Development/Tutorials/Qt4 Ruby Tutorial/Chapter 14: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
Neverendingo (talk | contribs) m (Text replace - "<code ruby>" to "<syntaxhighlight lang="ruby">") |
||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
The '''<tt>CannonField</tt>''' can now receive mouse events to make the user aim the barrel by clicking on it and dragging. '''<tt>CannonField</tt>''' also has a barrier wall. | The '''<tt>CannonField</tt>''' can now receive mouse events to make the user aim the barrel by clicking on it and dragging. '''<tt>CannonField</tt>''' also has a barrier wall. | ||
< | <syntaxhighlight lang="ruby"> | ||
@barrelPressed = false | @barrelPressed = false | ||
</code> | </code> | ||
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
This line has been added to the constructor. Initially, the mouse is not pressed on the barrel. | This line has been added to the constructor. Initially, the mouse is not pressed on the barrel. | ||
< | <syntaxhighlight lang="ruby"> | ||
elsif shotR.x() > width() || shotR.y() > height() || | elsif shotR.x() > width() || shotR.y() > height() || | ||
shotR.intersects(barrierRect()) | shotR.intersects(barrierRect()) | ||
| Line 39: | Line 39: | ||
Now that we have a barrier, there are three ways to miss. We test for the third, too. (In '''<tt>moveShot()</tt>'''.) | Now that we have a barrier, there are three ways to miss. We test for the third, too. (In '''<tt>moveShot()</tt>'''.) | ||
< | <syntaxhighlight lang="ruby"> | ||
def mousePressEvent(event) | def mousePressEvent(event) | ||
unless event.button() == Qt::LeftButton | unless event.button() == Qt::LeftButton | ||
| Line 57: | Line 57: | ||
Notice that the [http://doc.qt.nokia.com/latest/qmouseevent.html#pos Qt::MouseEvent::pos()] function returns a point in the widget's coordinate system. | Notice that the [http://doc.qt.nokia.com/latest/qmouseevent.html#pos Qt::MouseEvent::pos()] function returns a point in the widget's coordinate system. | ||
< | <syntaxhighlight lang="ruby"> | ||
def mouseMoveEvent(event) | def mouseMoveEvent(event) | ||
unless @barrelPressed | unless @barrelPressed | ||
| Line 88: | Line 88: | ||
Remember that '''<tt>setAngle()</tt>''' redraws the cannon. | Remember that '''<tt>setAngle()</tt>''' redraws the cannon. | ||
< | <syntaxhighlight lang="ruby"> | ||
def mouseReleaseEvent(event) | def mouseReleaseEvent(event) | ||
if event.button() == Qt::LeftButton | if event.button() == Qt::LeftButton | ||
| Line 102: | Line 102: | ||
The paint event has one extra line: | The paint event has one extra line: | ||
< | <syntaxhighlight lang="ruby"> | ||
paintBarrier(painter) | paintBarrier(painter) | ||
</code> | </code> | ||
| Line 108: | Line 108: | ||
'''<tt>paintBarrier()</tt>''' does the same sort of thing as '''<tt>paintShot()</tt>''', '''<tt>paintTarget()</tt>''', and '''<tt>paintCannon()</tt>'''. | '''<tt>paintBarrier()</tt>''' does the same sort of thing as '''<tt>paintShot()</tt>''', '''<tt>paintTarget()</tt>''', and '''<tt>paintCannon()</tt>'''. | ||
< | <syntaxhighlight lang="ruby"> | ||
def paintBarrier( painter ) | def paintBarrier( painter ) | ||
painter.setBrush(Qt::Brush.new(Qt::yellow)) | painter.setBrush(Qt::Brush.new(Qt::yellow)) | ||
| Line 118: | Line 118: | ||
This function paints the barrier as a rectangle filled with yellow and with a black outline. | This function paints the barrier as a rectangle filled with yellow and with a black outline. | ||
< | <syntaxhighlight lang="ruby"> | ||
def barrierRect() | def barrierRect() | ||
return Qt::Rect.new(145, height() - 100, 15, 99) | return Qt::Rect.new(145, height() - 100, 15, 99) | ||
| Line 126: | Line 126: | ||
This function returns the rectangle of the barrier. We fix the bottom edge of the barrier to the bottom edge of the widget. | This function returns the rectangle of the barrier. We fix the bottom edge of the barrier to the bottom edge of the widget. | ||
< | <syntaxhighlight lang="ruby"> | ||
def barrelHit(pos) | def barrelHit(pos) | ||
matrix = Qt::Matrix.new() | matrix = Qt::Matrix.new() | ||
| Line 146: | Line 146: | ||
