Development/Tutorials/Qt4 Ruby Tutorial/Chapter 3/fi: Difference between revisions
Centerlink (talk | contribs) (Created page with "=== Läpikäynti rivi riviltä ===") |
Centerlink (talk | contribs) (Created page with "Luomme tässä yksinkertaisesti pelkän käyttöliittymäkomponenttiobjektin. Luokka [http://doc.qt.nokia.com/latest/qwidget.html Qt::Widget] on käyttöliittymäobjektien perusl...") |
||
| Line 44: | Line 44: | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
Luomme tässä yksinkertaisesti pelkän käyttöliittymäkomponenttiobjektin. Luokka [http://doc.qt.nokia.com/latest/qwidget.html Qt::Widget] on käyttöliittymäobjektien perusluokka. Käyttöliittymäkomponentti on käyttölittymän ydin: Se vastaanotta hiiren, näppäimistön ja muita tapahtumia ikkunointijärjestelmästä, piirtää esityksen itsestään näytölle. Vanhempikomponentti ja käyttöliittymäkomponentin edustalla sijaitsevat komponentit leikkaavat käyttöliittymäkomnponenttia. | |||
A widget that isn't embedded in a parent widget, like this particular widget, is called a window. Usually, windows have their own window frame and taskbar entry, provided by the window system. A widget without a parent widget is always an independent window. Its initial position on the screen is controlled by the window system. | A widget that isn't embedded in a parent widget, like this particular widget, is called a window. Usually, windows have their own window frame and taskbar entry, provided by the window system. A widget without a parent widget is always an independent window. Its initial position on the screen is controlled by the window system. | ||
Revision as of 15:24, 25 September 2011
Development/Tutorials/Qt4 Ruby Tutorial/Chapter 3
Languages: عربي | Asturianu | Català | Česky | Kaszëbsczi | Dansk | Deutsch | English | Esperanto | Español | Eesti | فارسی | Suomi | Français | Galego | Italiano | 日本語 | 한국어 | Norwegian | Polski | Português Brasileiro | Română | Русский | Svenska | Slovenčina | Slovenščina | српски | Türkçe | Tiếng Việt | Українська | 简体中文 | 繁體中文
| Tutorial Series | Qt4 Ruby -oppikurssi |
| Previous | Oppikurssi 2 - Poistutaan kutsumalla |
| What's Next | Oppikurssi 4 - Olkoon siellä käyttöliittymäkomponentteja |
| Further Reading | n/a |
Perhearvot
Tiedostot:
Yleistä
Tämä esimerkki näyttää, kuinka luodaan vanhempi- ja lapsikäyttöliittymäkomponentteja.
Pidämme asiat yksinkertaisina ja käytämme vain yhtä vanhempaa ja yksinäistä lasta.
require 'Qt4'
app = Qt::Application.new(ARGV)
window = Qt::Widget.new()
window.resize(200, 120)
quit = Qt::PushButton.new('Poistu', window)
quit.font = Qt::Font.new('Times', 18, Qt::Font::Bold)
quit.setGeometry(10, 40, 180, 40)
Qt::Object.connect(quit, SIGNAL('clicked()'), app, SLOT('quit()'))
window.show()
app.exec()
Läpikäynti rivi riviltä
window = Qt::Widget.new()
Luomme tässä yksinkertaisesti pelkän käyttöliittymäkomponenttiobjektin. Luokka Qt::Widget on käyttöliittymäobjektien perusluokka. Käyttöliittymäkomponentti on käyttölittymän ydin: Se vastaanotta hiiren, näppäimistön ja muita tapahtumia ikkunointijärjestelmästä, piirtää esityksen itsestään näytölle. Vanhempikomponentti ja käyttöliittymäkomponentin edustalla sijaitsevat komponentit leikkaavat käyttöliittymäkomnponenttia.
A widget that isn't embedded in a parent widget, like this particular widget, is called a window. Usually, windows have their own window frame and taskbar entry, provided by the window system. A widget without a parent widget is always an independent window. Its initial position on the screen is controlled by the window system.
window.resize(200, 120)
We set the window's width to 200 pixels and its height to 120 pixels.
quit = Qt::PushButton.new('Quit', window)
A child is born. This Qt::PushButton is created with a parent widget (window). A child widget is always displayed within its parent's area. When displayed, it is clipped by its parent's bounds. By default, it is rooted at the top-left corner of its parent, at position (0, 0).
quit.setGeometry(10, 40, 180, 40)
The Qt::Widget::setGeometry() function takes four arguments: The first two arguments are the x and y coordinates of the button's top-left corner. The coordinates are relative to the parent widget. The last two arguments are the button's width and height. The result is a button that extends from position (10, 40) to position (190, 80).
window.show()
When a parent widget is shown, it will call show for all its children (except those that were explicitly hidden using Qt::Widget::hide()).
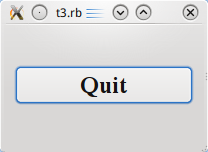
Running the Application
The button no longer fills the entire window. Instead, it stays at position (10, 40) within the window and with a size of (180, 40), because of the Qt::Widget::setGeometry() call.
Exercises
Try resizing the window. How does the button change? What happens to the button's height if you run the program with a bigger font? What happens if you try to make the window really small?
