Development/Tutorials/KSpread Scripting
Intro
KSpread
KOffice is an interated Office Suite consisting of several applications where KSpread is the scriptable spreadsheet program which provides both table-oriented sheets and support for complex mathematical formulas and statistics.
The KSpread Scripting Plugin implements a plugin to dynamic access the scripting functionality from within KSpread. The plugin realizes usage-scenarios like;
- Extend KSpread with new functionality
- Dynamic add new formula functions
- Use the KSpread library from a script to automate things
The whole KSpread Scripting Plugin that does handle all things related to scripting for KSpread consist of only 3 files;
- The ScriptingPart class (dox svn) implements a KParts::Plugin component to integrate scripting into KSpread.
- The ScriptingModule class (dox svn) enables access to the KSpread functionality from within the scripting backends. To access functionality KSpread offers classes like KoApplicationAdaptor, KoDocumentAdaptor, SheetAdaptor and ViewAdaptor are distributed to the scripting backends.
- The ScriptingFunction class (dox svn) provides access to the KSpread::Function functionality to deal with formula functions that are written in a scripting language like Python or Ruby.
Kross
The Kross scripting framework provides full Python, Ruby and KDE JavaScript scripting support. The KSpread scripting plugin uses this framework to deal with scripting on an abstract level. Kross does handle interpreter-backend details while KSpread does not need to know anything about Kross, Python, Ruby or KDE JavaScript.
The goal was to limit the work needed on an application to have it full scriptable. To achieve this internaly Qt's introspection-functionality like signals, slots, properties, enums, QObject's and QMetaObject/QMetaType/etc. is used to deal with functionality at runtime. To get a more detailed overview you may like to take a look at my talk about scripting with Kross.
Kross is included in the kdelibs4 (KDE4 libraries). The Kross scripting framework consists of the Kross library which handles the Kross interpreter-backend details and the "kross" commandline-application which could be used to execute Python, Ruby or KDE JavaScript scripts direct from the commandline rather then embedded in an application like KSpread.
Scripting Handbook
The KSpread Scripting Handbook contains a full reference of all objects and methods accessible from within the scripting backends.
The Handbook is generated from the sourcecode using doxygen and the doxy2doc.py Python script as postprocessor to create visible output from the by doxygen produced XML files.
Links
- KSpread Homepage
- KSpread Wiki
- KSpread Scripting Plugin code
- KSpread Scripting Plugin ReadMe
- Kross Homepage
- Kross Wiki Page
- Kross Tutorial
Scripting Extensions
Extensions are used to extend KSpread with additional functionality written with Python, Ruby or KDE JavaScript scripts.
The htmlexport.py Python script demonstrates how extensions could be used. The script exports the content of the current sheet to a HTML file.
Extensions are located in the "Scripts"-menu and are either distributed with KSpread, so some default extensions like the htmlexport.py script are installed together with KSpread as part of it, or could be later added and configured on demand using the "Script Manager".
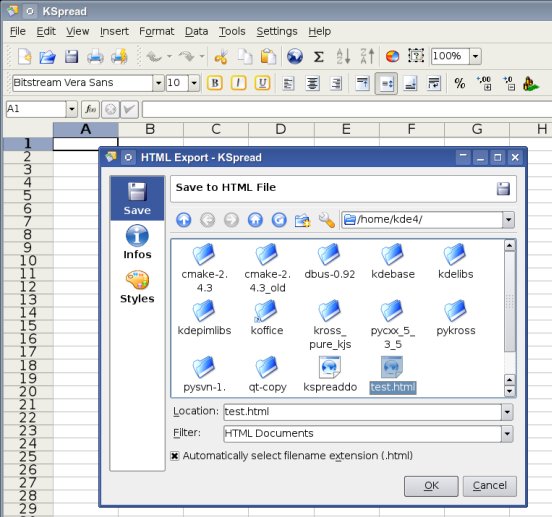
Once the htmlexport.py Python script got executed, it displays the "HTML Export" dialog to let the user define the HTML file that should be written and some additional details like Document Informations or Styles. For GUI-related things you are also able to use PyQt4 or Tkinter in your python scripts, Korundum/QtRuby in your Ruby scripts, KjsEmbed4 (KjsEmbded4 is included in kdelibs4 now) in your JavaScript scripts or the more high-level Kross forms (used in the htmlexport.py as shown in the screenshot below) in all interpreter-backends.
