Development/Tutorials/Plasma4/GettingStarted (ru): Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 97: | Line 97: | ||
==== void paintInterface(QRectF contentsRect) ==== | ==== void paintInterface(QRectF contentsRect) ==== | ||
Эта функция считается главной, так как рисует мини-приложение на экране. Здесь вы можете определить, как ваше приложение будет выглядеть. | |||
Вы должны рисовать в пределах, определённых через contentsRect и избегать выхода за них с помощью функции geometry(). Когда мини-приложение не имеет собственного стандартного фона, например он был отключён в функции setBackgroundHints() или он является панелью, geometry() и boundingRect() ведут себя так же, однако, когда стандартный фон включены (обычный случай), аплет будет иметь места, где лучше не рисовать. | |||
==== K_EXPORT_PLASMA_APPLET ( <name>, <class> ) ==== | ==== K_EXPORT_PLASMA_APPLET ( <name>, <class> ) ==== | ||
Это маленькая, но очень важная часть связывающая имя вашего класса с именем апплета, определённом в .desktop файле. | |||
Если ваш апплет не загружается. то одной из причин может быть именно несоответствие в этом месте. | |||
{{tip| | {{tip| | ||
Макрос K_EXPORT_PLASMA_APPLET добавляет "plasma_applet_", пожалуйста, учитывайте это, когда настраиваете ваш .desktop файл, чтобы избежать различий в именах. | |||
}} | }} | ||
Revision as of 10:29, 17 September 2008
Development/Tutorials/Plasma/GettingStarted
Languages: عربي | Asturianu | Català | Česky | Kaszëbsczi | Dansk | Deutsch | English | Esperanto | Español | Eesti | فارسی | Suomi | Français | Galego | Italiano | 日本語 | 한국어 | Norwegian | Polski | Português Brasileiro | Română | Русский | Svenska | Slovenčina | Slovenščina | српски | Türkçe | Tiếng Việt | Українська | 简体中文 | 繁體中文
| Tutorial Series | Plasma Tutorial |
| Previous | C++, Qt, KDE4 development environment |
| What's Next | |
| Further Reading | CMake |
Предисловие
Данное руководство требует для удачной сборки kde 4.1. В данном руководстве мы создадим простое мини-приложение. Чтобы сохранить простоту мы создадим статическое мини-приложение с использованием следующих компонентов:
- SVG рисунок
- Иконка
- Какой-либо простой текст
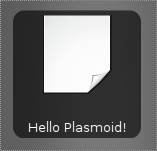
Код мини-приложения
.desktop файл
Каждое мини-приложение должно иметь в своём составе .desktop файл для указания плазме как и под каким именем его запускать.
plasma-applet-tutorial1.desktop
[Desktop Entry]
Name=Tutorial 1
Comment=Plasma Tutorial 1
Type=Service
X-KDE-ServiceTypes=Plasma/Applet
X-KDE-Library=plasma_applet_tutorial1
X-KDE-PluginInfo-Author=Bas Grolleman
[email protected]
X-KDE-PluginInfo-Name=tutorial1
X-KDE-PluginInfo-Version=0.1
X-KDE-PluginInfo-Website=http://plasma.kde.org/
X-KDE-PluginInfo-Category=Examples
X-KDE-PluginInfo-Depends=
X-KDE-PluginInfo-License=GPL
X-KDE-PluginInfo-EnabledByDefault=true
Наиболее важными являются пункты X-KDE-Library и X-KDE-PluginInfo-Name, они являются "клеем" между вашим классом и плазмой, без них ничего не заработает. Для X-KDE-PluginInfo-Category, см. PIG.
