Development/Tutorials/Using Actions/pt-br
| Tutorial Series | Tutorial para Iniciantes |
| Previous | Tutorial 2 - KXmlGuiWindow, Conhecimento básico do XML |
| What's Next | Tutorial 4 - Saving and loading |
| Further Reading | None |
Resumo
Este tutorial apresenta o conceito de actions. Actions são uma maneira unificada de fornecer ao usuário maneiras de interagir com seu programa.
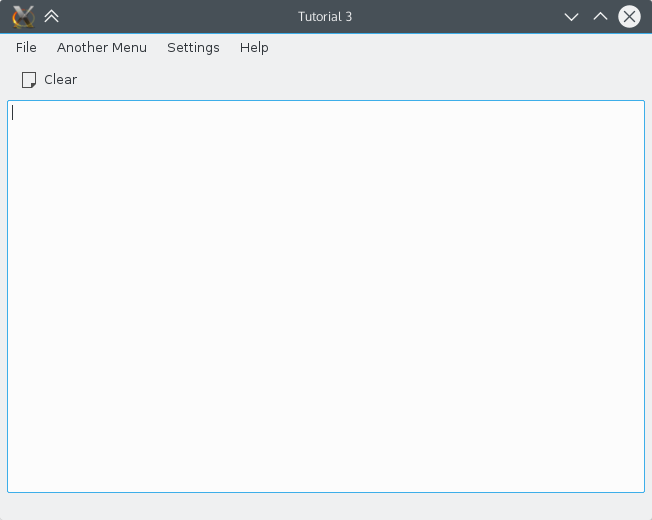
Por exemplo, se quisermos permitir que o usuário do Tutorial 2 limpe a caixa de texto clicando em um botão na barra de ferramentas, em uma opção no menu Arquivo ou através de um atalho do teclado, ele poderá fazer tudo isso com um QAction.
QAction
Um QAction é um objeto que contém todas as informações sobre o ícone e os atalhos associados a um determinado action. O action é então conectado a um slot que executa o trabalho da sua action.
O Código
main.cpp
#include <cstdlib>
#include <QApplication>
#include <QCommandLineParser>
#include <KAboutData>
#include <KLocalizedString>
#include "mainwindow.h"
int main (int argc, char *argv[])
{
QApplication app(argc, argv);
KLocalizedString::setApplicationDomain("tutorial3");
KAboutData aboutData(
// The program name used internally. (componentName)
QStringLiteral("tutorial3"),
// A displayable program name string. (displayName)
i18n("Tutorial 3"),
// The program version string. (version)
QStringLiteral("1.0"),
// Short description of what the app does. (shortDescription)
i18n("A simple text area using QAction etc."),
// The license this code is released under
KAboutLicense::GPL,
// Copyright Statement (copyrightStatement = QString())
i18n("(c) 2015"),
// Optional text shown in the About box.
// Can contain any information desired. (otherText)
i18n("Some text..."),
// The program homepage string. (homePageAddress = QString())
QStringLiteral("http://example.com/"),
// The bug report email address
// (bugsEmailAddress = QLatin1String("[email protected]")
QStringLiteral("[email protected]"));
aboutData.addAuthor(i18n("Name"), i18n("Task"), QStringLiteral("[email protected]"),
QStringLiteral("http://your.website.com"), QStringLiteral("OSC Username"));
KAboutData::setApplicationData(aboutData);
QCommandLineParser parser;
aboutData.setupCommandLine(&parser);
parser.process(app);
aboutData.processCommandLine(&parser);
MainWindow* window = new MainWindow();
window->show();
return app.exec();
}
Desta vez, muito pouco mudou no main.cpp, apenas o construtor KAboutData foi atualizado para mostrar que agora estamos no tutorial 3.
mainwindow.h
#ifndef MAINWINDOW_H
#define MAINWINDOW_H
#include <KXmlGuiWindow>
class KTextEdit;
class MainWindow : public KXmlGuiWindow
{
public:
explicit MainWindow(QWidget *parent = nullptr);
private:
KTextEdit* textArea;
void setupActions();
};
#endif
Somente uma função void setupActions() foi adicionada, que fará todo o trabalho de configuração das QActions.
mainwindow.cpp
#include <QApplication>
#include <QAction>
#include <KTextEdit>
#include <KLocalizedString>
#include <KActionCollection>
#include <KStandardAction>
#include "mainwindow.h"
MainWindow::MainWindow(QWidget *parent) : KXmlGuiWindow(parent)
{
textArea = new KTextEdit();
setCentralWidget(textArea);
setupActions();
}
void MainWindow::setupActions()
{
QAction* clearAction = new QAction(this);
clearAction->setText(i18n("&Clear"));
clearAction->setIcon(QIcon::fromTheme("document-new"));
actionCollection()->setDefaultShortcut(clearAction, Qt::CTRL + Qt::Key_W);
actionCollection()->addAction("clear", clearAction);
connect(clearAction, SIGNAL(triggered(bool)), textArea, SLOT(clear()));
KStandardAction::quit(qApp, SLOT(quit()), actionCollection());
setupGUI(Default, "tutorial3ui.rc");
}
Explicação
Isso se baseia no código do KXmlGuiWindow do Tutorial 2. A maioria das alterações é no mainwindow.cpp, uma mudança estrutural importante é que o construtor do MainWindow agora chama setupActions() em vez de setupGUI(). setupActions() é o local onde o novo código QAction vai antes de finalmente chamar setupGUI().
