Development/Tutorials/Games/Palapeli Slicers: Difference between revisions
m moved Development/Tutorials/Games/Palapeli Patterns to Development/Tutorials/Games/Palapeli Slicers: Name change in libpala |
new version for libpala is ready |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{TutorialBrowser | {{TutorialBrowser | ||
|series=Programming with the Palapeli API | |series=Programming with the Palapeli API | ||
|name=Creating a Palapeli | |name=Creating a slicer plugin for Palapeli | ||
|pre=[[Development/Tutorials/Programming_Tutorial_KDE_4|Introduction to KDE4 programming]] | |pre=[[Development/Tutorials/Programming_Tutorial_KDE_4|Introduction to KDE4 programming]] | ||
|reading=API reference for [http://api.kde.org/playground-api/games-apidocs/palapeli/libpala/html/index.html libpala] | |reading=API reference for [http://api.kde.org/playground-api/games-apidocs/palapeli/libpala/html/index.html libpala] | ||
}} | }} | ||
== Abstract == | == Abstract == | ||
| Line 20: | Line 18: | ||
Slicer writers do not have to bother with the changes that occur in the Palapeli application every now and then. Slicer plugins are not linked against Palapeli, but against ''libpala'', a light-weight library that is designed for the sole purpose of slicing management. To Palapeli, it serves as an interface to talk with arbitrary slicer plugins. To slicer plugins, it provides an API to get and perform slicing jobs. | Slicer writers do not have to bother with the changes that occur in the Palapeli application every now and then. Slicer plugins are not linked against Palapeli, but against ''libpala'', a light-weight library that is designed for the sole purpose of slicing management. To Palapeli, it serves as an interface to talk with arbitrary slicer plugins. To slicer plugins, it provides an API to get and perform slicing jobs. | ||
A slicer plugin needs to define a subclass of [http://api.kde.org/playground-api/games-apidocs/palapeli/libpala/html/classPala_1_1Slicer.html <tt>Pala::Slicer</tt>]. Of course, you can also define more classes, but libpala will only talk to the single <tt>Pala::Slicer</tt> subclass. | |||
A slicer plugin needs to define a subclass of [http://api.kde.org/playground-api/games-apidocs/palapeli/libpala/html/classPala_1_1Slicer.html Pala::Slicer]. Of course, you can also define more classes, but libpala will only talk to the single Pala::Slicer | |||
< | |||
== The code: | == The code: myslicer.h == | ||
<code cppqt n> | <code cppqt n> | ||
#ifndef | #ifndef MYSLICER_H | ||
#define | #define MYSLICER_H | ||
#include < | #include <Pala/Slicer> | ||
#include < | #include <Pala/SlicerJob> | ||
#include <Pala/SlicerProperty> | |||
class | class MySlicer : public Pala::Slicer | ||
{ | { | ||
Q_OBJECT | |||
public: | |||
MySlicer(QObject* parent = 0, const QVariantList& args = QVariantList()); | |||
virtual bool run(Pala::SlicerJob* job); | |||
}; | }; | ||
#endif // MYSLICER_H | |||
#endif // | |||
</code> | </code> | ||
As described above, we | As described above, we need to create a subclass of <tt>Pala::Slicer</tt>. (We also include the other two classes from libpala, <tt>Pala::SlicerJob</tt> and <tt>Pala::SlicerProperty</tt>, which we'll be using in the code.) For this example, we only need to implement the minimum of two functions: | ||
* The constructor of the <tt>Pala::Slicer</tt> subclass needs to have '''exactly that signature''', because this constructor is called by the <tt>KPluginLoader</tt> in this way. The arguments need to be passed to the <tt>Pala::Slicer</tt> constructor, which might want to handle them. (You as a slicer developer will never have to bother with them.) | |||
* <tt>Pala::Slicer</tt> has one pure virtual method <tt>run()</tt>, which does the actual work. | |||
== The code: | == The code: myslicer.cpp == | ||
<code cppqt n> | <code cppqt n> | ||
#include " | #include "myslicer.h" | ||
#include <KLocalizedString> | #include <KLocalizedString> | ||
#include <KPluginFactory> | #include <KPluginFactory> | ||
#include <KPluginLoader> | #include <KPluginLoader> | ||
K_PLUGIN_FACTORY( | K_PLUGIN_FACTORY(MySlicerFactory, registerPlugin<MySlicer>();) | ||
K_EXPORT_PLUGIN( | K_EXPORT_PLUGIN(MySlicerFactory("myslicer")) | ||
MySlicer::MySlicer(QObject* parent, const QVariantList& args) | |||
