Archive:Development/Tutorials/Qt4 Ruby Tutorial/Chapter 14 (zh TW): Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 80: | Line 80: | ||
這是另一個 Qt 事件處理器。當使用者已經在這個 widget 內按下滑鼠按鈕,然後移動/拖動滑鼠時被呼叫。(即使沒有任何按鍵被按下,您也可以讓 Qt 發送滑鼠移動事件。參閱 [http://doc.qt.nokia.com/latest/qwidget.html#mouseTracking-prop Qt::Widget::setMouseTracking()]。) | 這是另一個 Qt 事件處理器。當使用者已經在這個 widget 內按下滑鼠按鈕,然後移動/拖動滑鼠時被呼叫。(即使沒有任何按鍵被按下,您也可以讓 Qt 發送滑鼠移動事件。參閱 [http://doc.qt.nokia.com/latest/qwidget.html#mouseTracking-prop Qt::Widget::setMouseTracking()]。) | ||
這個處理器會根據游標的位置,重新定位砲管。 | |||
首先,如果砲管沒有被按下,我們返回。下一步,我們取得游標的位置。如果游標移到 widget 的左邊或底部,我們調整這個點到 widget 的內部。 | |||
然後,我們計算 widget 底邊,與 widget 左下角和游標位置構成假想線之間的角度。最後,我們設定加農砲的角度為換算成度的新值。 | |||
記得用 '''<tt>setAngle()</tt>''' 重繪加農砲。 | |||
<code ruby> | <code ruby> | ||
| Line 96: | Line 96: | ||
</code> | </code> | ||
無論使用者何時釋放滑鼠按鈕,且它是在這個 widget 裡面按下時,這個 Qt 事件處理器被呼叫。 | |||
如果左邊的按鈕被釋放,我們可以確定砲管已不再被按住了。 | |||
繪圖事件還多了一行: | |||
<code ruby> | <code ruby> | ||
| Line 106: | Line 106: | ||
</code> | </code> | ||
'''<tt>paintBarrier()</tt>''' | '''<tt>paintBarrier()</tt>''' 與 '''<tt>paintShot()</tt>'''、'''<tt>paintTarget()</tt>''',和 '''<tt>paintCannon()</tt>''' 作同類的事情。 | ||
<code ruby> | <code ruby> | ||
| Line 116: | Line 116: | ||
</code> | </code> | ||
這個函式繪製一個填充黃色和黑色外框的矩形作為障礙。 | |||
<code ruby> | <code ruby> | ||
| Line 124: | Line 124: | ||
</code> | </code> | ||
這個函式返回障礙的矩形。我們把障礙的底邊固定在 widget 的底邊。 | |||
<code ruby> | <code ruby> | ||
| Line 136: | Line 136: | ||
</code> | </code> | ||
如果點在砲管裡,這個函式返回 '''<tt>true</tt>''';否則返回 '''<tt>false</tt>'''。 | |||
這裡我們使用 [http://doc.qt.nokia.com/latest/qmatrix.html Qt::Matrix] 類別。[http://doc.qt.nokia.com/latest/qmatrix.html Qt::Matrix] 定義了一個坐標系統映射。它可以執行與 [http://doc.qt.nokia.com/latest/qpainter.html Qt::Painter] 相同的轉換。 | |||
這裡,我們執行與 '''<tt>paintCannon()</tt>''' 函式中繪製砲管的同樣轉換步驟。首先,我們轉移坐標系,然後旋轉。 | |||
現在我們需要檢查點 '''<tt>pos</tt>'''(在 widget 坐標)是否位於砲管內。為了做到這一點,我們倒轉這個轉移矩陣。倒轉矩陣執行了我們使用在繪製砲管的倒轉轉移。我們使用倒轉矩陣來映射點 '''<tt>pos</tt>'''。如果它在原來砲管的矩形裡面,返回 '''<tt>true</tt>'''。 | |||
'''[http://www.darshancomputing.com/qt4-qtruby-tutorial/tutorial/t14/gamebrd.rb gamebrd.rb]''' | '''[http://www.darshancomputing.com/qt4-qtruby-tutorial/tutorial/t14/gamebrd.rb gamebrd.rb]''' | ||
Revision as of 13:09, 16 January 2010
Template:I18n/Language Navigation Bar (zh TW) Template:TutorialBrowser (zh TW)
Facing the Wall
檔案:
概覽
這是最後的範例:一個完整的遊戲。
