Development/Tutorials/Plasma4/Python/Using widgets: Difference between revisions
m Fix typo |
fixed grammar, some formatting. |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Abstract == | == Abstract == | ||
Using paintInterface to display applets is powerful, and sometimes even necessary | Using the <tt>paintInterface()</tt> method to display applets is a powerful, and sometimes even necessary way of working. For example, when you want to display a SVG graphic. But it is not the only method available to create a Plasmoid, however. Plasma comes with a number of widgets "tailored" for use in Plasmoids. In this tutorial we will create a very simple "Hello, world!" Plasmoid using Plasma widgets. | ||
== Prerequisites == | == Prerequisites == | ||
Set up your applet directory and create a metadata.desktop file as described in the [[../ | main tutorial]]. | Set up your applet directory and create a <tt>metadata.desktop</tt> file as described in the [[../ | main tutorial]]. | ||
== The 'main.py' file == | == The 'main.py' file == | ||
Here | Here is how our main.py file will look like: | ||
<code python> | <code python> | ||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
class HelloWorldApplet(plasmascript.Applet): | class HelloWorldApplet(plasmascript.Applet): | ||
def __init__(self,parent,args=None): | def __init__(self,parent,args=None): | ||
plasmascript.Applet.__init__(self,parent) | plasmascript.Applet.__init__(self,parent) | ||
def init(self): | def init(self): | ||
self.setHasConfigurationInterface(False) | self.setHasConfigurationInterface(False) | ||
self.setAspectRatioMode(Plasma.Square) | self.setAspectRatioMode(Plasma.Square) | ||
| Line 43: | Line 41: | ||
</code> | </code> | ||
Let's take a deeper look at it. As in the main tutorial, we create our class by deriving from plasmascript.Applet. In __init__, we initialize the class. | Let's take a deeper look at it. As in the main tutorial, we create our class by deriving from the <tt>plasmascript.Applet</tt> class. In <tt>__init__()</tt>, we quickly initialize the class. We use the <tt>init()</tt> method instead to do all the dirty work of creating the applet and adding the widget needed to display the text. | ||
First of all | First of all we tell Plasma that this applet does not have a configuration dialog (<tt>self.setHasConfigurationInterface(False)</tt>). We then set the aspect ratio mode to a square (<tt>Plasma.Square</tt>). This is taken into account when someone resizes the applet. Next, we add a background to the applet using a SVG image provided by the standard Plasma theme. We do so by creating an instance of <tt>Plasma.Svg</tt>, assigning it to <tt>self.theme</tt>, and then specifying the SVG graphic we want to use via <tt>self.setImagePath()</tt>. This way the applet will use the standard "background" SVG provided by the "widgets" directory of our current Plasma theme. We can also use relative paths or absolute paths to SVGs of our choice, should we need to. The <tt>setBackgroundHints()</tt> method sets the Plasmoid's background to the default Plasma background (<tt>Plasma.Applet.DefaultBackground</tt>) saving us from having to manually draw the background ourselves. | ||
The third and most important step deals with creating a layout. It is a bit | The third and most important step deals with creating a layout. It is a bit different than the standard <tt>QLinearLayout</tt> seen in Qt and PyQt, because it is done inside a <tt>QGraphicsView</tt> used by Plasma. We want a simple, linear layout, and so we use a QGraphicsLinearLayout, setting it to be horizontal (Qt.Horizontal). | ||
Next we create a Plasma.Label. This is a widget that is Plasma aware and therefore uses all of the goodies provided by Plasma. For example, automatically changing its text color if the Plasma theme changes. We then use the <tt>setText()</tt> method (analogous to the normal <tt>QLabel.setText()</tt> method) to set our label text ("Hello, world!") and then add the label to the layout. Finally we resize the applet to 125 x 125 pixels. | |||
Once packaged and installed (see [[../ | the main tutorial]]), the Plasmoid will look like this: | Once packaged and installed (see [[../ | the main tutorial]]), the Plasmoid will look like this: | ||
| Line 57: | Line 55: | ||
== Conclusion == | == Conclusion == | ||
This brief tutorial shows how to use Plasma widgets with your applet. | This brief tutorial shows how to use Plasma widgets with your applet. Beside <tt>Plasma.Label</tt> there are many more widgets that you can use. | ||
Notice that at the moment you can | Notice that at the moment you can only add widgets and create layouts directly in code. This means you can't use an application like Qt Designer to design the appearance of your applet. | ||
Revision as of 16:57, 17 January 2009
Abstract
Using the paintInterface() method to display applets is a powerful, and sometimes even necessary way of working. For example, when you want to display a SVG graphic. But it is not the only method available to create a Plasmoid, however. Plasma comes with a number of widgets "tailored" for use in Plasmoids. In this tutorial we will create a very simple "Hello, world!" Plasmoid using Plasma widgets.