If the user clicks on the "Ok" button the export-process starts and a progress-dialog is displayed to offer visual feedback while the Python script reads the content from the current sheet and writes it to a HTML file.
Ideas for additional extensions users may like;
- SVN import/export or even something like a change-managment using PySVN
- PDF creator using ReportLab
- Connector to the Zope open source application server. See also the Connect KSpread with the Zope application server using XML-RPC sample script.
- Connect with OpenOffice.org using PyUNO
- Use the Python DBus module to e.g. connect with amarok, Kopete, Kontact, ...
Scripting Formula Functions
KSpread has a rich set of formula functions for nearly every purpose. KSpread implements the whole set of the OpenFormula specification and could be easy extended with additional formula functions written in a scripting language.
The functions.py Python script demonstrates this by defining the KSpread formula function "SCRIPT_TEST1";
# create the new formula function "SCRIPT_TEST1"
functest1 = self.kspread.function("SCRIPT_TEST1")
# set the minimal number of parameters
functest1.minparam = 1
# set the maximal number of parameters, -1 means unlimited.
functest1.maxparam = 1
# set the comment displayed at "Help"
functest1.comment = (
"The SCRIPT_TEST1() function demonstrates how to use scripting"
"functions. All it does is to take a string as argument and"
"return the same string."
)
# set the syntax which is displayed at "Help".
functest1.syntax = "SCRIPT_TEST1(string)"
# set details about the parameter the formula functions expects.
functest1.addParameter("String", "The string that should be returned")
# add an example displayed at "Help".
functest1.addExample("SCRIPT_TEST1(\"Some string\")")
# this python function will be called by the KSpread formula function
def functest1callback(argument):
# just return the first argument
functest1.result = "%s" % argument[0]
# connect the python function with the KSpread formula function
functest1.connect("called(QVariantList)", functest1callback)
# and finally register the function to be able to use it within KSpread
functest1.registerFunction()
Now we run KSpread with the --scriptfile argument that points to the delivered functions.py example.
# make the script executable chmod 755 `kde4-config --install data`/kspread/scripts/functions/functions.py # run KSpread kspread --scriptfile `kde4-config --install data`/kspread/scripts/functions/functions.py
The screenshot below shows KSpread using the new formula function "SCRIPT_TEST1" which was added and is handled in the functions.py script.
All at the functions.py script added formula functions are accessible via "Insert=>Function..." in the "Scripts" category.
File:Kspread2scripting screeny2.jpg
Ideas for additional formula functions users may like;
- Additional formula functions KSpread does not support yet. Not only useful for rapid prototyping but also to just integrate fast and flexible functionality written in a scripting-language like Python, Ruby or KDE JavaScript.
- Collaboration e.g. synchronous editing between 2 or more people. Propably using Kopete/dbus...
- Tunnel all formula functions through a script to be able to implement transparent logging, access-levels, merging, ...
Scripting with KSpread Library Samples
The functionality KSpread offers could also be used direct from the commandline without a running KSpread instance. In that case a script written in Python, Ruby or KDE JavaScript controls what should be done and the KSpread library is loaded and used in the background to deal with the whole KSpread-stack on a high-level. This enables to batch-process or automated creation and/or manipulation of OpenDocument Spreadsheet files. Complex calculations, document-manipulations and workflows without any user-interaction could be scripted and executed from the commandline that way.
Following samples are implementations of use-case scenarios KSpread could be used for. The scripts are simple executable files that run from within the commandline by using the "kross" application which is installed together with the Kross scripting framework.
Export OpenDocument Spreadsheet file to a CSV file
The following Python script reads the OpenDocument Spreadsheet file "/home/kde4/invoicetemplate.ods" and writes the first sheet to a CSV (Comma Separated Value) file.
