User:DarioAndres/CreateUsefulReports
Introduction
This document describes how to create useful bug reports for crashes of KDE applications. The first section should be enough for most bug reporters and triagers.
There is a second section which details how to create backtraces with additional tools like the GNU Debugger and Valgrind (advanced).

How to create useful crash reports
A good crash report consists of two parts: a description of how to reproduce the crash and a backtrace of the crash. With any of those elements missing, it is very hard (if not impossible) for developers to tackle the problem.
Description
A description should describe everything that you were doing prior to the crash. It should not just say "it crashed". Did you click on a button, did you open a particular website or file which caused problems? These little details, which may look useless to you, may be useful for the developers, so just write them down.
- The KDE version is an important detail that is often missing in bug reports.
If you do not know what KDE version are you using, you can get it by selecting the "About KDE" option in the Help menu of every KDE application, or by running the command kde4-config --version in Konsole. You will get an output like this:
Qt: 4.5.3 KDE: 4.3.2 (KDE 4.3.2) kde4-config: 1.0

A more insightful article on how to write good bug descriptions is available at this link, please read that before reporting bugs.
Application specific details
For several applications it can be useful to have specific details in bug reports:
- Plasma (the KDE Desktop): Plasmoids you have in your desktop (both official and unofficial), desktop settings (wallpaper plugin, themes), activities and dashboard configuration.
- KWin (the KDE Window Manager): state of compositing(desktop effects): enabled / suspended / disabled, kind of effects enabled, window decoration.
- Konqueror: Sites you were visiting, number of opened tabs, plugins you have installed, non-default settings.
- Dolphin: file view mode, grouping and sorting settings, preview settings, directory you were browsing.
- Kopete: IM protocols you use, plugins you use.
- KMail: Mail protocols and account-types you use.
- KWrite/Kate/KOffice: Type of the document you were editing.
- Multimedia Players (Juk/Dragon/Amarok): Type of media (extension and format) you were watching and/or listening to.
Backtraces
Backtraces are essential. They may look meaningless to you, but they might actually contain a wealth of useful information. A backtrace basically describes what was happening inside the application when it crashed, in a way that developers may track down where the mess started.
- Don't attach the backtrace to the bug report. Instead, simply paste it. This way it is much easier for developers to search for duplicate reports, because attachments can not be searched.

Even though pasting backtraces directly is preferred over adding an attachment, please do not paste other things like logs (valgrind, strace or terminal output) or example data (mails, HTML files and so on). Use attachments for these items.
Having good backtraces has a downside: Libraries and executables occupy much more disk space than their optimized counter parts. That's the reason why many distros choose to install stripped files, which results in useless backtraces:
(no debugging symbols found) Using host libthread_db library "/lib/tls/i686/cmov/libthread_db.so.1". debugging using libthread_db enabled] [New Thread -1233848624 (LWP 12212)] [New Thread -1255081072 (LWP 12820)] [New Thread -1240921200 (LWP 12819)] [New Thread -1266680944 (LWP 12818)] (no debugging symbols found) (no debugging symbols found) (no debugging symbols found) 0xffffe410 in __kernel_vsyscall () #0 0xffffe410 in __kernel_vsyscall () #1 0xb6a1210b in ?? () from /lib/tls/i686/cmov/libpthread.so.0 #2 0xb6a85afe in ?? () from /usr/lib/libX11.so.6 #3 0x00000003 in ?? () #4 0x082149c0 in ?? () #5 0x00003ffc in ?? () #6 0x00000000 in ?? ()
But no worries, with some modifications you can create full blown backtraces for KDE applications.
Preparing your KDE packages

