Development/Tutorials/KWord Scripting: Difference between revisions
screeny |
|||
| Line 190: | Line 190: | ||
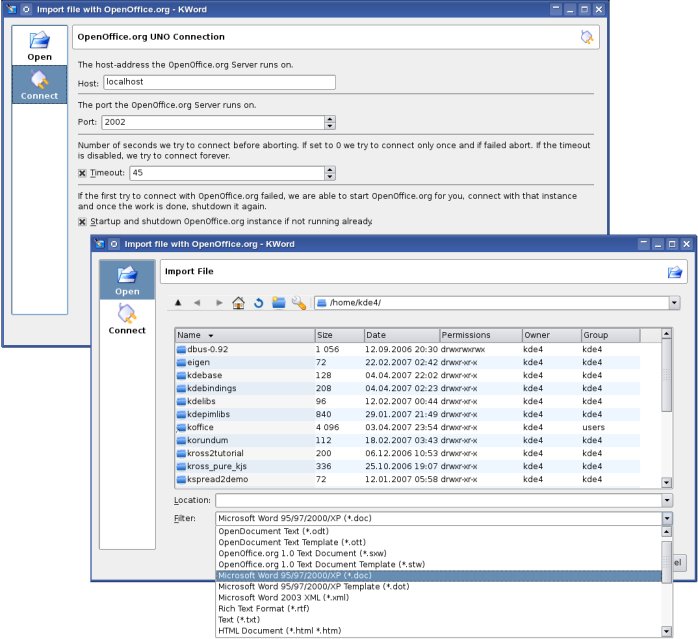
The python script [http://websvn.kde.org/trunk/koffice/kword/plugins/scripting/scripts/ooimport.py?view=markup ooimport.py] uses the PyUNO module to access OpenOffice.org and import content from any by OpenOffice.org supported fileformat. | The python script [http://websvn.kde.org/trunk/koffice/kword/plugins/scripting/scripts/ooimport.py?view=markup ooimport.py] uses the PyUNO module to access OpenOffice.org and import content from any by OpenOffice.org supported fileformat. | ||
For this an optional hidden OpenOffice.org instance need to be started. Then the script connects as client to this OpenOffice.org server instance and controls it. If the script got executed and the connecting to the server failed, then it will startup such a hidden OpenOffice.org server instance and shuts it down again once the work is done. | For this an optional hidden OpenOffice.org instance need to be started. Then the script connects as client to this OpenOffice.org server instance and controls it. If the script got executed and the connecting to the server failed, then it will startup such a hidden OpenOffice.org server instance and shuts it down again once the work is done. | ||
[[Image:kwordscriptingooimport.jpg]] | |||
Revision as of 02:53, 5 April 2007
Intro
KWord uses Kross to provide scripting with Python, Ruby and KDE JavaScript.
The Scripting Plugin
The KWord Scripting Plugin implements a plugin to dynamic access the scripting functionality from within KWord.
- The KWScriptingPart class implements a KPart component to integrate scripting as plugin into KWord.
- The Scripting::Module class enables access to the KWord functionality from within the scripting backends.
- The FrameSet and Frame classes are holding the content that is displayed on screen.
- The TextDocument class represents a QTextDocument within the Scribe text-engine KWord uses to enable editing of text content. The TextCursor implements a control structure for the successive traversal of content within such a TextDocument .
Scripting Handbook
The KWord Scripting Handbook contains a full reference of all objects and methods accessible from within the scripting backends.
The Handbook is generated from the sourcecode using doxygen and the doxy2doc.py Python script as postprocessor to create visible output from the by doxygen produced XML files.
Samples
Load and save documents
Following Python script demonstrates how to load and save files;
import KWord
KWord.document().openURL("/home/myuser/myDoc.odt")
KWord.document().saveAs("/home/myuser/myDocCopy.odt")
KWord.document().saveAs("/home/myuser/myDocAsText.txt")
All slots and signals within the KoDocumentAdaptor are accessible as KWord.document().