: Pala::Slicer(parent, args) | |||
{ | { | ||
Pala::SlicerProperty* prop; | |||
prop = new Pala::SlicerProperty(Pala::SlicerProperty::Integer, i18n("Piece count in horizontal direction")); | |||
prop->setRange(3, 100); | |||
prop->setDefaultValue(10); | |||
addProperty("XCount", prop); | |||
prop = new Pala::SlicerProperty(Pala::SlicerProperty::Integer, i18n("Piece count in vertical direction")); | |||
prop->setRange(3, 100); | |||
prop->setDefaultValue(10); | |||
addProperty("YCount", prop); | |||
} | } | ||
bool MySlicer::run(Pala::SlicerJob* job) | |||
{ | { | ||
//read job | |||
const int xCount = job->argument("XCount").toInt(); | |||
const int yCount = job->argument("YCount").toInt(); | |||
const QImage image = job->image(); | |||
//calculate some metrics | |||
const int pieceWidth = image.width() / xCount; | |||
const int pieceHeight = image.height() / yCount; | |||
const QSize pieceSize(pieceWidth, pieceHeight); | |||
//create pieces | |||
for (int x = 0; x < xCount; ++x) | |||
{ | |||
for (int y = 0; y < yCount; ++y) | |||
{ | |||
//calculate more metrics | |||
const QPoint offset(x * pieceWidth, y * pieceHeight); | |||
const QRect pieceBounds(offset, pieceSize); | |||
//copy image part to piece | |||
const QImage pieceImage = image.copy(pieceBounds); | |||
job->addPiece(x + y * xCount, pieceImage, offset); | |||
} | |||
} | |||
//create relations | |||
for (int x = 0; x < xCount; ++x) | |||
{ | |||
for (int y = 0; y < yCount; ++y) | |||
{ | |||
//along X axis (pointing left) | |||
if (x != 0) | |||
job->addRelation(x + y * xCount, (x - 1) + y * xCount); | |||
//along Y axis (pointing up) | |||
if (y != 0) | |||
job->addRelation(x + y * xCount, x + (y - 1) * xCount); | |||
} | |||
} | |||
return true; | |||
} | } | ||
#include "myslicer.moc" | |||
</code> | |||
The two <tt>KPlugin</tt> headers are necessary for the plugin integration, which happens in line 7 and 8. Note that the string constant in line 8 (<tt>"myslicer"</tt>) needs to match your library name. | |||
</ | |||
The constructor of a <tt>Pala::Slicer</tt> has two tasks: It needs to pass its arguments to the base class constructor, and define the properties of the slicer. Properties make it possible for the user to configure the slicer. In our case, we let the user choose how much pieces are generated. See the <a href="http://api.kde.org/playground-api/games-apidocs/palapeli/libpala/html/classPala_1_1SlicerProperty.html"><tt>Pala::SlicerProperty</tt></a> documentation for more details on what types of properties can be defined. (''Warning:'' libpala's slicer properties have nothing to do with QObject's meta properties.) | |||
We do not save pointers to the <tt>Pala::SlicerProperty</tt> instances that we add to the slicer. The properties are only passed internally to the application, which will construct an appropriate interface, and allow the user to enter values for the properties. When the user has configured everything, both the source image and the selected property values are packed into a <tt>Pala::SlicerJob</tt> object. The <tt>MySlicer::run</tt> method is then called for this job. | |||
In the <tt>run</tt> method, we read both the image and the property values from the job. After having calculated some metrics, we start to split the image into pieces. The process is straight-forward because all pieces are perfectly rectangular. When piece images are ready, we use the <tt>Pala::SlicerJob::addPiece</tt> method to add them to the result mass. Note that we need to define piece IDs for each piece (the first parameter of the <tt>addPiece</tt> call in line 44). These IDs can be arbitrary non-negative numbers, but have to be unique among all pieces. | |||
After we have added all pieces, we need to define neighbor relations between pieces. Neighbor relations are used to snap pieces together when they're near enough. Consider three pieces in a row: If piece 1 is near piece 3, nothing should snap because they do not have a common edge. If piece 1 is moved near piece 2, these should snap together. Therefore, we define a relation between piece 1 and piece 2 (and piece 2 and piece 3, respectively). The relation is added through the <tt>Pala::SlicerJob::addRelation</tt> method, which takes the IDs of two neighboring pieces. (The neighbor relation only needs to be defined in one direction: If piece 1 is a neighbor of piece 2, then piece 2 is also a neighbor of piece 1.) | |||