Criando o objeto QAction
O QAction é construído em várias etapas. A primeira é a inclusão no cabeçalho do QAction e a criação do QAction:
#include <QAction>
...
QAction* clearAction = new QAction(this);
Isso cria um novo QAction chamado clearAction.
Definindo propriedades QAction
Texto
Agora que temos nosso objeto QAction, podemos começar a definir suas propriedades. O código a seguir define o texto que será exibido no menu e com o ícone do QAction na barra de ferramentas, dependendo do estilo do widget (seja ao lado ou abaixo do ícone) ou da configuração (se deseja exibir o texto da ação ou não).
clearAction->setText(i18n("&Clear"));
Observe que o texto é passado através da função i18n(); isso é necessário para que a interface do usuário seja traduzível (mais informações sobre isso podem ser encontradas no tutorial i18n).
O texto do action deve conter um & porque isso facilita a tradução em idiomas non-latin1. Em japonês, a tradução pode ser ソース(&S) e sem o & no texto em inglês os tradutores não podem saber se precisam adicionar um & ou não.
Ícone
Se o action for exibido em uma barra de ferramentas, é legal ter um ícone representando a ação. O ícone também pode ser exibido ao lado do action nos menus, dependendo do estilo do widget. O código a seguir define o ícone padrão como document-new através do uso da função setIcon():
clearAction->setIcon(QIcon::fromTheme("document-new"));
Atalho do teclado
Definir um atalho do teclado para executar nossa ação é igualmente simples:
actionCollection()->setDefaultShortcut(clearAction, Qt::CTRL + Qt::Key_W);
This associates Ctrl+W with the QAction.
Adding to the Collection
In order for the action to be accessed by the XMLGUI framework (explained in depth later) it must be added to the application's action collection. The action collection is accessed via the actionCollection() function like this:
actionCollection()->addAction("clear", clearAction);
Here, the clearAction QAction is added to the collection and given a name of clear. This name (clear) is used by the XMLGUI framework to refer to the action, ergo, it should not be localized, since it is used internally only.
Connecting the action
Now that the action is fully set up, it needs to be connected to something useful. In this case (because we want to clear the text area), we connect our action to the clear() action belonging to a KTextEdit (which, unsurprisingly, clears the KTextEdit)
connect( clearAction, SIGNAL( triggered(bool) ),
textArea, SLOT( clear() ) );
KStandardAction
For actions which would likely appear in almost every KDE application such as 'quit', 'save', and 'load' there are pre-created convenience QActions, accessed through KStandardAction.
They are very simple to use. Once the library has been included (#include <KStandardAction>), simply supply it with what you want the function to do and which QActionCollection to add it to. For example:
KStandardAction::quit(qApp, SLOT(quit()), actionCollection());
Here we call the QApplicaton's quit method whenever the KStandardAction quit is triggered. We are able to access that QApplication method via the qApp macro.
In the end, this creates a QAction with the correct icon, text and shortcut and even adds it to the File menu.
At the moment, the new "Clear" action has been created but it hasn't been associated with any menus or toolbars. This is done with a KDE technology called XMLGUI, which does nice things like movable toolbars for you.
The Help menu has been standardized to ease the lives of both developers and users, which is why all KDE software Help menus look the same. If you want to create your own help menu, search for the explanation around showAboutApplication() in from the KHelpMenu class in XMLGUI.
XMLGUI
The setupGUI() function in KXmlGuiWindow depends on the XMLGUI system to construct the GUI, which XMLGUI does by parsing an XML file description of the interface.
The rule for naming this XML file is appnameui.rc, where appname is the name you set in KAboutData (in this case, tutorial3). So in our example, the file is called tutorial3ui.rc, and is located in the build directory. Where the file will ultimately be placed is handled by CMake.
appnameui.rc file
Since the description of the UI is defined with XML, the layout must follow strict rules. This tutorial will not go into great depth on this topic, but for more information, see the detailed XMLGUI page.
tutorial3ui.rc
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<gui name="tutorial3"
version="1"
xmlns="http://www.kde.org/standards/kxmlgui/1.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.kde.org/standards/kxmlgui/1.0
http://www.kde.org/standards/kxmlgui/1.0/kxmlgui.xsd" >
<MenuBar>
<Menu name="file" >
<Action name="clear" />
</Menu>
<Menu >
<text>A&nother Menu</text>
<Action name="clear" />
</Menu >
</MenuBar>
<ToolBar name="mainToolBar" >
<text>Main Toolbar</text>
<Action name="clear" />
</ToolBar>
</gui>
The <Toolbar> tag allows you to describe the toolbar, which is the bar across the top of the window normally with icons. Here it is given the unique name mainToolBar and its user visible name set to Main Toolbar using the <text> tag. The clear action is added to the toolbar using the <Action> tag, the name parameter in this tag being the string that was passed to the KActionCollection with addAction() in mainwindow.cpp.