'''[http://www.darshancomputing.com/qt4-qtruby-tutorial/tutorial/t14/gamebrd.rb gamebrd.rb]''' | '''[http://www.darshancomputing.com/qt4-qtruby-tutorial/tutorial/t14/gamebrd.rb gamebrd.rb]''' | ||
< | <syntaxhighlight lang="ruby"> | ||
cannonBox = Qt::Frame.new() | cannonBox = Qt::Frame.new() | ||
cannonBox.setFrameStyle(Qt::Frame::WinPanel | Qt::Frame::Sunken) | cannonBox.setFrameStyle(Qt::Frame::WinPanel | Qt::Frame::Sunken) | ||
| Line 153: | Line 153: | ||
We create and set up a [http://doc.qt.nokia.com/latest/qframe.html Qt::Frame], and set its frame style. This results in a 3D frame around the '''<tt>CannonField</tt>'''. | We create and set up a [http://doc.qt.nokia.com/latest/qframe.html Qt::Frame], and set its frame style. This results in a 3D frame around the '''<tt>CannonField</tt>'''. | ||
< | <syntaxhighlight lang="ruby"> | ||
Qt::Shortcut.new(Qt::KeySequence.new(Qt::Key_Enter.to_i), | Qt::Shortcut.new(Qt::KeySequence.new(Qt::Key_Enter.to_i), | ||
self, SLOT('fire()')) | self, SLOT('fire()')) | ||
| Line 168: | Line 168: | ||
Qt::CTRL, Qt::Key_Enter, Qt::Key_Return, and Qt::Key_Q are all constants declared in the Qt namespace. Unfortunately, in the current version of qtruby, they need to be converted to integers before we can use them in our shortcuts. | Qt::CTRL, Qt::Key_Enter, Qt::Key_Return, and Qt::Key_Q are all constants declared in the Qt namespace. Unfortunately, in the current version of qtruby, they need to be converted to integers before we can use them in our shortcuts. | ||
< | <syntaxhighlight lang="ruby"> | ||
leftLayout = Qt::VBoxLayout.new() | leftLayout = Qt::VBoxLayout.new() | ||
leftLayout.addWidget(angle) | leftLayout.addWidget(angle) | ||
Revision as of 20:43, 29 June 2011
Development/Tutorials/Qt4 Ruby Tutorial/Chapter 14
Languages: عربي | Asturianu | Català | Česky | Kaszëbsczi | Dansk | Deutsch | English | Esperanto | Español | Eesti | فارسی | Suomi | Français | Galego | Italiano | 日本語 | 한국어 | Norwegian | Polski | Português Brasileiro | Română | Русский | Svenska | Slovenčina | Slovenščina | српски | Türkçe | Tiếng Việt | Українська | 简体中文 | 繁體中文
| Tutorial Series | Qt4 Ruby Tutorial |
| Previous | Tutorial 13 - Game Over |
| What's Next | n/a |
| Further Reading | n/a |
Facing the Wall
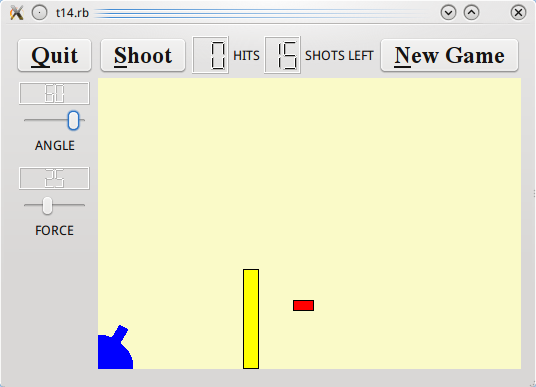
Files:
Overview
This is the final example: a complete game.
We add keyboard accelerators and introduce mouse events to CannonField. We put a frame around the CannonField and add a barrier (wall) to make the game more challenging.
Line by Line Walkthrough
The CannonField can now receive mouse events to make the user aim the barrel by clicking on it and dragging. CannonField also has a barrier wall.
<syntaxhighlight lang="ruby"> @barrelPressed = false
This line has been added to the constructor. Initially, the mouse is not pressed on the barrel.
<syntaxhighlight lang="ruby"> elsif shotR.x() > width() || shotR.y() > height() ||
shotR.intersects(barrierRect())
Now that we have a barrier, there are three ways to miss. We test for the third, too. (In moveShot().)
<syntaxhighlight lang="ruby"> def mousePressEvent(event)
unless event.button() == Qt::LeftButton return end
if barrelHit(event.pos()) @barrelPressed = true end
end
This is a Qt event handler. It is called when the user presses a mouse button when the mouse cursor is over the widget.
If the event was not generated by the left mouse button, we return immediately. Otherwise, we check if the position of the mouse cursor is within the cannon's barrel. If it is, we set barrelPressed to true.
Notice that the Qt::MouseEvent::pos() function returns a point in the widget's coordinate system.
<syntaxhighlight lang="ruby"> def mouseMoveEvent(event)
unless @barrelPressed return end
pos = event.pos();
if pos.x() <= 0 pos.setX(1) end
if pos.y() >= height() pos.setY(height() - 1) end
rad = atan2((rect().bottom() - pos.y()), pos.x()) setAngle((rad * 180 / 3.14159265).round())
end
This is another Qt event handler. It is called when the user already has pressed the mouse button inside this widget and then moves/drags the mouse. (You can make Qt send mouse move events even when no buttons are pressed. See Qt::Widget::setMouseTracking().)
This handler repositions the cannon's barrel according to the position of the mouse cursor.