We see that the <tt>Pala::SlicerJob</tt> object is used as a two-way communication channel between the slicer plugin and the application: Palapeli places the source image and the property values in it; the slicer reads these and writes the pieces and the relations into it; and in the end, Palapeli reads the pieces and the relations. | |||
This simple implementation of a <tt>Pala::Slicer::run</tt> method always returns ''true''. You can return ''false'' if something went wrong during the slicing (e. g. because some external resources could not be located). | |||
== Integrate into Palapeli: | == Integrate into Palapeli: myslicer.desktop == | ||
<code> | <code> | ||
[Desktop Entry] | [Desktop Entry] | ||
X-KDE-Library= | Name=My very first slicer | ||
X-KDE-PluginInfo-Author= | Name[de]=Mein erstes Schnittmuster | ||
X-KDE-PluginInfo-Email= | Comment=It's quite simple, actually. | ||
X-KDE-PluginInfo-Name= | Comment[de]=Eigentlich ist das ganz einfach. | ||
Type=Service | |||
Icon=myslicer | |||
X-KDE-Library=myslicer | |||
X-KDE-ServiceTypes=Libpala/SlicerPlugin | |||
X-KDE-PluginInfo-Author=Kandalf | |||
X-KDE-PluginInfo-Email=kandalf@kde-hackers.example.org | |||
X-KDE-PluginInfo-Name=myslicer | |||
X-KDE-PluginInfo-Version=1.0 | X-KDE-PluginInfo-Version=1.0 | ||
X-KDE-PluginInfo-Website=http://kde-hackers.example.org/ | X-KDE-PluginInfo-Website=http://kde-hackers.example.org/myslicer | ||
X-KDE-PluginInfo-Category= | X-KDE-PluginInfo-Category= | ||
X-KDE-PluginInfo-Depends= | X-KDE-PluginInfo-Depends= | ||
X-KDE-PluginInfo-License=GPL | X-KDE-PluginInfo-License=GPL | ||
X-KDE-PluginInfo-EnabledByDefault=true | X-KDE-PluginInfo-EnabledByDefault=true | ||
</code> | </code> | ||
We need to tell the Palapeli library that there is a new plugin out there. We need a desktop entry file like shown here. You can mostly copy everything you see here; | We need to tell the Palapeli library that there is a new plugin out there. We need a desktop entry file like shown here. You can mostly copy everything you see here; the most important thing is to keep the fields <tt>X-KDE-Library</tt> and <tt>X-KDE-PluginInfo-Name</tt> in sync with the library name (see next section). Note that the name is used in the "New puzzle" dialog to identify this pattern. (It can be translated; for example, a German translation has been added in the above example.) | ||
== Build everything: CMakeLists.txt == | == Build everything: CMakeLists.txt == | ||
<code> | <code> | ||
project( | project(myslicer) | ||
find_package(KDE4 REQUIRED) | find_package(KDE4 REQUIRED) | ||
find_package( | find_package(LibPala REQUIRED) | ||
add_definitions(${ | add_definitions(${LIBPALA_DEFINITIONS}) | ||
include_directories(${ | include_directories(${LIBPALA_INCLUDES}) | ||
kde4_add_plugin(myslicer myslicer.cpp) | |||
target_link_libraries(myslicer ${LIBPALA_LIBRARIES}) | |||
) | |||
install(TARGETS myslicer DESTINATION ${PLUGIN_INSTALL_DIR}) | |||
install(FILES myslicer.desktop DESTINATION ${SERVICES_INSTALL_DIR}) | |||
</code> | |||
Everything of this is pretty straightforward if you have previous experience with CMake (and this is what I assume). Make sure you compile everything as a plugin, and install it into the plugin directory. The find script for libpala sets some convenience variables that shorten the code in lines 5, 6 and 9. After having installed the plugin, run <tt>kbuildsycoca4</tt>. This will locate your plugin, and enable Palapeli to use it. Here is how it should look like then: | |||
install | |||
</ | |||
{{Box|Warning|This image is outdated. It will be replaced by a current image, when the new version of Palapeli gains an interface for creating new puzzles.}} | |||
[[Image:Palapeli Pattern Tutorial1.png]] | [[Image:Palapeli Pattern Tutorial1.png]] | ||
Revision as of 14:50, 27 September 2009
| Tutorial Series | Programming with the Palapeli API |
| Previous | Introduction to KDE4 programming |
| What's Next | n/a |
| Further Reading | API reference for libpala |
Abstract
This tutorial shows you how to create a slicer for Palapeli, that is: a plugin for Palapeli that splits an image into pieces.