Besides having the action in the toolbar, it can also be added to the menubar. Here the action is being added to the File menu of the MenuBar the same way it was added to the toolbar.
Change the 'version' attribute of the <gui> tag if you changed .rc file since the last install to force a system cache update. Be sure it is an integer, if you use a decimal value, it will not work, but will not notify that it didn't. '

Some notes on the interaction between code and the .rc file: Menus appear automatically and should have a <text/> child tag unless they refer to standard menus. Actions need to be created manually and inserted into the actionCollection() using the name in the .rc file. Actions can be hidden or disabled, whereas menus can't.
CMake
Finally, the tutorial3ui.rc needs to go somewhere where KDE can find it (can't just leave it in the source directory!). This means the project needs to be installed somewhere, unlike in the previous tutorials.
CMakeLists.txt
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.0)
project (tutorial3)
set(QT_MIN_VERSION "5.3.0")
set(KF5_MIN_VERSION "5.2.0")
find_package(ECM 1.0.0 REQUIRED NO_MODULE)
set(CMAKE_MODULE_PATH ${ECM_MODULE_PATH} ${ECM_KDE_MODULE_DIR} ${CMAKE_CURRENT_SOURCE_DIR}/cmake)
include(KDEInstallDirs)
include(KDECMakeSettings)
include(KDECompilerSettings NO_POLICY_SCOPE)
include(FeatureSummary)
find_package(Qt5 ${QT_MIN_VERSION} CONFIG REQUIRED COMPONENTS
Core # QCommandLineParser, QStringLiteral
Widgets # QApplication, QAction
)
find_package(KF5 ${KF5_MIN_VERSION} REQUIRED COMPONENTS
CoreAddons # KAboutData
I18n # KLocalizedString
XmlGui # KXmlGuiWindow, KActionCollection
TextWidgets # KTextEdit
ConfigWidgets # KStandardActions
)
feature_summary(WHAT ALL INCLUDE_QUIET_PACKAGES FATAL_ON_MISSING_REQUIRED_PACKAGES)
set(tutorial3_SRCS main.cpp mainwindow.cpp)
add_executable(tutorial3 ${tutorial3_SRCS})
target_link_libraries(tutorial3
Qt5::Widgets
KF5::CoreAddons
KF5::I18n
KF5::XmlGui
KF5::TextWidgets
KF5::ConfigWidgets
)
install(TARGETS tutorial3 ${KDE_INSTALL_TARGETS_DEFAULT_ARGS})
install(FILES tutorial3ui.rc DESTINATION ${KDE_INSTALL_KXMLGUI5DIR}/tutorial3)
This file is almost identical to the one for tutorial2, but with two extra lines at the end that describe where the files are to be installed. Firstly, the tutorial3 target is installed to the KDE_INSTALL_TARGETS_DEFAULT_ARGS then the tutorial3ui.rc file that describes the layout of the user interface is installed to the application's data directory under KDE_INSTALL_KXMLGUI5DIR.
Make, Install And Run
This is probably the trickiest part. Where you install the files, especially tutorial3ui.rc is important. Normally, you'd want to install it where KDE software is installed by your distribution, which is usually under /usr. That, however, would require root/admin access and If you don't have that, you can install it to a folder in your home directory.
To tell CMake where to install the program, set the DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX switch. You probably just want to install it somewhere local for testing (it's probably a bit silly to go to the effort of installing these tutorials to your KDE directory), so the following might be appropriate:
mkdir build && cd build
cmake .. -DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=$HOME
make install
which will create a KDE-like directory structure in your user's home directory. Specifically, it will create the directories $HOME/bin/ and $HOME/share/ and will install the executable to $HOME/bin/tutorial3 and the tutorial3ui.rc file to $HOME/share/kxmlgui/tutorial3/tutorial3ui.rc.
However, to be able to run the program properly, you will need to let the system know where the XMLGUI file is. Since we installed it in a nonstandard location, we'll have to explicitly to do so every time. The following command would suffice:
XDG_DATA_DIRS=$HOME/share:$XDG_DATA_DIRS $HOME/bin/tutorial3
This temporarily adds (prepends) the newly created "share" location to XDG_DATA_DIRS, the standard path for application data files.
Moving On
Now you can move on to saving and loading.
Or you can learn how to add icons to your application.
Or you can learn how to place your application in the K-Menu using .desktop files.