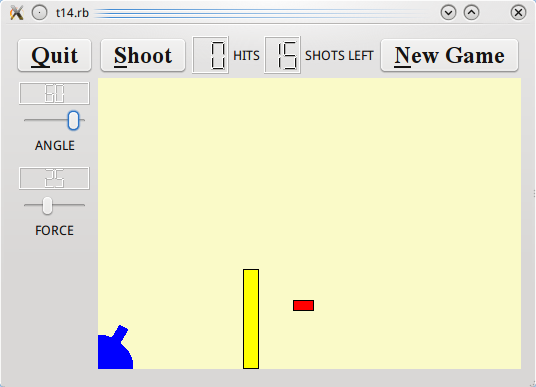
我們加上鍵盤快捷鍵(accelerator)和引入滑鼠事件到 CannonField。我們放置了一個環繞 CannonField 的外框,並加上一個障礙(牆),使遊戲更具挑戰性。
一行一行的瀏覽
CannonField 現在可以接收滑鼠事件,讓使用者透過按下並拖動砲管來瞄準。CannonField 也有障礙牆了。
@barrelPressed = false
這行加入到建構子。最初,滑鼠沒有在砲管上按下。
elsif shotR.x() > width() || shotR.y() > height() ||
shotR.intersects(barrierRect())
現在,我們有一個障礙,也就是第三種不擊中的方法。我們也測試第三種。(在 moveShot()。)
def mousePressEvent(event)
unless event.button() == Qt::LeftButton
return
end
if barrelHit(event.pos())
@barrelPressed = true
end
end
這是一個 Qt 事件處理器。當游標在 widget 上,且使用者按下滑鼠按鈕時,它會被呼叫。
如果事件不是滑鼠左鍵產生的,我們立即返回。否則,我們檢查游標的位置是否在加農砲的砲管內。假如是,我們就設定 barrelPressed 為 true。
請注意,Qt::MouseEvent::pos() 函式會返回一個 Widget 坐標系統中的點。
def mouseMoveEvent(event)
unless @barrelPressed
return
end
pos = event.pos();
if pos.x() <= 0
pos.setX(1)
end
if pos.y() >= height()
pos.setY(height() - 1)
end
rad = atan2((rect().bottom() - pos.y()), pos.x())
setAngle((rad * 180 / 3.14159265).round())
end
這是另一個 Qt 事件處理器。當使用者已經在這個 widget 內按下滑鼠按鈕,然後移動/拖動滑鼠時被呼叫。(即使沒有任何按鍵被按下,您也可以讓 Qt 發送滑鼠移動事件。參閱 Qt::Widget::setMouseTracking()。)
這個處理器會根據游標的位置,重新定位砲管。
首先,如果砲管沒有被按下,我們返回。下一步,我們取得游標的位置。如果游標移到 widget 的左邊或底部,我們調整這個點到 widget 的內部。
然後,我們計算 widget 底邊,與 widget 左下角和游標位置構成假想線之間的角度。最後,我們設定加農砲的角度為換算成度的新值。
記得用 setAngle() 重繪加農砲。
def mouseReleaseEvent(event)
if event.button() == Qt::LeftButton
@barrelPressed = false
end
end
無論使用者何時釋放滑鼠按鈕,且它是在這個 widget 裡面按下時,這個 Qt 事件處理器被呼叫。
如果左邊的按鈕被釋放,我們可以確定砲管已不再被按住了。
繪圖事件還多了一行:
paintBarrier(painter)
paintBarrier() 與 paintShot()、paintTarget(),和 paintCannon() 作同類的事情。
def paintBarrier( painter )
painter.setBrush(Qt::Brush.new(Qt::yellow))
painter.setPen(Qt::Color.new(Qt::black))
painter.drawRect(barrierRect())
end
這個函式繪製一個填充黃色和黑色外框的矩形作為障礙。
def barrierRect()
return Qt::Rect.new(145, height() - 100, 15, 99)
end
這個函式返回障礙的矩形。我們把障礙的底邊固定在 widget 的底邊。
def barrelHit(pos)
matrix = Qt::Matrix.new()
matrix.translate(0, height())
matrix.rotate(-@currentAngle)
matrix = matrix.inverted()
return @barrelRect.contains(matrix.map(pos))
end
如果點在砲管裡,這個函式返回 true;否則返回 false。
這裡我們使用 Qt::Matrix 類別。Qt::Matrix 定義了一個坐標系統映射。它可以執行與 Qt::Painter 相同的轉換。
這裡,我們執行與 paintCannon() 函式中繪製砲管的同樣轉換步驟。首先,我們轉移坐標系,然後旋轉。
現在我們需要檢查點 pos(在 widget 坐標)是否位於砲管內。為了做到這一點,我們倒轉這個轉移矩陣。倒轉矩陣執行了我們使用在繪製砲管的倒轉轉移。我們使用倒轉矩陣來映射點 pos。如果它在原來砲管的矩形裡面,返回 true。
cannonBox = Qt::Frame.new()
cannonBox.setFrameStyle(Qt::Frame::WinPanel | Qt::Frame::Sunken)