If your distribution has debugging-enabled packages, install them:
It is easy to see which debug packages you are missing from looking at the backtrace. For example, take the following line from a backtrace:
#6 0xb7975bdc in ?? () from /usr/lib/libkmailprivate.so.4
The ?? indicates that the library libkmailprivate.so.4 does not have debug information, which might be available in a separate debug package. In this case, it is pretty easy to guess that you need to install the debug package for KMail to get a better backtrace.
Sometimes, you need to install more than one debug package to get a good backtrace. This depends on how the distribution splits up the packages. For example, for some distributions it is enough to install the debug package for kdepim to get enough debugging information for a crash in KMail, for other distributions there is an additional debug package just for KMail.
How to obtain debug package for several distributions
- Debian - Debian offers -dbg packages to easily create useful backtraces. Just install the corresponding -dbg package. e.g. kdepim-dbg for KMail crashes. The dependencies of -dbg makes sure to pull in the other right packages (kdelibs-dbg, gdb, and so on).
- FreeBSD ports - Please refer to the KDE on FreeBSD FAQ.
- Gentoo - Gentoo has its own document describing how to proceed.
- Mandriva - Mandriva 2007.0 and up has additional debugging packages for all of KDE (in fact, for all of its packages). Just install the corresponding -debug package, like kdebase-debug and kdemultimedia-debug. You probably want to install kdelibs-debug anyways.
- Note: the -debug packages are in separate repositories. For instance, for all packages in main, you'll find the debugging package in repository debug_main.
- Kubuntu/Ubuntu - The Ubuntu family makes things quite easy. Every official KDE module has an additional package in the repository, suffixed with -dbg. Always install kdelibs5-dbg, because all KDE applications use kdelibs. Then you should install a -dbg package for the application which crashed. For example if KOrganizer crashed you should install kdepim-dbg as well. If the program is not from an official KDE module and has no -dbg package, you can install the -dbgsym package from the repository listed on this Debugging Program Crashes page.
- openSUSE - You should only install the -debuginfo packages, for example: kdepimlibs4-debuginfo. You can find these packages in KDE repositories. There is also a dedicated openSUSE debugging page.
- Fedora - Fedora has its own document describing how to proceed. (A debuginfo repository has to be enabled.)
- ArchLinux - If you are using the KDEMod repository you can install the -debug packages for each KDE module. If you are using the standard Arch repositories you need to recompile your packages manually. You will find more help in this article: Debug, Getting Traces
If your distribution doesn't have debugging-enabled packages for KDE, you'll have to compile KDE from sources:
- With KDE 4, at the cmake stage, you should supply the parameter -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=debugfull. If you want to specify your own CXXFLAGS, then use -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=None CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS="-O0 -g". You can change the CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS as appropriate for your needs.
Then it's just make and make install as you're used to.
Reproducing the crash
Now it's time to crash your application (reproducing the steps that caused the application to crash the first time).
The KDE Crash Handler Dialog should appear right after the crash:
KDE 4.3 and later
Since KDE 4.3 there is a new version of the crash handler dialog:
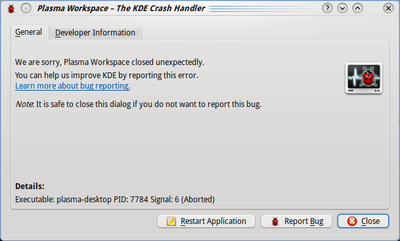
In order to get a backtrace directly you need to click the "Developer Information" tab.

KDE 4.0 - 4.2
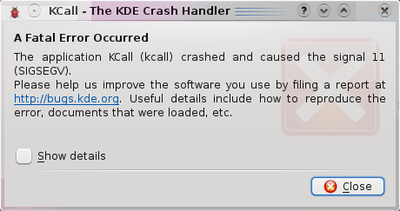
In order to get the backtrace you need to click the "Show details" checkbox.
Backtrace Generation
This process may take quite some memory and CPU, so things may go sluggish all of a sudden. But the result should look much better. For example:
Thread 1 (Thread 0x7f3579b39750 (LWP 14011)):
[KCrash Handler]
- 5 setCaretInvisibleIfNeeded (part=0x16e2ca0) at
/home/kde-devel/kde/src/KDE/kdelibs/khtml/khtml_part.cpp:2796
- 6 0x00007f356a8b92b5 in KHTMLPart::setCaretMode (this=0x16e2ca0,
enable=false) at /home/kde-devel/kde/src/KDE/kdelibs/khtml/khtml_part.cpp:2812
- 7 0x00007f356a8c98bd in KHTMLPart::qt_metacall (this=0x16e2ca0,
_c=QMetaObject::InvokeMetaMethod, _id=<value optimized out>, _a=0x7fff81c7a800)
at /home/kde-devel/kde/build/KDE/kdelibs/khtml/khtml_part.moc:327
- 8 0x00007f3577276ac0 in QMetaObject::activate (sender=0x1884c90,
from_signal_index=<value optimized out>, to_signal_index=6, argv=0x1cb7f00) at
kernel/qobject.cpp:3028
- 9 0x00007f3576612a57 in QAction::triggered (this=0x0, _t1=false) at
.moc/debug-shared/moc_qaction.cpp:216
- 10 0x00007f3576613204 in QAction::activate (this=0x1884c90, event=<value
optimized out>) at kernel/qaction.cpp:1125
- 11 0x00007f3576616862 in QAction::event (this=0x1884c90, e=0x7fff81c7ad90) at
kernel/qaction.cpp:1044
- 12 0x00007f3577faa503 in KAction::event (this=0x0, event=0x7fff81c7ad90) at
/home/kde-devel/kde/src/KDE/kdelibs/kdeui/actions/kaction.cpp:88
- 13 0x00007f35766180ad in QApplicationPrivate::notify_helper (this=0x10be800,
receiver=0x1884c90, e=0x7fff81c7ad90) at kernel/qapplication.cpp:3803
- 14 0x00007f357661f40e in QApplication::notify (this=0x7fff81c7c510,
receiver=0x1884c90, e=0x7fff81c7ad90) at kernel/qapplication.cpp:3768
- 15 0x00007f357808155b in KApplication::notify (this=0x7fff81c7c510,
receiver=0x1884c90, event=0x7fff81c7ad90) at
/home/kde-devel/kde/src/KDE/kdelibs/kdeui/kernel/kapplication.cpp:307
- 16 0x00007f3577261d90 in QCoreApplication::notifyInternal
(this=0x7fff81c7c510, receiver=0x1884c90, event=0x7fff81c7ad90) at
kernel/qcoreapplication.cpp:583
This looks better, right? It shows memory addresses, the source files and line numbers and the parameters passed to functions. Which make it more helpful to the developer where to look for the problem.