As an example for a very basic slicer, we will discuss the structure of the rectangle slicer, which splits the image into a configurable number of evenly-sized pieces.
Technical overview
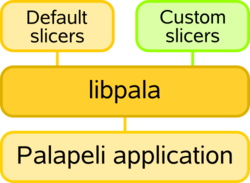
Slicer writers do not have to bother with the changes that occur in the Palapeli application every now and then. Slicer plugins are not linked against Palapeli, but against libpala, a light-weight library that is designed for the sole purpose of slicing management. To Palapeli, it serves as an interface to talk with arbitrary slicer plugins. To slicer plugins, it provides an API to get and perform slicing jobs.
A slicer plugin needs to define a subclass of Pala::Slicer. Of course, you can also define more classes, but libpala will only talk to the single Pala::Slicer subclass.
The code: myslicer.h
- ifndef MYSLICER_H
- define MYSLICER_H
- include <Pala/Slicer>
- include <Pala/SlicerJob>
- include <Pala/SlicerProperty>
class MySlicer : public Pala::Slicer
{
Q_OBJECT
public:
MySlicer(QObject* parent = 0, const QVariantList& args = QVariantList());
virtual bool run(Pala::SlicerJob* job);
};
- endif // MYSLICER_H
As described above, we need to create a subclass of Pala::Slicer. (We also include the other two classes from libpala, Pala::SlicerJob and Pala::SlicerProperty, which we'll be using in the code.) For this example, we only need to implement the minimum of two functions:
- The constructor of the Pala::Slicer subclass needs to have exactly that signature, because this constructor is called by the KPluginLoader in this way. The arguments need to be passed to the Pala::Slicer constructor, which might want to handle them. (You as a slicer developer will never have to bother with them.)
- Pala::Slicer has one pure virtual method run(), which does the actual work.
The code: myslicer.cpp
- include "myslicer.h"
- include <KLocalizedString>
- include <KPluginFactory>
- include <KPluginLoader>
K_PLUGIN_FACTORY(MySlicerFactory, registerPlugin<MySlicer>();)
K_EXPORT_PLUGIN(MySlicerFactory("myslicer"))
MySlicer::MySlicer(QObject* parent, const QVariantList& args)
: Pala::Slicer(parent, args)
{
Pala::SlicerProperty* prop;
prop = new Pala::SlicerProperty(Pala::SlicerProperty::Integer, i18n("Piece count in horizontal direction"));
prop->setRange(3, 100);
prop->setDefaultValue(10);
addProperty("XCount", prop);
prop = new Pala::SlicerProperty(Pala::SlicerProperty::Integer, i18n("Piece count in vertical direction"));
prop->setRange(3, 100);
prop->setDefaultValue(10);
addProperty("YCount", prop);
}
bool MySlicer::run(Pala::SlicerJob* job)
{
//read job
const int xCount = job->argument("XCount").toInt();
const int yCount = job->argument("YCount").toInt();
const QImage image = job->image();
//calculate some metrics
const int pieceWidth = image.width() / xCount;
const int pieceHeight = image.height() / yCount;
const QSize pieceSize(pieceWidth, pieceHeight);
//create pieces
for (int x = 0; x < xCount; ++x)
{
for (int y = 0; y < yCount; ++y)
{
//calculate more metrics
const QPoint offset(x * pieceWidth, y * pieceHeight);
const QRect pieceBounds(offset, pieceSize);
//copy image part to piece
const QImage pieceImage = image.copy(pieceBounds);
job->addPiece(x + y * xCount, pieceImage, offset);
}
}
//create relations
for (int x = 0; x < xCount; ++x)
{
for (int y = 0; y < yCount; ++y)
{
//along X axis (pointing left)
if (x != 0)
job->addRelation(x + y * xCount, (x - 1) + y * xCount);
//along Y axis (pointing up)
if (y != 0)
job->addRelation(x + y * xCount, x + (y - 1) * xCount);
}
}
return true;
}
- include "myslicer.moc"
The two KPlugin headers are necessary for the plugin integration, which happens in line 7 and 8. Note that the string constant in line 8 ("myslicer") needs to match your library name.
