Archive:Development/Tutorials/Qt4 Ruby Tutorial/Chapter 08 (zh TW): Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 97: | Line 97: | ||
</code> | </code> | ||
這是我們第一次嘗試寫繪圖事件處理器。事件參數包含了繪圖事件的描述。[http://doc.qt.nokia.com/latest/qpaintevent.html Qt::PaintEvent] 包含 widget 中必須更新的區域。暫時,讓我們懶惰的直接畫出所有東西。 | |||
我們的程式碼會在 Widget 中一個固定的位置顯示角度值。我們建立了一個在這個 widget 運作的 [http://doc.qt.nokia.com/latest/qpainter.html Qt::Painter],並用它畫出字串。我們之後會再回到 [http://doc.qt.nokia.com/latest/qpainter.html Qt::Painter],它可以做很多事情。 | |||
'''[http://www.darshancomputing.com/qt4-qtruby-tutorial/tutorial/t8/t8.rb t8.rb]''' | '''[http://www.darshancomputing.com/qt4-qtruby-tutorial/tutorial/t8/t8.rb t8.rb]''' | ||
| Line 108: | Line 108: | ||
</code> | </code> | ||
在建構子中,我們建立並設定 LCDRange widget。 我們設定 LCDRange 接受5到70度的角度。 | |||
<code ruby> | <code ruby> | ||
| Line 114: | Line 114: | ||
</code> | </code> | ||
我們建立了 CannonField widget。 | |||
<code ruby> | <code ruby> | ||
| Line 123: | Line 123: | ||
</code> | </code> | ||
在這裡,我們連接 '''<tt>LCDRange</tt>''' 的 '''<tt>valueChanged()</tt>''' 訊號到 '''<tt>CannonField</tt>''' 的 '''<tt>setValue()</tt>''' 槽。每當使用者操作 '''<tt>LCDRange</tt>''' 時,這將更新 '''<tt>CannonField</tt>''' 的角度值。我們也做出反向連接,以便 '''<tt>CannonField</tt>''' 改變角度,也會更新 '''<tt>LCDRange</tt>''' 的數值。在我們的例子中,我們不會直接改變 '''<tt>CannonField</tt>''' 的角度。但藉由最後的 connect(),我們可以確保沒有改變會破壞這兩個值之間的同步。 | |||
這說明了組件程式設計和適當封裝的威力。 | |||
請注意,只有在角度實際改變時,發出 '''<tt>angleChanged()</tt>''' 訊號是多麼重要。如果 '''<tt>LCDRange</tt>''' 和 '''<tt>CannonField</tt>''' 同時省略了這個檢查,在第一次改變其中一個值後,這支程式將進入一個無限循環。 | |||
<code ruby> | <code ruby> | ||
| Line 133: | Line 133: | ||
</code> | </code> | ||
到目前為止,我們都是使用 [http://doc.qt.nokia.com/latest/qgridlayout.html Qt::VBoxLayout] 作為幾何管理。但現在,我們希望有更多一點的佈局控制,所以我們切換到更強大的 [http://doc.qt.nokia.com/latest/qgridlayout.html Qt::GridLayout] 類別。[http://doc.qt.nokia.com/latest/qgridlayout.html Qt::GridLayout] 不是一個 widget。它是另一個可以管理任何子 widget 的類別。 | |||
我們不需要在 [http://doc.qt.nokia.com/latest/qvboxlayout.html Qt::GridLayout] 的建構子裡指定任何尺寸。[http://doc.qt.nokia.com/latest/qgridlayout.html Qt::GridLayout] 會根據我們放入的網格決定列和行的數目。 | |||
[[Image:Qt4_Ruby_Tutorial_Screenshot_8-layout.png]][[Image:Qt4_Ruby_Tutorial_Screenshot_8-reallayout.png]] | [[Image:Qt4_Ruby_Tutorial_Screenshot_8-layout.png]][[Image:Qt4_Ruby_Tutorial_Screenshot_8-reallayout.png]] | ||
上圖展示了我們試著去實現的佈局。左邊展示的是佈局示意圖,右邊是一個程式的實際截圖。''(這兩張圖的版權為諾基亞所有。)'' | |||
<code ruby> | <code ruby> | ||
Revision as of 13:22, 12 January 2010