Import and export content
The sample_importfile.py Python script implements import of content from a text or html file.
import KWord
doc = KWord.mainFrameSet().document()
f = open("/home/myuser/mytextfile.txt", "r")
doc.setText( ' '.join(f.readlines()) )
#doc.setHtml( ' '.join(f.readlines()) )
f.close()
The sample_exportfile.py Python script implements export of content to a text or html file.
import KWord
doc = KWord.mainFrameSet().document()
f = open("/home/myuser/mytextfile.txt", "w")
f.write( doc.toText() )
#f.write( doc.toHtml() )
f.close()
Document Structure Viewer
The sample_doctree.rb QtRuby script implement a document structur viewer.
The viewer displays the framesets, frames, documents and there objects as tree where each node may provide additional functionality like a collection of properties, text or styles.
Framesets, Frames and Shapes
The following python script adds a polygon shape and then prints the name and the ID of each shape.
import KWord
KWord.addFrame("mypoly", "KoRegularPolygonShape")
for i in range( KWord.frameCount() ):
f = KWord.frame(i)
print "%s %s" % (f.frameSet().name(),f.shapeId())
The sample_insertshape.py Python script implements inserting of a shape into the document.
import KWord
textshape = KWord.addTextFrame("MyTextShape")
textshape.document().setText("Some text")
The sample_allshapes.py Python script just adds all shapes into the document.
import KWord
for shapeId in KWord.shapeKeys():
frame = KWord.addFrame("myshape", shapeId)
if frame:
frame.setTextRunAround(frame.RunThrough)
frame.setPosition(200, 50)
frame.resize(160, 80)
Text content
The sample_text.py Python script demonstrates usage of the text engine.
The following python sample adds some text at the end of the main framesets document.
import KWord
doc = KWord.mainFrameSet().document()
cursor = doc.rootFrame().lastCursorPosition()
cursor.insertHtml("<b>Some text</b>")
This python sample adds some text and sets the page header and the page footer.
import KWord
doc = KWord.mainFrameSet().document()
doc.lastCursor().insertHtml("Even more <b>Hello World</b>")
KWord.firstPageHeaderFrameSet().document().setText("Header")
KWord.firstPageFooterFrameSet().document().setText("Footer")
Python sample that prints the url and some metainformations of the document.
import KWord print KWord.document().url() print KWord.document().documentInfoTitle() print KWord.document().documentInfoAuthorName()
The sample_lists_html.py Python script demonstrates how to create lists with HTML.
The sample_lists_cursor.py Python script demonstrates how to create lists with a cursor.
The sample_tables.py Python script demonstrates how to deal with tables.
Variables
The sample_variables.py Python script demonstrates how to handle variables.
import KWord
doc = KWord.mainFrameSet().document()
for v in doc.variableNames():
print "name=%s value=%s" % (v, doc.variableValue(v))
The variable_readfile.py Python script to read a variable from a file.
KWord
The sample_cursor.rb Ruby script demonstrates how to control the cursor.
The sample_actions.py Python script demonstrates usage of actions.
import KWord
KWord.shell().slotFileNew()
KWord.mainWindow().setCaption("My Caption")
The sample_toolactions.py Python script demonstrates how to trigger actions the current tool provides.
import KWord
tool = KWord.tool()
for n in tool.actionNames():
print "%s: %s" % (n, tool.actionText(n))
tool.triggerAction(n)
The sample_progressbar.py Python script demonstrates how to use the progressbar.
import KWord
for i in range(1,101):
KWord.shell().slotProgress(i)
KWord.shell().slotProgress(-1)
The sample_onlinehelp.py Python script uses the KHTML Part to display the KWord Scripting online help.
import Kross
forms = Kross.module("forms")
dialog = forms.createDialog("KHTML Part")
page = dialog.addPage("", "")
url = "http://wiki.koffice.org"
part = forms.loadPart(page, "libkhtmlpart", url)
dialog.exec_loop()
Connect KWord with OpenOffice.org
The python script ooimport.py uses the PyUNO module to access OpenOffice.org and import content from any by OpenOffice.org supported fileformat. For this an optional hidden OpenOffice.org instance need to be started. Then the script connects as client to this OpenOffice.org server instance and controls it. If the script got executed and the connecting to the server failed, then it will startup such a hidden OpenOffice.org server instance and shuts it down again once the work is done.