Additional Tools
Retrieving a backtrace with GDB
In some cases, it is not possible to create a backtrace with the KDE Crash Dialog. This may be caused by an application which entered an infinite loop, or the crash dialog did not appear at all for some reason. You can try to grab a backtrace with gdb, the GNU Debugger. GDB is widely available through distribution packages.
Invoking GDB differs from the situation. You can run an application from inside gdb, or attach gdb to an already running process. The latter may be useful when an application already has entered an infinite loop. But we will first start with running an application inside gdb. From the shell, run:
$ gdb someKDEapp
The GDB prompt will appear. Note that this does not start the application itself, you should run it by invoking the run command:
(gdb) run
This will run the application like you are used to, and you can work with it like normal (it only consumes far more memory and may feel sluggish). Now it's time to reproduce your crash. When you succeed, the application just closes and you should return to your GDB prompt. Now it's time to run the 'backtrace' command:

(gdb) thread apply all backtrace
This should give a good backtrace which can be posted at the KDE Bugzilla.
In case you want to attach to an existing process, run the following command in the shell:
$ gdb someKDEapp pid
where pid is the process ID of the process you want to attach to. Once attached, and the process is in an infinite loop, after using the 'backtrace' command again a useful backtrace will appear. You can use 'continue' command to let the application run again and press Ctrl+C in gdb to be able to again enter commands.
Retrieving a backtrace with Valgrind
When it comes to crashes, Valgrind is also a useful tool to create a backtrace. It's not a substitution for GDB, but rather a supplement.
When you run an application in valgrind, every piece of memory read or written by the application is being checked. Valgrind will report erroneous memory operations in the standard output or in a log file. Since most crashes are due to an invalid memory read, valgrind can be useful to track down where the problem occurs.

Like GDB, Valgrind makes running an application much slower, while consuming a lot more resources.
Start the application within valgrind:
$ valgrind --log-file=someKDEapp someKDEapp
Now reproduce the crash. As soon as this happens, the application and valgrind will terminate. What's left is a file named someKDEapp.pid where pid is replaced by the process ID of the valgrind process. The file may list more errors than the one causing the crash. Here's the bit causing the crash which corresponds to the GDB backtrace above:
==4538== Invalid read of size 4
==4538== at 0xA143AAF: setCaretInvisibleIfNeeded(KHTMLPart*) (khtml_part.cpp:2846)
==4538== by 0xA14CCC9: KHTMLPart::setCaretMode(bool) (khtml_part.cpp:2862)
==4538== by 0xA14CDA9: KHTMLPart::slotToggleCaretMode() (khtml_part.cpp:7155)
==4538== by 0xA177107: KHTMLPart::qt_metacall(QMetaObject::Call, int, void**) (khtml_part.moc:337)
==4538== by 0x4ED79C9: QMetaObject::activate(QObject*, int, int, void**) (qobject.cpp:3112)
==4538== by 0x4ED7E0C: QMetaObject::activate(QObject*, QMetaObject const*, int, int, void**) (qobject.cpp:3206)
==4538== by 0x51884F7: QAction::triggered(bool) (moc_qaction.cpp:236)
==4538== by 0x5187ABC: QAction::activate(QAction::ActionEvent) (qaction.cpp:1160)
==4538== by 0x518781C: QAction::event(QEvent*) (qaction.cpp:1079)
==4538== by 0x46FF902: KAction::event(QEvent*) (kaction.cpp:88)
==4538== by 0x51972DA: QApplicationPrivate::notify_helper(QObject*, QEvent*) (qapplication.cpp:4056)
==4538== by 0x519573B: QApplication::notify(QObject*, QEvent*) (qapplication.cpp:3603)
==4538== Address 0x0 is not stack'd, malloc'd or (recently) free'd
But to be sure, just attach the whole log file to the crash report.