Template:I18n/Language Navigation Bar (zh TW)
Template:TutorialBrowser (zh TW)
Preparing for Battle
檔案:
概覽
在這個範例中,我們介紹第一個可以描繪本身的自定 widget。我們還增加一個有用的鍵盤介面(用兩行程式碼)。
一行一行的瀏覽
這個檔案非常類似第7章的 lcdrange.rb。但我們新增了一個槽:setRange()。
我們現在加入設定 LCDRange 範圍的可能性。到目前為止,它都被固定在0到99之間。
def setRange(minVal, maxVal)
if minVal < 0 || maxVal > 99 || minVal > maxVal
qWarning("LCDRange::setRange(#{minVal}, #{maxVal})\n" +
"\tRange must be 0..99\n" +
"\tand minVal must not be greater than maxVal")
return
end
@slider.setRange(minVal, maxVal)
end
setRange() 槽設定了 LCDRange 中 slider 的範圍。因為我們已經設立了 QLCDNumber 是顯示兩位數。所以我們希望盡可能限制 minVal 和 maxVal 的範圍,避免QLCDNumber 的溢位。(我們也可以允許值下限至-9,但我們沒有選擇這麼做。)如果參數是非法的,我們使用 Qt 的 QtGlobal::qWarning() 函式對使用者發出警告並立即返回。QtGlobal::qWarning() 是一個類似 printf 的函式,預設情況下它會輸出至 $stderr。如果您願意,您可以使用 QtGlobal::qInstallMsgHandler() 安裝自己的處理函式。
lcd.setSegmentStyle(Qt::LCDNumber::Filled)
這使得我們的 lcd 數字顯示方式更好。我不敢肯定,但我相信做到這一點是因為設定一個調色板(請見下一節)。我所知道的是,我在前面的章節嘗試時,這條線不會生效,但在這裡可以運作。
@currentAngle = 45
setPalette(Qt::Palette.new(Qt::Color.new(250, 250, 200)))
setAutoFillBackground(true)
建構子初始化角度為45度,並為這個 widget 設定一個自定調色板(palette)。
這個調色板使用指定的顏色作為背景,並挑選其他適當的顏色。(對這個 widget 而言,只有背景和文字顏色會真正用到。)然後,我們呼叫 setAutoFillBackground(true) 告訴 Qt 自動填充背景。
Qt::Color 用來指定一組 RGB(紅-綠-藍),每個值介於0(暗)和255(亮)之間。我們也可以使用一個預先定義的顏色,例如 Qt::yellow,來代替指定RGB值。
def setAngle(angle)
if angle < 5
angle = 5
elsif angle > 70
angle = 70
end
if @currentAngle == angle
return
end
@currentAngle = angle
update()
emit angleChanged(@currentAngle)
end def setAngle(degrees)
這個函式設定角度值。我們選擇了5到70的合法範圍,並依此調整給予的角度數值。如果新的角度超出範圍,我們選擇了不發出警告。
如果新的角度和舊的相等,我們立即返回。重要的是,只有當角度真的發生變化,才發出angleChanged() 訊號。
然後我們設定新的角度值,並重繪我們的 widget。Qt::Widget::update() 函式會清空這個 widget(通常用它的背景顏色填滿),並發送一個繪圖(paint)事件給這個 widget。結果就是呼叫了這個 widget 的繪圖事件函式。
最後,我們發出 angleChanged() 訊號來告訴外界角度改變了。emit 關鍵字是 Qt 特有的,並不是標準的 Ruby 語法。
def paintEvent(event)
painter = Qt::Painter.new(self)
painter.drawText(200, 200, tr("Angle = #{@currentAngle}"))
painter.end()
end
這是我們第一次嘗試寫繪圖事件處理器。事件參數包含了繪圖事件的描述。Qt::PaintEvent 包含 widget 中必須更新的區域。暫時,讓我們懶惰的直接畫出所有東西。
我們的程式碼會在 Widget 中一個固定的位置顯示角度值。我們建立了一個在這個 widget 運作的 Qt::Painter,並用它畫出字串。我們之後會再回到 Qt::Painter,它可以做很多事情。
angle = LCDRange.new()
angle.setRange(5, 70)
在建構子中,我們建立並設定 LCDRange widget。 我們設定 LCDRange 接受5到70度的角度。
cannonField = CannonField.new()
我們建立了 CannonField widget。
connect(angle, SIGNAL('valueChanged(int)'),
cannonField, SLOT('setAngle(int)'))
connect(cannonField, SIGNAL('angleChanged(int)'),
angle, SLOT('setValue(int)'))
