Archive:Development/Tutorials/Saving and loading (zh TW): Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 251: | Line 251: | ||
</code> | </code> | ||
<tt>fileName.clear()</tt> 會設定 <tt>fileName</tt> QString 是空的,以反映該文件還沒有存在於硬碟的事實。<tt>textArea->clear()</tt> | <tt>fileName.clear()</tt> 會設定 <tt>fileName</tt> QString 是空的,以反映該文件還沒有存在於硬碟的事實。<tt>textArea->clear()</tt> 會清除中央的文字區塊,使用在教學 3我們連接 <tt>clear</tt> <tt>KAction</tt> 的相同功能函式。 | ||
===儲存檔案=== | ===儲存檔案=== | ||
| Line 323: | Line 323: | ||
最後,載入硬碟的檔案的功能。所有程式碼,包含在<tt>MainWindow::openFile()</tt>。 | 最後,載入硬碟的檔案的功能。所有程式碼,包含在<tt>MainWindow::openFile()</tt>。 | ||
首先,我們必須詢問使用者他們希望打開的檔案名稱。我們是用另一個<tt>KFileDialog</tt> 的函式,這次用<tt>getOpenFileName()</tt>: | 首先,我們必須詢問使用者他們希望打開的檔案名稱。我們是用另一個 <tt>KFileDialog</tt> 的函式,這次用 <tt>getOpenFileName()</tt>: | ||
<code cppqt> | <code cppqt> | ||
QString fileNameFromDialog = KFileDialog::getOpenFileName(); | QString fileNameFromDialog = KFileDialog::getOpenFileName(); | ||
| Line 332: | Line 332: | ||
KIO::NetAccess::download(fileNameFromDialog, tmpFile, this) | KIO::NetAccess::download(fileNameFromDialog, tmpFile, this) | ||
</code> | </code> | ||
第一個參數是您要下載檔案的名稱。第二個是僅次於下載完成後的 QString,將包含檔案暫時備份的位置。我們將從現在開始工作這個 <tt>tmpFile</tt> 。 | |||
該函數返回<tt>true</tt>或<tt>false</tt>取決於轉換是否成功。如果失敗,我們顯示一個訊息框提供錯誤: | |||
<code cppqt> | <code cppqt> | ||
KMessageBox::error(this, KIO::NetAccess::lastErrorString()); | KMessageBox::error(this, KIO::NetAccess::lastErrorString()); | ||
</code> | </code> | ||
否則,我們繼續打開檔案。 | |||
我們傳遞<tt>NetAccess::download()</tt>創建的臨時檔案,給新創建 QFile 的建構子,然後在唯讀模式打開它 | |||
<code cppqt> | <code cppqt> | ||
QFile file(tmpFile); | QFile file(tmpFile); | ||
| Line 347: | Line 347: | ||
</code> | </code> | ||
為了顯示檔案的內容,我們必須使用{{qt|QTextStream}}。創建他並將傳遞的檔案的內容給它的建構子,然呼叫 QFile 的 <tt>readAll()</tt> 函數從檔案中取得文字。然後傳遞給文字區塊的 <tt>setPlainText()</tt> 函數。 | |||
<code cppqt> | <code cppqt> | ||
| Line 353: | Line 353: | ||
</code> | </code> | ||
然後,存儲我們剛才打開檔案的路徑: | |||
<code cppqt> | <code cppqt> | ||
fileName = fileNameFromDialog; | fileName = fileNameFromDialog; | ||
</code> | </code> | ||
最後,刪除 <tt>NetAccess::download()</tt> 建立的臨時檔案: | |||
<code cppqt> | <code cppqt> | ||
KIO::NetAccess::removeTempFile(tmpFile); | KIO::NetAccess::removeTempFile(tmpFile); | ||
Revision as of 14:12, 28 November 2009
Development/Tutorials/Saving_and_loading
Languages: عربي | Asturianu | Català | Česky | Kaszëbsczi | Dansk | Deutsch | English | Esperanto | Español | Eesti | فارسی | Suomi | Français | Galego | Italiano | 日本語 | 한국어 | Norwegian | Polski | Português Brasileiro | Română | Русский | Svenska | Slovenčina | Slovenščina | српски | Türkçe | Tiếng Việt | Українська | 简体中文 | 繁體中文