Файл заголовка
Это пример файла заголовка. Комментарии в код добавлены для ясности.
plasma-tutorial1.h
// Здесь мы избегаем загрузки заголовков несколько раз
- ifndef Tutorial1_HEADER
- define Tutorial1_HEADER
// Нам необходимо загрузить заголовок Applet плазмы
- include <KIcon>
- include <Plasma/Applet>
- include <Plasma/Svg>
class QSizeF;
// Определяем наш Applet плазмы
class PlasmaTutorial1 : public Plasma::Applet
{
Q_OBJECT
public:
// Базовые конструктор и деструктор
PlasmaTutorial1(QObject *parent, const QVariantList &args);
~PlasmaTutorial1();
// paintInterface - процедура рисующая Applet на экране
void paintInterface(QPainter *painter,
const QStyleOptionGraphicsItem *option,
const QRect& contentsRect);
void init();
private:
Plasma::Svg m_svg;
KIcon m_icon;
};
// Данная команда связывает ваш Applet с .desktop файлом
K_EXPORT_PLASMA_APPLET(tutorial1, PlasmaTutorial1)
- endif
QRectF boundingRect()
Функция boundingRect() сообщает плазме актуальные размеры мини-приложения. Это важно, так как мы должны знать сколько местя занимаем на экране.

void paintInterface(QRectF contentsRect)
Эта функция считается главной, так как рисует мини-приложение на экране. Здесь вы можете определить, как ваше приложение будет выглядеть. Вы должны рисовать в пределах, определённых через contentsRect и избегать выхода за них с помощью функции geometry(). Когда мини-приложение не имеет собственного стандартного фона, например он был отключён в функции setBackgroundHints() или он является панелью, geometry() и boundingRect() ведут себя так же, однако, когда стандартный фон включены (обычный случай), аплет будет иметь места, где лучше не рисовать.
K_EXPORT_PLASMA_APPLET ( <name>, <class> )
Это маленькая, но очень важная часть связывающая имя вашего класса с именем апплета, определённом в .desktop файле.
Если ваш апплет не загружается. то одной из причин может быть именно несоответствие в этом месте.

The actual work file
Here is the body of the function, again with a lot of comments in between.
plasma-tutorial1.cpp
- include "plasma-tutorial1.h"
- include <QPainter>
- include <QFontMetrics>
- include <QSizeF>
- include <plasma/svg.h>
- include <plasma/theme.h>
PlasmaTutorial1::PlasmaTutorial1(QObject *parent, const QVariantList &args)
: Plasma::Applet(parent, args),
m_svg(this),
m_icon("document")
{
m_svg.setImagePath("widgets/background");
// this will get us the standard applet background, for free!
setBackgroundHints(DefaultBackground);
resize(200, 200);
}
PlasmaTutorial1::~PlasmaTutorial1()
{
if (hasFailedToLaunch()) {
// Do some cleanup here
} else {
// Save settings
}
}
void PlasmaTutorial1::init()
{
// A small demonstration of the setFailedToLaunch function
if (m_icon.isNull()) {
setFailedToLaunch(true, "No world to say hello");
}
}
void PlasmaTutorial1::paintInterface(QPainter *p,
const QStyleOptionGraphicsItem *option, const QRect &contentsRect)
{
p->setRenderHint(QPainter::SmoothPixmapTransform);
p->setRenderHint(QPainter::Antialiasing);
// Now we draw the applet, starting with our svg
m_svg.resize((int)contentsRect.width(), (int)contentsRect.height());
m_svg.paint(p, (int)contentsRect.left(), (int)contentsRect.top());
// We place the icon and text
p->drawPixmap(7, 0, m_icon.pixmap((int)contentsRect.width(),(int)contentsRect.width()-14));
p->save();
p->setPen(Qt::white);
p->drawText(contentsRect,
Qt::AlignBottom | Qt::AlignHCenter,
"Hello Plasmoid!");
p->restore();
}
- include "plasma-tutorial1.moc"
Plasma/Svg
As you can see in the example code we are using the Plasma::Svg object, there are some important things to note here.
First we're using a relative path widgets/background which causes Plasma::Svg to use Plasma::Theme to locate the SVG data. While Plasma::Svg does support loading arbitrary files when passed an absolute path, use relative paths from the theme as often as possible as it makes Plasma skinable and the individual plasmoids look like a combined whole instead of a group of separate unrelated applications. You can see a list of available image components on the Plasma Theme page.