在這裡,我們連接 LCDRange 的 valueChanged() 訊號到 CannonField 的 setValue() 槽。每當使用者操作 LCDRange 時,這將更新 CannonField 的角度值。我們也做出反向連接,以便 CannonField 改變角度,也會更新 LCDRange 的數值。在我們的例子中,我們不會直接改變 CannonField 的角度。但藉由最後的 connect(),我們可以確保沒有改變會破壞這兩個值之間的同步。
這說明了組件程式設計和適當封裝的威力。
請注意,只有在角度實際改變時,發出 angleChanged() 訊號是多麼重要。如果 LCDRange 和 CannonField 同時省略了這個檢查,在第一次改變其中一個值後,這支程式將進入一個無限循環。
gridLayout = Qt::GridLayout.new()
到目前為止,我們都是使用 Qt::VBoxLayout 作為幾何管理。但現在,我們希望有更多一點的佈局控制,所以我們切換到更強大的 Qt::GridLayout 類別。Qt::GridLayout 不是一個 widget。它是另一個可以管理任何子 widget 的類別。
我們不需要在 Qt::GridLayout 的建構子裡指定任何尺寸。Qt::GridLayout 會根據我們放入的網格決定列和行的數目。
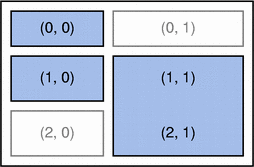
上圖展示了我們試著去實現的佈局。左邊展示的是佈局示意圖,右邊是一個程式的實際截圖。(這兩張圖的版權為諾基亞所有。)
gridLayout.addWidget(quit, 0, 0)
We add the Quit button in the top-left cell of the grid, i.e., the cell with coordinates (0, 0).
gridLayout.addWidget(angle, 1, 0)
We put the angle LCDRange cell (1, 0).
gridLayout.addWidget(cannonField, 1, 1, 2, 1)
We let the CannonField object occupy cells (1, 1) and (2, 1).
gridLayout.setColumnStretch(1, 10)
We tell Qt::GridLayout that the right column (column 1) is stretchable, with a stretch factor of 10. Because the left column isn't (its stretch factor is 0, the default value), Qt::GridLayout will try to let the left-hand widgets' sizes be unchanged and will resize just the CannonField when the MyWidget is resized.
In this particular example, any stretch factor greater than 0 for column 1 would have the same effect. In more complex layouts, you can use the stretch factors to tell that a particular column or row should stretch twice as fast as another by assigning appropriate stretch factors.
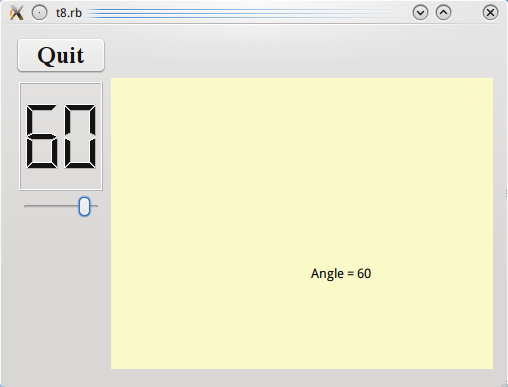
angle.setValue(60)
We set an initial angle value. Note that this will trigger the connection from LCDRange to CannonField.
angle.setFocus()
Our last action is to set angle to have keyboard focus so that keyboard input will go to the LCDRange widget by default.
執行應用程式
When the slider is operated, the CannonField displays the new angle value. Upon resizing, CannonField is given as much space as possible.
練習
Try to resize the window. What happens if you make it really narrow or really squat?
If you give the left-hand column a non-zero stretch factor, what happens when you resize the window?
Try to change "Quit" to "&Quit". How does the button's look change? ( Whether it does change or not depends on the platform.) What happens if you press Alt+Q while the program is running?
Center the text in the CannonField.