Template:TutorialBrowser (zh TW)
摘要
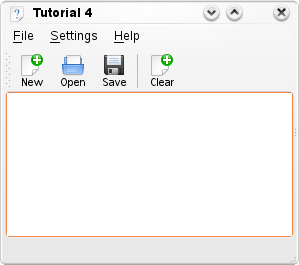
現在我們擁有了一個基本的文字編輯器界面,開始要讓他做一些有用的事情了。最根本的來說,一個文字編輯器需要能夠從硬碟中載入檔案,儲存你新增或編輯過的檔案。
KDE 提供了許多讓開發者能輕鬆操作檔案的類別。KIO 函式庫讓你可以十分容易地透過網路協定訪問檔案,而且提供標準的檔案對話框。
程式碼
main.cpp
- include <KApplication>
- include <KAboutData>
- include <KCmdLineArgs>
- include "mainwindow.h"
int main (int argc, char *argv[])
{
KAboutData aboutData( "tutorial4", "tutorial4",
ki18n("Tutorial 4"), "1.0",
ki18n("A simple text area which can load and save."),
KAboutData::License_GPL,
ki18n("Copyright (c) 2007 Developer") );
KCmdLineArgs::init( argc, argv, &aboutData );
KApplication app;
MainWindow* window = new MainWindow();
window->show();
return app.exec();
}
main.cpp 與教學 3中的相比沒什麼變化,除了說明參數從 tutorial 3 變為了 tutorial 4。
mainwindow.h
- ifndef MAINWINDOW_H
- define MAINWINDOW_H
- include <KXmlGuiWindow>
- include <KTextEdit>
class MainWindow : public KXmlGuiWindow
{
Q_OBJECT //與教學 3相比,新增加的
public:
MainWindow(QWidget *parent=0);
private:
KTextEdit* textArea;
void setupActions();
QString fileName; //新增的
private slots: //新增的
void newFile(); //新增的
void openFile(); //新增的
void saveFile(); //新增的
void saveFileAs(); //新增的
void saveFileAs(const QString &outputFileName); //新增的
};
- endif
由於我們想要加上載入和儲存檔案的能力,所以我們必須加入用來完成這些工作的函數。由於這些函數將會透過Qt的訊號/槽(signal/slot) 機制被呼叫,所以我們必須註明這些函數是槽(slots),就像我們在第19行做的那樣。由於我們在標頭檔中使用槽,所以我們同樣必須加入Q_OBJECT 巨集。
我們同樣想要跟踪當前打開檔案的名稱,所以我們宣告了一個QString fileName 。
mainwindow.cpp
- include "mainwindow.h"
- include <KApplication>
- include <KAction>
- include <KLocale>
- include <KActionCollection>
- include <KStandardAction>
- include <KFileDialog> //新增的
- include <KMessageBox> //新增的
- include <KIO/NetAccess> //新增的
- include <KSaveFile> //新增的
- include <QTextStream> //新增的
MainWindow::MainWindow(QWidget *parent)
: KXmlGuiWindow(parent),
fileName(QString()) //新增的
{
textArea = new KTextEdit;
setCentralWidget(textArea);
setupActions();
}
void MainWindow::setupActions()
{
KAction* clearAction = new KAction(this);
clearAction->setText(i18n("Clear"));
clearAction->setIcon(KIcon("document-new"));
clearAction->setShortcut(Qt::CTRL + Qt::Key_W);
actionCollection()->addAction("clear", clearAction);
connect(clearAction, SIGNAL(triggered(bool)),
textArea, SLOT(clear()));
KStandardAction::quit(kapp, SLOT(quit()),
actionCollection());
KStandardAction::open(this, SLOT(openFile()),
actionCollection()); //新增的
KStandardAction::save(this, SLOT(saveFile()),
actionCollection()); //新增的
KStandardAction::saveAs(this, SLOT(saveFileAs()),