First, if the barrel is not pressed, we return. Next, we fetch the mouse cursor's position. If the mouse cursor is to the left or below the widget, we adjust the point to be inside the widget.
Then we calculate the angle between the bottom edge of the widget and the imaginary line between the bottom-left corner of the widget and the cursor position. Finally we set the cannon's angle to the new value converted to degrees.
Remember that setAngle() redraws the cannon.
<syntaxhighlight lang="ruby"> def mouseReleaseEvent(event)
if event.button() == Qt::LeftButton @barrelPressed = false end
end
This Qt event handler is called whenever the user releases a mouse button and it was pressed inside this widget.
If the left button is released, we can be sure that the barrel is no longer pressed.
The paint event has one extra line:
<syntaxhighlight lang="ruby"> paintBarrier(painter)
paintBarrier() does the same sort of thing as paintShot(), paintTarget(), and paintCannon().
<syntaxhighlight lang="ruby"> def paintBarrier( painter )
painter.setBrush(Qt::Brush.new(Qt::yellow)) painter.setPen(Qt::Color.new(Qt::black)) painter.drawRect(barrierRect())
end
This function paints the barrier as a rectangle filled with yellow and with a black outline.
<syntaxhighlight lang="ruby"> def barrierRect()
return Qt::Rect.new(145, height() - 100, 15, 99)
end
This function returns the rectangle of the barrier. We fix the bottom edge of the barrier to the bottom edge of the widget.
<syntaxhighlight lang="ruby"> def barrelHit(pos)
matrix = Qt::Matrix.new() matrix.translate(0, height()) matrix.rotate(-@currentAngle) matrix = matrix.inverted() return @barrelRect.contains(matrix.map(pos))
end
This function returns true if the point is in the barrel; otherwise it returns false.
Here we use the class Qt::Matrix. Qt::Matrix defines a coordinate system mapping. It can perform the same transformations as the Qt::Painter.
Here we perform the same transformation steps as we do when drawing the barrel in the paintCannon() function. First we translate the coordinate system and then we rotate it.
Now we need to check whether the point pos (in widget coordinates) lies inside the barrel. To do this, we invert the transformation matrix. The inverted matrix performs the inverse transformation that we used when drawing the barrel. We map the point pos using the inverted matrix and return true if it is inside the original barrel rectangle.
<syntaxhighlight lang="ruby"> cannonBox = Qt::Frame.new() cannonBox.setFrameStyle(Qt::Frame::WinPanel | Qt::Frame::Sunken)
We create and set up a Qt::Frame, and set its frame style. This results in a 3D frame around the CannonField.
<syntaxhighlight lang="ruby"> Qt::Shortcut.new(Qt::KeySequence.new(Qt::Key_Enter.to_i),
self, SLOT('fire()'))
Qt::Shortcut.new(Qt::KeySequence.new(Qt::Key_Return.to_i),
self, SLOT('fire()'))
Qt::Shortcut.new(Qt::KeySequence.new(Qt::CTRL.to_i + Qt::Key_Q.to_i),
self, SLOT('close()'))
Here we create and set up three Qt::Shortcut objects. These objects intercept keyboard events to a widget and call slots if certain keys are pressed. Note that a Qt::Shortcut object is a child of a widget and will be destroyed when that widget is destroyed. Qt::Shortcut itself is not a widget and has no visible effect on its parent.
We define three shortcut keys. We want the fire() slot to be called when the user presses Enter or Return. We also want the application to quit when key Ctrl+Q is pressed. Instead of connecting to Qt::CoreApplication::quit(), we connect to Qt::Widget::close() this time. Since the GameBoard is the application's main widget, this has the same effect as QCoreApplication::quit().
Qt::CTRL, Qt::Key_Enter, Qt::Key_Return, and Qt::Key_Q are all constants declared in the Qt namespace. Unfortunately, in the current version of qtruby, they need to be converted to integers before we can use them in our shortcuts.
<syntaxhighlight lang="ruby"> leftLayout = Qt::VBoxLayout.new() leftLayout.addWidget(angle) leftLayout.addWidget(force)
gridLayout = Qt::GridLayout.new() gridLayout.addWidget(quit, 0, 0) gridLayout.addLayout(topLayout, 0, 1) gridLayout.addLayout(leftLayout, 1, 0) gridLayout.addWidget(@cannonField, 1, 1, 2, 1) gridLayout.setColumnStretch(1, 10) setLayout(gridLayout)
We give cannonBox its own Qt::VBoxLayout, and we add CannonField to that layout. This implicitly makes CannonField a child of cannonBox. Because nothing else is in the box, the effect is that the Qt::VBoxLayout will put a frame around the CannonField. We put cannonBox, not CannonField, in the grid layout.
Running the Application
The cannon now shoots when you press Enter. You can also position the cannon's angle using the mouse. The barrier makes it a little more challenging to play the game. We also have a nice looking frame around the CannonField.
Exercises
Write a space invaders game.
The new exercise is: Write a Breakout game.
Final exhortation: Go forth now and create masterpieces of the programming art!