We create and set up a Qt::Frame, and set its frame style. This results in a 3D frame around the CannonField.
Qt::Shortcut.new(Qt::KeySequence.new(Qt::Key_Enter.to_i),
self, SLOT('fire()'))
Qt::Shortcut.new(Qt::KeySequence.new(Qt::Key_Return.to_i),
self, SLOT('fire()'))
Qt::Shortcut.new(Qt::KeySequence.new(Qt::CTRL.to_i + Qt::Key_Q.to_i),
self, SLOT('close()'))
Here we create and set up three Qt::Shortcut objects. These objects intercept keyboard events to a widget and call slots if certain keys are pressed. Note that a Qt::Shortcut object is a child of a widget and will be destroyed when that widget is destroyed. Qt::Shortcut itself is not a widget and has no visible effect on its parent.
We define three shortcut keys. We want the fire() slot to be called when the user presses Enter or Return. We also want the application to quit when key Ctrl+Q is pressed. Instead of connecting to Qt::CoreApplication::quit(), we connect to Qt::Widget::close() this time. Since the GameBoard is the application's main widget, this has the same effect as QCoreApplication::quit().
Qt::CTRL, Qt::Key_Enter, Qt::Key_Return, and Qt::Key_Q are all constants declared in the Qt namespace. Unfortunately, in the current version of qtruby, they need to be converted to integers before we can use them in our shortcuts.
leftLayout = Qt::VBoxLayout.new()
leftLayout.addWidget(angle)
leftLayout.addWidget(force)
gridLayout = Qt::GridLayout.new()
gridLayout.addWidget(quit, 0, 0)
gridLayout.addLayout(topLayout, 0, 1)
gridLayout.addLayout(leftLayout, 1, 0)
gridLayout.addWidget(@cannonField, 1, 1, 2, 1)
gridLayout.setColumnStretch(1, 10)
setLayout(gridLayout)
We give cannonBox its own Qt::VBoxLayout, and we add CannonField to that layout. This implicitly makes CannonField a child of cannonBox. Because nothing else is in the box, the effect is that the Qt::VBoxLayout will put a frame around the CannonField. We put cannonBox, not CannonField, in the grid layout.
執行應用程式
The cannon now shoots when you press Enter. You can also position the cannon's angle using the mouse. The barrier makes it a little more challenging to play the game. We also have a nice looking frame around the CannonField.
練習
Write a space invaders game.
(This exercise was first done by Igor Rafienko. You can download his game.)
The new exercise is: Write a Breakout game.
Final exhortation: Go forth now and create masterpieces of the programming art!