actionCollection()); //新增的
KStandardAction::openNew(this, SLOT(newFile()),
actionCollection()); //新增的
setupGUI();
}
//從這裡開始都是新增加的
void MainWindow::newFile()
{
fileName.clear();
textArea->clear();
}
void MainWindow::saveFileAs(const QString &outputFileName)
{
KSaveFile file(outputFileName);
file.open();
QByteArray outputByteArray;
outputByteArray.append(textArea->toPlainText().toUtf8());
file.write(outputByteArray);
file.finalize();
file.close();
fileName = outputFileName;
}
void MainWindow::saveFileAs()
{
saveFileAs(KFileDialog::getSaveFileName());
}
void MainWindow::saveFile()
{
if(!fileName.isEmpty())
{
saveFileAs(fileName);
}
else
{
saveFileAs();
}
}
void MainWindow::openFile()
{
QString fileNameFromDialog = KFileDialog::getOpenFileName();
QString tmpFile;
if(KIO::NetAccess::download(fileNameFromDialog, tmpFile,
this))
{
QFile file(tmpFile);
file.open(QIODevice::ReadOnly);
textArea->setPlainText(QTextStream(&file).readAll());
fileName = fileNameFromDialog;
KIO::NetAccess::removeTempFile(tmpFile);
}
else
{
KMessageBox::error(this,
KIO::NetAccess::lastErrorString());
}
}
tutorial4ui.rc
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<gui name="tutorial4"
version="1"
xmlns="http://www.kde.org/standards/kxmlgui/1.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.kde.org/standards/kxmlgui/1.0
http://www.kde.org/standards/kxmlgui/1.0/kxmlgui.xsd" >
<MenuBar>
<Menu name="file" >
<Action name="clear" />
</Menu>
</MenuBar>
<ToolBar name="mainToolBar" >
<text>Main Toolbar</text>
<Action name="clear" />
</ToolBar>
</gui>
這和教學 3 的 tutorial3ui.rc 相同,除了 name 改為 'tutorial4' 以外。我們不需要加入任何 KStandardAction 的資訊來安置這些動作,KDE 會自動處理。
解釋
Okay,現在實現的程式碼將執行載入和儲存。這都實做在 mainwindow.cpp
首先我們加入
fileName(QString())
在 MainWindow 建構子列表的第16行。這可以確保 fileName一開始是空的。
加入動作
我們首先要做的是為使用者提供操作介面,使他們能夠告訴應用程式載入和儲存。類似教學3的 quit 動作,我們將使用 KStandardActions。在37至47行,我們用和 quit 動作同樣的方式加入動作。我們將每一項連接到適當的槽,並宣告在標頭檔中。
創建新文件
我們第一個創建的函數是 newFile() 。
void MainWindow::newFile()
{
fileName.clear();
textArea->clear();
}
fileName.clear() 會設定 fileName QString 是空的,以反映該文件還沒有存在於硬碟的事實。textArea->clear() 會清除中央的文字區塊,使用在教學 3我們連接 clear KAction 的相同功能函式。
儲存檔案
saveFileAs(QString)
現在,我們有了第一個檔案處理的程式碼。我們將實現一個函數,它將儲存文字區塊內容的檔案名給作為參數。KDE 提供了一個安全儲存檔案名的KSaveFile類別,來自 Qt 的QFile。
該函數的原型是
void MainWindow::saveFileAs(const QString &outputFileName)
然後,我們創建 KSaveFile 物件,並使用以下程式碼打開它
KSaveFile file(outputFileName);
file.open();
現在,我們有檔案寫入,我們需要格式化在文字區塊中的文字,為可以被寫入檔案的格式。因此,我們創建了一個QByteArray並填寫它,和任何在文字區塊中的純文字版本:
QByteArray outputByteArray;
outputByteArray.append(textArea->toPlainText().toUtf8());
