Development/Tutorials/KPlotWidget
Introduction and Scope
KPlotWidget is used for easily creating 2-D plots of data sets, complete with plot axes that include labeled tickmarks and optional axis labels. Data sets can be represented as any combination of: discrete points (using a variety of point shapes), connected line segments (using any QPen), or bar-graph rectangles (using any QPen/QBrush). In addition, any data point can have a label string attached to it.
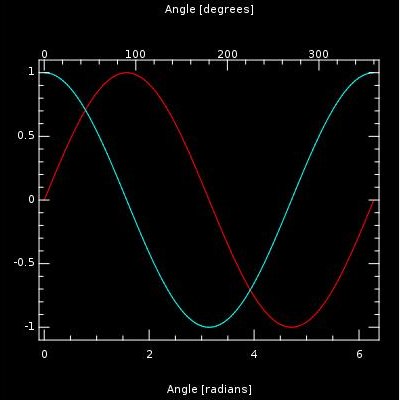
Here is a simple example showing sine and cosine curves:
This example demonstrates most of the commonly-used features of KPlotWidget. It is included in KDE, under kdelibs/kdeui/tests. The first part of this tutorial will explain how to produce this plot using KPlotWidget.
Basic Usage
The data to be plotted in KPlotWidget are stored as a list of KPlotObjects. Each KPlotObject itself consists of a list of KPlotPoints (which store the coordinates of each data point, as well as an optional text label), and methods to modify the parameters which control how they are drawn in the plot. KPlotWidget also contains four KPlotAxis objects, which encapsulate the plot axes, tickmarks, tickmark labels, and axis labels along the four edges bounding the plot.
KPlotWidget takes care of much of the plot rendering automatically, so simple data plots can be done with just a few lines of code:
- The area shown in the plot is determined from the range of the data in the KPlotObjects
- Tickmark positions are optimally computed, and synced between the top/bottom and left/right axes
- Tickmark labels are placed automatically along the left and bottom axes
- The padding area outside the axes is adjusted according to whether tickmark labels and/or axis labels are being drawn
- Data points are automatically transformed from their natural units to screen-pixel coordinates. In most cases, you will not have to care about pixel coordinates at all.
Basic usage of KPlotWidget is illustrated with the following example:
// Create a new KPlotWidget, provide a minimum size,
// and activate antialiased drawing:
KPlotWidget *plot = new KPlotWidget( parent );
plot->setMinimumSize( 400, 400 );
plot->setAntialiasing( true );
// Create a KPlotObject which will display data
// points by connecting them with red line segments
// with a width of 2 pixels:
KPlotObject *sineobj = new KPlotObject( Qt::red, KPlotObject::Lines, 2 );
// Add data points to the KPlotObject for a
// sine curve (these are stored internally
// as KPlotPoints):
for ( float t=0.0; t<=6.28; t+=0.04 )
sineobj->addPoint( t, sin(t) );
// Add the KPlotObject to the plot:
plot->addObject( sineobj );
// Add a text label to the bottom axis:
plot->axis( KPlotWidget::BottomAxis )->setLabel( i18n("Angle in radians") );
plot->update();
Rendering Options for KPlotObjects
The data points in a KPlotObject can be rendered in a number of ways: as discrete points, connected line segments, or bar-graph style rectangles. In fact, the same KPlotObject can be rendered in any combination of these styles; here is an example of a KPlotObject which will be rendered with all three styles:
po = new KPlotObject( Qt::white, KPlotObject::Points, 10, KPlotObject::Pentagon );
po->setShowLines( true );
po->setShowBars( true );
Note that when constructing a KPlotObject which will be rendered as Points, the third argument is the size of the points in pixels, and the fourth argument describes the shape to use when rendering each point. The options are:
- Circle
- Triangle
- Square
- Pentagon
- Hexagon
- Asterisk
- Star
By default, the same QPen and QBrush will be used to render the Points, Lines, and Bars. The color of the default pen and brush are set in the constructor. However, it is easy to provide custom pens and brushes for the different plot styles:
// Modify the pen used to draw Lines connecting
// data points in this KPlotObject:
po->setLinePen( QPen( Qt::red, 3.0, Qt::DashDotLine ) );
// Modify the brush used to fill Bars in this
// KPlotObject:
po->setBarBrush( QBrush( Qt::blue, Qt::BDiagPattern ) );
Traversing All Data Points
Both KPlotWidget and KPlotObject provide functions that return the list of KPlotObjects and KPlotPoints that they contain, so if one needed to access all of the data points in the plot, it can be done like this:
// "plot" is a KPlotWidget containing several KPlotObject data sets,
// each of which consists of several KPlotPoints
foreach( KPlotObject *po, plot->plotObjects() ) {
foreach( KPlotPoint *p, po->points() ) {
// Do stuff to each KPlotPoint
}
}
Labeling Data Points
Text labels can be attached to any point in a KPlotObject. The easiest way to accomplish this is to add the label text as the second argument to KPlotObject::addPoint( const QPointF&, const QString& ). There is also a KPlotPoint::setLabel( const QString& ) function, if you need to add a text label after the point has already been created.
Note that KPlotWidget will automatically try to place the labels intelligently, so that each label is close to its point without overlapping other labels or plot elements. If a label needs to be placed at some distance from its point, then the label and point will be connected with a line segment.
Customizing the plot
The basic usage outlined above will usually suffice for simple data plots. However, the time may come when you need more flexibility. Many aspects of the plot rendering which are normally done automatically can be manually overidden.