCS variable. Afterwards, we link our executable to the KDE4 kdeui library using target_link_libraries() and the KDE4_KDEUI_LIBS variable which was set by the find_package() function. The line starting with install writes a default "install" target into the Makefile.
Wëkònôj ë zrëszë
Mòżesz rãczno wëwòłac CMake:
mkdir build && cd build cmake .. # Bôczë na ne dwa pùnktë - to nie fela, le òdwòłanié do katalogù wëżi". make
Abò, żlë môsz ùstawioné òkrãżé jak je to òpisóné w Getting Started/Build/KDE4, mòżesz skòmpilowac kòd pòlétã:
cmakekde
Terôzkù zrëszë programã:
./tutorial1
Biéj dali
Terô mòżesz jic dali bë naùczëc so brëkòwaniô KXmlGuiWindow.