現在,我們有了 QByteArray,使用它和 KSaveFile::write() 寫入檔案。如果我們使用普通的 QFile,這將立即進行更改。但是,如果寫入中發生問題,該檔案將會損壞。為此,KSaveFile會先寫入文字到一個臨時檔案,然後,當你調用KSaveFile::finalize()再改變實際的檔案。
file.write(outputByteArray);
file.finalize();
file.close();
最後,我們設定 MainWindows 的 fileName 成員指向我們剛剛儲存的檔案名。
fileName = outputFileName;
saveFileAs()
這是一個連接 saveAs 槽的函數。它只是呼叫一般的 saveFileAs(QString) 函數並傳遞KFileDialog::getSaveFileName()返回的檔案名。
void MainWindow::saveFileAs()
{
saveFileAs(KFileDialog::getSaveFileName());
}
這是我們第一次實際使用 KIO 函式庫。KFileDialog 提供了一些顯示常見的檔案對話框的靜態函數。呼叫 KFileDialog::getSaveFileName() 將顯示一個對話框,使用者可以選擇已儲存的檔案名稱或選擇一個新名稱。該函數返回完整的檔案名稱,我們再傳遞到saveFileAs(QString)。
saveFile()
void MainWindow::saveFile()
{
if(!fileName.isEmpty())
{
saveFileAs(fileName);
}
else
{
saveFileAs();
}
}
這個沒有什麼令人興奮的新功能,只是決定是否顯示儲存對話框。如果fileName不為空,則該檔案儲存到fileName。但是,如果是空的話,該對話框會讓用戶選擇檔案名。
載入檔案
最後,載入硬碟的檔案的功能。所有程式碼,包含在MainWindow::openFile()。
首先,我們必須詢問使用者他們希望打開的檔案名稱。我們是用另一個 KFileDialog 的函式,這次用 getOpenFileName():
QString fileNameFromDialog = KFileDialog::getOpenFileName();
然後,我們使用 KIO 函式庫來檢索檔案。這使我們能夠用 QFile 打開檔案,即使它儲存在遠端例如 FTP 網站。我們呼叫 NetAccess 的 download() 函數
KIO::NetAccess::download(fileNameFromDialog, tmpFile, this)
第一個參數是您要下載檔案的名稱。第二個是僅次於下載完成後的 QString,將包含檔案暫時備份的位置。我們將從現在開始工作這個 tmpFile 。
該函數返回true或false取決於轉換是否成功。如果失敗,我們顯示一個訊息框提供錯誤:
KMessageBox::error(this, KIO::NetAccess::lastErrorString());
否則,我們繼續打開檔案。
我們傳遞NetAccess::download()創建的臨時檔案,給新創建 QFile 的建構子,然後在唯讀模式打開它
QFile file(tmpFile);
file.open(QIODevice::ReadOnly);
為了顯示檔案的內容,我們必須使用QTextStream。創建他並將傳遞的檔案的內容給它的建構子,然呼叫 QFile 的 readAll() 函數從檔案中取得文字。然後傳遞給文字區塊的 setPlainText() 函數。
textArea->setPlainText(QTextStream(&file).readAll());
然後,存儲我們剛才打開檔案的路徑:
fileName = fileNameFromDialog;
最後,刪除 NetAccess::download() 建立的臨時檔案:
KIO::NetAccess::removeTempFile(tmpFile);
編譯、安裝與執行
CMakeLists.txt
project(tutorial4)
find_package(KDE4 REQUIRED)
include_directories(${KDE4_INCLUDES})
set(tutorial4_SRCS
main.cpp
mainwindow.cpp
)
kde4_add_executable(tutorial4 ${tutorial4_SRCS})
target_link_libraries(tutorial4 ${KDE4_KDEUI_LIBS}
${KDE4_KIO_LIBS})
install(TARGETS tutorial4 DESTINATION ${BIN_INSTALL_DIR})
install(FILES tutorial4ui.rc
DESTINATION ${DATA_INSTALL_DIR}/tutorial4)
Since we are now using the KIO library, we must tell CMake to link against it. We do this by passing ${KDE4_KIO_LIBS} to the target_link_libraries() function.
With this file, the tutorial can be built and run in the same way as tutorial 3. For more information, see tutorial 3.
mkdir build && cd build
cmake .. -DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=$HOME
make install
$HOME/bin/tutorial4
繼續前進
現在你可以開始學習下一課:KCmdLineArgs 教學。