The constructor of a Pala::Slicer has two tasks: It needs to pass its arguments to the base class constructor, and define the properties of the slicer. Properties make it possible for the user to configure the slicer. In our case, we let the user choose how much pieces are generated. See the <a href="http://api.kde.org/playground-api/games-apidocs/palapeli/libpala/html/classPala_1_1SlicerProperty.html">Pala::SlicerProperty</a> documentation for more details on what types of properties can be defined. (Warning: libpala's slicer properties have nothing to do with QObject's meta properties.)
We do not save pointers to the Pala::SlicerProperty instances that we add to the slicer. The properties are only passed internally to the application, which will construct an appropriate interface, and allow the user to enter values for the properties. When the user has configured everything, both the source image and the selected property values are packed into a Pala::SlicerJob object. The MySlicer::run method is then called for this job.
In the run method, we read both the image and the property values from the job. After having calculated some metrics, we start to split the image into pieces. The process is straight-forward because all pieces are perfectly rectangular. When piece images are ready, we use the Pala::SlicerJob::addPiece method to add them to the result mass. Note that we need to define piece IDs for each piece (the first parameter of the addPiece call in line 44). These IDs can be arbitrary non-negative numbers, but have to be unique among all pieces.
After we have added all pieces, we need to define neighbor relations between pieces. Neighbor relations are used to snap pieces together when they're near enough. Consider three pieces in a row: If piece 1 is near piece 3, nothing should snap because they do not have a common edge. If piece 1 is moved near piece 2, these should snap together. Therefore, we define a relation between piece 1 and piece 2 (and piece 2 and piece 3, respectively). The relation is added through the Pala::SlicerJob::addRelation method, which takes the IDs of two neighboring pieces. (The neighbor relation only needs to be defined in one direction: If piece 1 is a neighbor of piece 2, then piece 2 is also a neighbor of piece 1.)
We see that the Pala::SlicerJob object is used as a two-way communication channel between the slicer plugin and the application: Palapeli places the source image and the property values in it; the slicer reads these and writes the pieces and the relations into it; and in the end, Palapeli reads the pieces and the relations.
This simple implementation of a Pala::Slicer::run method always returns true. You can return false if something went wrong during the slicing (e. g. because some external resources could not be located).
Integrate into Palapeli: myslicer.desktop
[Desktop Entry]
Name=My very first slicer
Name[de]=Mein erstes Schnittmuster
Comment=It's quite simple, actually.
Comment[de]=Eigentlich ist das ganz einfach.
Type=Service
Icon=myslicer
X-KDE-Library=myslicer
X-KDE-ServiceTypes=Libpala/SlicerPlugin
X-KDE-PluginInfo-Author=Kandalf
[email protected]
X-KDE-PluginInfo-Name=myslicer
X-KDE-PluginInfo-Version=1.0
X-KDE-PluginInfo-Website=http://kde-hackers.example.org/myslicer
X-KDE-PluginInfo-Category=
X-KDE-PluginInfo-Depends=
X-KDE-PluginInfo-License=GPL
X-KDE-PluginInfo-EnabledByDefault=true
We need to tell the Palapeli library that there is a new plugin out there. We need a desktop entry file like shown here. You can mostly copy everything you see here; the most important thing is to keep the fields X-KDE-Library and X-KDE-PluginInfo-Name in sync with the library name (see next section). Note that the name is used in the "New puzzle" dialog to identify this pattern. (It can be translated; for example, a German translation has been added in the above example.)
Build everything: CMakeLists.txt
project(myslicer)
find_package(KDE4 REQUIRED)
find_package(LibPala REQUIRED)
add_definitions(${LIBPALA_DEFINITIONS})
include_directories(${LIBPALA_INCLUDES})
kde4_add_plugin(myslicer myslicer.cpp)
target_link_libraries(myslicer ${LIBPALA_LIBRARIES})
install(TARGETS myslicer DESTINATION ${PLUGIN_INSTALL_DIR})
install(FILES myslicer.desktop DESTINATION ${SERVICES_INSTALL_DIR})
Everything of this is pretty straightforward if you have previous experience with CMake (and this is what I assume). Make sure you compile everything as a plugin, and install it into the plugin directory. The find script for libpala sets some convenience variables that shorten the code in lines 5, 6 and 9. After having installed the plugin, run kbuildsycoca4. This will locate your plugin, and enable Palapeli to use it. Here is how it should look like then:

