Development/Tutorials/Akonadi/Application (fr)
| Tutorial Series | Akonadi Tutorial |
| Previous | C++, Qt, KDE4 development environment |
| What's Next | |
| Further Reading | CMake, Akonadi Development Tools |
Ce tutoriel vous guidera à travers les différentes étapes pour la création d'une application Akonadi, une interface utilisateur qui affichera et manipulera les données PIM fournies par Akonadi.
Si vous recherchez un tutorial sur la façon de fournir des données pour Akonadi: voir Akonadi Resource Tutorial
Prérequis

cleanup confusing sections and fix sections which contain a todo
Describe required versions and build setup
Exemple
Le but de ce tutoriel est de créer une application simple permettant à un utilisateur de récupérer les pièces jointes de ses courriels, i.e les sauvegarder sur disque et de les retirer des messages.
Pour rester concentré sur les différentes étapes liés à Akonadi, toutes les étapes relatives à l'interface graphique seront réduites au minimum.
Preparation
Nous pouvons rapidement démarrer la création de l'application en utilisant le Générateur de modèles pour KDE, qui peut être trouvé dans la section Développement du menu KDE, ou en lançant kapptemplate dans un terminal.
en premier, Sélectionnez Application avec interface graphique pour KDE4 dans la section C++ du générateur, donnez un nom à votre projet et continuez à travers les pages suivantes pour terminer la création.
Un coup d’œil dans le répertoire racine du projet généré montre les fichiers suivantes:
CMakeLists.txt
detacher/
doc/
icons/
README
src/
et les fichiers suivants dans le sous répertoire src:
CMakeLists.txt
detacher.cpp
detacher.desktop
detacher.h
detacher.kcfg
detacherui.rc
detacherview_base.ui
detacherview.cpp
detacherview.h
main.cpp
Messages.sh
settings.kcfgc
prefs_base.ui
A cette étape il est déjà possible de compiler cette application, ainsi nous pouvons déjà vérifier que l'environnement de développement est correctement configuré en créant le répertoire build et grâce à CMake qui permet de générer des Makefiles ou des fichiers projet pour KDevelop.
Générer des Makefiles
Depuis le répertoire racine du projet généré:
mkdir build
cd build
cmake -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=debugfull ..
Et lancer la génération en utilisant make comme à l'habitude.
Générer un fichier projet pour KDevelop
Depuis le répertoire racine du projet généré:
mkdir build
cd build
cmake -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=debugfull -G KDevelop3 ..
Et ouvrir le projet généré avec KDevelop and lancer la génération depuis cet outil.
Ajuster le fichier principal de Qt Designer
Ouvrir le fichier detacherview_base.ui dans Qt Designer et enlever le label d'exemple. Remove the widget's main layout by clicking on the now empty widget and use the Break Layout menu entry in the Form menu.
Now, from left to right, place two Tree Views and one List Widget side-by-side. Select all three boxes by holding SHIFT and clicking each box with the left mouse button. Use Layout Horizontally in a Splitter in the Form menu and then create a main layout by clicking on their parent widget and using Layout Vertically in the Form menu.
A preview (Form -> Preview) should now look like this:

Finally, change the object names for the three widgets by right clicking it and choosing Change objectName. The left widget should be named folderView, the middle one messageView and the right one attachmentList.
In order to make it build again, edit the file detacherview.cpp and remove the code from the settingsChanged method. The application should now build again and be able to run.

Promoting Views
The KDE client library for Akonadi has a couple of convenience classes which make our life as application developers more pleasant. Two of these classes are specialized view widgets, one for displaying collections and one for displaying items.
