Development/Tutorials/Using KXmlGuiWindow: Difference between revisions
m Corrected some typos |
|||
| Line 99: | Line 99: | ||
set(tutorial2_SRCS | set(tutorial2_SRCS | ||
main.cpp | main.cpp | ||
MainWindow.cpp | |||
) | ) | ||
kde4_add_executable(tutorial2 ${tutorial2_SRCS}) | kde4_add_executable(tutorial2 ${tutorial2_SRCS}) | ||
target_link_libraries( tutorial2 ${KDE4_KDEUI_LIBS}) | target_link_libraries( tutorial2 ${KDE4_KDEUI_LIBS}) | ||
</code> | </code> | ||
==Moving On== | ==Moving On== | ||
Now you can move on to [[Development/Tutorials/Programming_Tutorial_KDE_4/Using_KActions|using KActions]]. | Now you can move on to [[Development/Tutorials/Programming_Tutorial_KDE_4/Using_KActions|using KActions]]. | ||
[[Category:C++]] | [[Category:C++]] | ||
Revision as of 01:25, 17 January 2007
| Tutorial Series | Beginner Tutorial |
| Previous | Tutorial 1 - Hello World |
| What's Next | Tutorial 3 - KActions and XmlGui |
| Further Reading | KMainWindow |
Abstract
This tutorial carries on from First Program Tutorial and will introduce the KMainWindow class.
In the previous tutorial, the program caused a dialog box to pop up but we're going to take steps towards a functioning application.
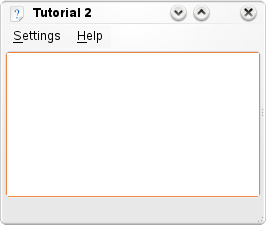
Using KMainWindow
In order to have a useful KMainWindow, we must sub class it. So we create two files, a MainWindow.cpp and a MainWindow.h which will contain our code.
MainWindow.h
- ifndef MAINWINDOW_H
- define MAINWINDOW_H
- include <KMainWindow>
- include <KTextEdit>
class MainWindow : public KMainWindow
{
public:
MainWindow(QWidget *parent=0);
private:
KTextEdit* textArea;
};
- endif
First we Subclass KMainWindow on line 7 with with class MainWindow : public KMainWindow.
Then we declare the constructor with MainWindow(QWidget *parent=0);.
And finally we declare a pointer to the object that will make up the bulk of our program. KTextEdit is a generic richtext editor with some KDE niceties like cursor auto-hiding.
MainWindow.cpp
- include "mainwindow.h"
MainWindow::MainWindow(QWidget *parent) : KMainWindow(parent)
{
textArea = new KTextEdit;
setCentralWidget(textArea);
setupGUI();
}
First, of course, on line 1 we have to include the header file containing the class declaration.
On line 5, we initialise our text editor with an object. Then on line 6 we use the built-in setCentralWidget() function which tells the KMainWindow what should appear in the central section of the window.
Finally, KMainWindow::setupGUI() is called which does a lot of behind the scene's stuff and creates the default menu bars (Settings, Help).
Back to main.cpp
In order to actually run this window, we need to add a few lines in main.cpp:
main.cpp
- include <KApplication>
- include <KAboutData>
- include <KCmdLineArgs>
- include "mainwindow.h"
int main (int argc, char *argv[])
{
KAboutData aboutData( "tutorial2",
"Tutorial2", "1.0", "A simple text area",
KAboutData::License_GPL, "(c) 2006" );
KCmdLineArgs::init( argc, argv, &aboutData );
KApplication app;
MainWindow* window = new MainWindow();
window->show();
return app.exec();
}
The only new lines here (compared to Tutorial 1) are 16 and 17. On line 16, we create our MainWindow object and then on line 17, we display it.
CMake
The best way to build the program is to use CMake. All that's changed since tutorial 1 is that mainwindow.cpp has been added to the sources list and any tutorial1 has become tutorial2.
CMakeLists.txt
project (tutorial2)
find_package(KDE4 REQUIRED)
include_directories( ${KDE4_INCLUDES} )
set(tutorial2_SRCS
main.cpp
MainWindow.cpp
)
kde4_add_executable(tutorial2 ${tutorial2_SRCS})
target_link_libraries( tutorial2 ${KDE4_KDEUI_LIBS})
Moving On
Now you can move on to using KActions.