Prerequisites
Set up your applet directory and create a metadata.desktop file as described in the main tutorial.
The 'main.py' file
Here is how our main.py file will look like:
- Copyright stuff
from PyQt4.QtCore import *
from PyQt4.QtGui import *
from PyKDE4.plasma import Plasma
from PyKDE4 import plasmascript
class HelloWorldApplet(plasmascript.Applet):
def __init__(self,parent,args=None):
plasmascript.Applet.__init__(self,parent)
def init(self):
self.setHasConfigurationInterface(False)
self.setAspectRatioMode(Plasma.Square)
self.theme = Plasma.Svg(self)
self.theme.setImagePath("widgets/background")
self.setBackgroundHints(Plasma.Applet.DefaultBackground)
self.layout = QGraphicsLinearLayout(Qt.Horizontal, self.applet)
label = Plasma.Label(self.applet)
label.setText("Hello world!")
self.layout.addItem(label)
self.resize(125,125)
def CreateApplet(parent):
return HelloWorldApplet(parent)
Let's take a deeper look at it. As in the main tutorial, we create our class by deriving from the plasmascript.Applet class. In __init__(), we quickly initialize the class. We use the init() method instead to do all the dirty work of creating the applet and adding the widget needed to display the text.
First of all we tell Plasma that this applet does not have a configuration dialog (self.setHasConfigurationInterface(False)). We then set the aspect ratio mode to a square (Plasma.Square). This is taken into account when someone resizes the applet. Next, we add a background to the applet using a SVG image provided by the standard Plasma theme. We do so by creating an instance of Plasma.Svg, assigning it to self.theme, and then specifying the SVG graphic we want to use via self.setImagePath(). This way the applet will use the standard "background" SVG provided by the "widgets" directory of our current Plasma theme. We can also use relative paths or absolute paths to SVGs of our choice, should we need to. The setBackgroundHints() method sets the Plasmoid's background to the default Plasma background (Plasma.Applet.DefaultBackground) saving us from having to manually draw the background ourselves.
The third and most important step deals with creating a layout. It is a bit different than the standard QLinearLayout seen in Qt and PyQt, because it is done inside a QGraphicsView used by Plasma. We want a simple, linear layout, and so we use a QGraphicsLinearLayout, setting it to be horizontal (Qt.Horizontal).
Next we create a Plasma.Label. This is a widget that is Plasma aware and therefore uses all of the goodies provided by Plasma. For example, automatically changing its text color if the Plasma theme changes. We then use the setText() method (analogous to the normal QLabel.setText() method) to set our label text ("Hello, world!") and then add the label to the layout. Finally we resize the applet to 125 x 125 pixels.
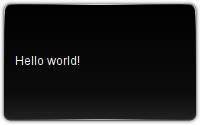
Once packaged and installed (see the main tutorial), the Plasmoid will look like this:
Conclusion
This brief tutorial shows how to use Plasma widgets with your applet. Beside Plasma.Label there are many more widgets that you can use.
Notice that at the moment you can only add widgets and create layouts directly in code. This means you can't use an application like Qt Designer to design the appearance of your applet.