The complete csvexport.py script including the invoicetemplate.ods OpenDocument Spreadsheet file used as template is available as csvexport.tar.gz. Download, extract, edit the csvexport.py to change the "filename" and "csvfile" variables to point to the correct locations and execute the csvexport.py Python script ("chmod 755 csvexport.py" to make the script executable and "./csvexport.py" to execute the script).
The csvexport.py Python script looks like;
#!/usr/bin/env kross
# The OpenDocument Spreadsheet file that we like to read.
filename = "/home/kde4/invoicetemplate.ods"
# The CSV file we like to write to.
csvfile = "/home/kde4/invoicetemplate.csv"
# Import Kross and fetch the KSpread module.
import Kross
kspread = Kross.module("kspread")
# Try to open the file.
if not kspread.openUrl(filename):
raise "Failed to open the file \"%s\"." % filename
# Import the Python CSV module and create a writer.
import csv
csvwriter = csv.writer( open(csvfile,'w') )
# Get the sheet we like to export to the CSV file.
sheet = kspread.sheetByName( kspread.sheetNames()[0] )
# Iterate now through all cells on the sheet.
for row in range(1, sheet.lastRow() + 1):
# Put the content of the row into the record-list.
record = []
for col in range(sheet.lastColumn() + 1, 1, -1):
value = sheet.text(col, row)
if value or len(record) > 0:
record.insert(0,value)
# If the record has at least one cell print it.
if len(record) > 0:
csvwriter.writerow( record )
Export OpenDocument Spreadsheet file to a HTML file
The htmlexport.py Python script distributed with KSpread could also be executed from the commandline;
# make the script executable chmod 755 `kde4-config --install data`/kspread/scripts/extensions/htmlexport.py # run the script `kde4-config --install data`/kspread/scripts/extensions/htmlexport.py
Export OpenDocument Spreadsheet file to a custom OpenDocument file
The odfpyexport.py Python script distributed with KSpread uses the OdfPy Python module to write an OpenDocument text file (ODT) from KSpread. Take the script as example how easy scripting with KSpread is and modify it to your needs to produce custom OpenDocument files.
Write OpenDocument Spreadsheet file from invoice template
The following Python script reads the OpenDocument Spreadsheet template-file "/home/kde4/invoicetemplate.ods", fills some cells within a sheet and writes a new OpenDocument Spreadsheet file.
The complete invoice-example including the invoice.py Python script and the invoicetemplate.ods OpenDocument Spreadsheet file used as template is available as invoice.tar.gz. Download, extract, edit the invoice.py to change the "templatefile" and "savefile" variables to point to the correct locations and execute the invoice.py Python script ("chmod 755 invoice.py" to make the script executable and "./invoice.py" to execute the script).
The invoice.py Python script looks like;
#!/usr/bin/env kross
# The OpenDocument Spreadsheet file that we like to read from.
templatefile = "/home/kde4/invoicetemplate.ods"
# The OpenDocument Spreadsheet file that we like to write to.
savefile = "/home/kde4/invoice.ods"
# Import Kross and fetch the KSpread module.
import Kross
kspread = Kross.module("kspread")
# Try to open the file.
if not kspread.openUrl(templatefile):
raise "Failed to open the file \"%s\"." % templatefile
# Get the sheet we like to manipulate.
sheet = kspread.sheetByName( kspread.sheetNames()[0] )
# Set the content of some cells.
sheet.setText(1,7,"Joe User")
sheet.setText(1,8,"Userstreet. 1")
sheet.setText(1,9,"Testcasecity")
# Finally write the new OpenDocument Spreadsheet file.
if not kspread.saveUrl(savefile):
raise "Failed to save the file \"%s\"." % savefile
Connect KSpread with the Zope application server using XML-RPC
Zope is an open source application server for building content management systems, intranets, portals, and custom applications with a large community of hundreds of companies and thousands of developers all over the world. Zope is written in Python, a highly-productive, object-oriented scripting language and supports the XML-RPC and SOAP protocols.
The kspread2zope.tar.gz tarball includes a Python script that demonstrates how to connect KSpread with the Zope application server using XML-RPC. What the script does is to download a resource from the Zope server, then parses it into KSpread sheets, changes some content and then either save it as OpenDocument Spreadsheet file or upload the content at the Zope server.