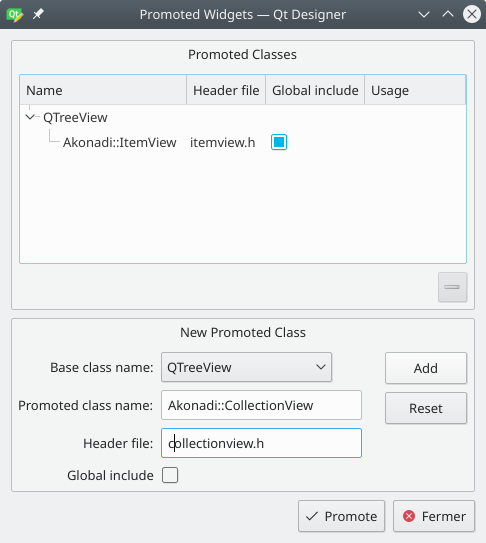
In order to use these widgets instead of ones from Qt we need to use a Qt Designer feature called "promoting". Right click the left widget and choose Promote to. Then fill the form like shown in the next screenshot.
Click add and promote. Repeat the same for the middle widget, this time using Akonadi::ItemView as the class name and akonadi/itemview.h for the header file.
This change also requires a change in the CMakeLists.txt file in the top level directory and in the one from the source directory.
In the file from the top level directory add the following line
find_package (KdepimLibs REQUIRED)
and change
include_directories( ${KDE4_INCLUDES} ${QT_INCLUDES} )
into
include_directories( ${KDE4_INCLUDES} ${KDEPIMLIBS_INCLUDE_DIRS} ${QT_INCLUDES} )
In the file from the source directory the line
target_link_libraries(detacher ${KDE4_KDEUI_LIBS})
has to be changed to
target_link_libraries(detacher ${KDE4_KDEUI_LIBS} ${KDEPIMLIBS_AKONADI_LIBS})
Initialization
Since the application will depend on Akonadi running, we can ensure this by starting it if it is not. This is handled by the Akonadi::Control class.
In detacher.h we add another slot called delayedInit() which will perform this initialization. A slot so we can delay its executing using a single shot timer, a technique called "Delayed Initialization", i.e. letting the application create and show its GUI as fast as possible and do any probably time consuming initialization after that.
private slots:
void fileNew();
void optionsPreferences();
void delayedInit();
In detacher.cpp we need two new include directives:
#include <QtCore/QTimer>
#include <akonadi/control.h>
and the slot's implementation
void Detacher::delayedInit()
{
if ( !Akonadi::Control::start( this ) ) {
qApp->exit( -1 );
return;
}
}
If the application fails to start Akonadi, it simply quits. A real application should probably tell the user about that though.
Since we want the slot to be executed delayed, add the following line at the end of the class' constructor
QTimer::singleShot( 0, this, SLOT( delayedInit() ) );
Lets add a new public method to the view class. In detacherview.h add
void createModels();
and for now with an empty body in detacherview.cpp (we will get to the implementation shortly)
void DetacherView::createModels()
{
}
and call it from Detacher::delayedInit() after the Akonadi start succeeded
void Detacher::delayedInit()
{
if ( !Akonadi::Control::start( this ) ) {
qApp->exit( -1 );
return;
}
m_view->createModels();
}
Connecting Views to Akonadi
The actual data connection between our views and Akonadi is conveniently handled by specialized models which are also provided by the KDE client library for Akonadi.
Actually, the data type the application will be working on, MIME messages, has an even further specialized model in a type specific sub library.
To properly link this additional library change the source directory's CMakeLists.txt to this
target_link_libraries(detacher ${KDE4_KDEUI_LIBS} ${KDEPIMLIBS_AKONADI_LIBS} ${KDEPIMLIBS_AKONADI_KMIME_LIBS})
In 'detacherview.cpp add the following include directives
#include <akonadi/collectionfilterproxymodel.h>
#include <akonadi/collectionmodel.h>
#include <akonadi/kmime/messagemodel.h>
With that we can now properly implement the createModels() method:
void DetacherView::createModels()
{
Akonadi::CollectionModel *collectionModel = new Akonadi::CollectionModel( this );
Akonadi::CollectionFilterProxyModel *filterModel = new Akonadi::CollectionFilterProxyModel( this );
filterModel->setSourceModel( collectionModel );
filterModel->addMimeTypeFilter( QLatin1String( "message/rfc822" ) );
Akonadi::ItemModel *itemModel = new Akonadi::MessageModel( this );
ui_detacherview_base.folderView->setModel( filterModel );
ui_detacherview_base.messageView->setModel( itemModel );
connect( ui_detacherview_base.folderView, SIGNAL( currentChanged( Akonadi::Collection ) ),
itemModel, SLOT( setCollection( Akonadi::Collection ) ) );
}
The first line creates a CollectionModel which will get all "folders" from Akonadi and keep this data updated as long as the application is running.
However, since this includes collections for other data types as well, we need to filter for the data type we are interested in, MIME messages or in terms of MIME type message/rfc822. This kind of filtering is conveniently supplied in the form of a proxy model called CollectionFilterProxyModel.
The next model, MessageModel is an ItemModel specialized in dealing with our data type, messages.
Setting the models on the respective view almost completes the setup process, the only thing left is to connect the CollectionView to the MessageModel so it changes its data depending on which folder gets selected.
At this stage the application is already capable of showing all your mail folders and headers of all your e-mails!
Getting at the Attachments
This task can be split into two steps:
- Getting the message from Akonadi
- Getting the attachments from the message
Getting the message from Akonadi
While we could have instructed the MessageModel to get all data for each of its entries, the proper way is to retrieve it only for the items that get selected. Moreover we want to do this asynchronously because we don't want to block the application even is a message is really huge.
The KDE client library for Akonadi offers this kind of functionality through a job-based API, in this case ItemFetchJob.
Using this is quite simple. First we add a new include and a class forward declaration for detacherview.h
#include <akonadi/item.h>
class KJob;
In the private member section add an Item member:
private:
Ui::detacherview_base ui_detacherview_base;
Akonadi::Item mItem;
and two new slots in the private slots section:
private slots:
void switchColors();
void settingsChanged();
void itemChanged( const Akonadi::Item &item );
void itemFetchDone( KJob *job );
In the source file detacherview.cpp two new includes are required
#include <akonadi/itemfetchjob.h>
#include <akonadi/itemfetchscope.h>
for the implementation of the two new slots
void DetacherView::itemChanged( const Akonadi::Item &item )
{
// clear attachment list
ui_detacherview_base.attachmentList->clear();
// re-initialize the member we use for referencing the current item
mItem = Akonadi::Item();
// create fetch job and let it get the whole message
Akonadi::ItemFetchJob *fetchJob = new Akonadi::ItemFetchJob( item, this );
fetchJob->fetchScope().fetchFullPayload();
connect( fetchJob, SIGNAL( result( KJob* ) ), SLOT( itemFetchDone( KJob* ) ) );
}
void DetacherView::itemFetchDone( KJob *job )
{
Akonadi::ItemFetchJob *fetchJob = static_cast<Akonadi::ItemFetchJob*>( job );
if ( job->error() ) {
kError() << job->errorString();
return;
}
if ( fetchJob->items().isEmpty() ) {
kWarning() << "Job did not retrieve any items";
return;
}
mItem = fetchJob->items().first();
if ( !mItem.isValid() ) {
kWarning() << "Item not valid";
return;
}
}
To trigger the item fetching we connect the first new slot to a signal of the MessageView. In DetacherView::createModels() add another connect statement:
connect( ui_detacherview_base.messageView, SIGNAL( currentChanged( Akonadi::Item ) ),
SLOT( itemChanged( Akonadi::Item ) ) );
Getting the attachments from the message
With the item now fully available, we can proceed to check whether the message has any attachments and if it has display them in the right most widget of our GUI.
MIME messages in KDE are handled by the kmime library.
For the application this means two more includes and a typedef:
#include <kmime/kmime_message.h>
#include <boost/shared_ptr.hpp>
typedef boost::shared_ptr<KMime::Message> MessagePtr;
KMime::Message is the data type and we need the boost::shared_ptr to provide us with the value based behavior required by the item's payload methods.
Equipped with this new tools we can extend DetacherView::itemFetchDone() by adding the following code at its end:
if ( !mItem.hasPayload<MessagePtr>() ) {
kWarning() << "Item does not have message payload";
return;
}
const MessagePtr message = mItem.payload<MessagePtr>();
const KMime::Content::List attachments = message->attachments();
foreach ( KMime::Content *attachment, attachments ) {
const QString fileName = attachment->contentDisposition()->filename();
if ( fileName.isEmpty() )
continue;
ui_detacherview_base.attachmentList->addItem( fileName );
}

Detaching an Attachment
This task can again be split into sub tasks:
- Saving the selected attachment into a file
- Removing the selected attachment from the message
Saving Attachment into File
First we need a new slot in the private slots section of detacherview.h
void detachAttachment();
To implement the first sub task, saving the selected attachment into a file, the following new includes are needed in detacherview.cpp
#include <kaction.h>
#include <kfiledialog.h>
#include <kstandardaction.h>
In the class' constructor create and connect an action and make it available as the attachment list widget's context menu:
KAction *detachAction = KStandardAction::cut( this, SLOT( detachAttachment() ), this );
detachAction->setText( i18nc( "@action:button remove an attachment from an email",
"Detach..." ) );
ui_detacherview_base.attachmentList->addAction( detachAction );
ui_detacherview_base.attachmentList->setContextMenuPolicy( Qt::ActionsContextMenu );

In case the i18nc function or the text used in it are unexpected, see the Semantic Markup Tutorial.
Saving the attachment means we need to ask for a saving location, probably including a filename override and get the data from the message.
This can be implemented like this
void DetacherView::detachAttachment()
{
const QList<QListWidgetItem*> items = ui_detacherview_base.attachmentList->selectedItems();
if ( items.isEmpty() ) {
kDebug() << "No attachment selected";
return;
}
if ( !mItem.hasPayload<MessagePtr>() ) {
kWarning() << "Item no longer has a payload";
return;
}
// get the selected list item's text. it is the attachment's filename
const QString fileName = items.first()->text();
// ask for a saving location, using the attachment's filename as a
// suggestion
KFileDialog dialog( KUrl(), QString(), this );
dialog.setMode( KFile::Files | KFile::LocalOnly );
dialog.setOperationMode( KFileDialog::Saving );
dialog.setConfirmOverwrite( true );
dialog.setSelection( fileName );
if ( dialog.exec() != QDialog::Accepted ) {
kDebug() << "Saving cancelled. Aborting detaching";
return;
}
const QString saveFileName = dialog.selectedFile();
if ( saveFileName.isEmpty() ) {
kDebug() << "Empty target file name. Aborting detaching";
return;
}
// find the corresponding attachment data structure
const MessagePtr message = mItem.payload<MessagePtr>();
const KMime::Content::List attachments = message->attachments();
KMime::Content *selectedAttachment = 0;
foreach ( KMime::Content *attachment, attachments ) {
if ( fileName == attachment->contentDisposition()->filename() ) {
selectedAttachment = attachment;
break;
}
}
if ( selectedAttachment == 0 ) {
kWarning() << "Selected attachment file name no longer available in message. Aborting detaching";
return;
}
QFile file( saveFileName );
if ( !file.open( QIODevice::WriteOnly ) ) {
kError() << "Cannot open target file for writing. Aborting detaching.";
return;
}
file.write( selectedAttachment->decodedContent() );
file.close();
}

Removing the Attachment
After successfully saving the attachment we can proceed with removing the attachment from the message data and finally update the item in Akonadi to make it a permanent change.
For the last step another job class is needed: ItemModifyJob
#include <akonadi/itemmodifyjob.h>
and can be implemented by appending the following code to DetacherView::detachAttachment()
// remove attachment from message
message->removeContent( selectedAttachment, true );
// and from the listwidget
delete items.first();
// prepare Akonadi update
Akonadi::Item item( mItem );
item.setPayload<MessagePtr>( message );
Akonadi::ItemModifyJob *modifyJob = new Akonadi::ItemModifyJob( item, this );
if ( !modifyJob->exec() ) {
kError() << modifyJob->errorString();
return;
}