In either mode, Plasma::Svg can be used to draw a subset of the SVG file by passing it an element id that appears in the SVG document. As a good example, if you open the clock.svg file that ships with the default theme, you will see that it has a background, 3 handles (hour, minute and seconds) and a foreground (the glass). Due to the ability to put all the elements in one file the SVG file shows a clock. This is much nicer for artists compared to editing 5 separate files that they have to imagine on top of each other, and much nicer for performance as only one SVG renderer and one file read from disk is necessary.
setBackgroundHints(DefaultBackground)
Since drawing a background is a common function there is fast and easier way of doing it. By adding setBackgroundHints(DefaultBackground) to the code, the default Plasma background gets drawn behind your plasmoid. This not only saves you time and code, but creates a more consistent presentation for the user.
The init() method
In the constructor you only tell plasma about the background and configuration file if any. You also set the start size in the constructor. After that, plasma will take care of any resizing and you never have to worry about size. In the init() method you initialize everything that needs to be initialize such as reading config data for example.
hasFailedToLaunch()
If for some reason, the applet fails to get up on its feet (the library couldn't be loaded, necessary hardware support wasn't found, etc..) this method returns true. Using this function gives your application a chance to cleanup before quiting.
setFailedToLaunch(bool, QString)
When your application is unable to start, this function allows you to inform Plasma and give an optional reason why. Plasma will then draw a standardized error interface to inform the user of the situation and your applet will not be called upon to do any drawing on its own from that point forward. If your plasmoid becomes more complex and depends on multiple factors this is the nicest way to cleanup.
dataUpdated
If you would connect to any of plasma's data-engines you would have to implement a function called dataUpdated in your plasmoid. The latter is called if the data-engine sends you data, i.e. your plasmoid should recalculate its contents.
Determine the applet size and geometry: geometry() and contentsRect()
If you need to know, in your applet code, what the applet size and geometry is, call contentsRect() and contentsRect().size(). Avoid calling geometry() and size() because they don't take into account the margin's size set by the applets default background. Also avoid using absolute numbers to position items in the applet like QPoint(0, 0) to indicate the top-left point of your applet, instead use contentsRect().topLeft().
Building it all, the CMakeLists.txt
Finally, to put everything together you need to build everything. To tell cmake what needs to go where there is the CMakeLists.txt file.
For more details on CMake please read Development/Tutorials/CMake
- Project Needs a name ofcourse
project(plasma-tutorial1)
- Find the required Libaries
find_package(KDE4 REQUIRED)
include(KDE4Defaults)
find_package(Plasma REQUIRED)
add_definitions (${QT_DEFINITIONS} ${KDE4_DEFINITIONS})
include_directories(
${CMAKE_SOURCE_DIR}
${CMAKE_BINARY_DIR}
${KDE4_INCLUDES}
)
- We add our source code here
set(tutorial1_SRCS plasma-tutorial1.cpp)
- Now make sure all files get to the right place
kde4_add_plugin(plasma_applet_tutorial1 ${tutorial1_SRCS})
target_link_libraries(plasma_applet_tutorial1
${PLASMA_LIBS} ${KDE4_KDEUI_LIBS})
install(TARGETS plasma_applet_tutorial1
DESTINATION ${PLUGIN_INSTALL_DIR})
install(FILES plasma-applet-tutorial1.desktop
DESTINATION ${SERVICES_INSTALL_DIR})
Testing the Applet
If your current Development Environment differs from the Test Installation, you have to run cmake with -DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=/usr/lib/kde4/ (replace with your $KDEDIR). Then run make. If succesfull the applet can be installed by running sudo make install or
- cp ./lib/plasma_applet_tutorial1.so $KDEDIR/lib
- cp ./plasma-applet-tutorial1.desktop $KDEDIR/share/kde4/services/
and run kbuildsycoca4 (so that KDE apps will know about the new desktop files).
In order to test your Applet you can use the plasmoidviewer program:
plasmoidviewer applet_name
Where applet_name is the value specified into .desktop for the X-KDE-PluginInfo-Name key.
Otherwise you can restart plasma, so the Applet will be displayed in the Applet Browser:
kbuildsycoca4
kquitapp plasma
plasma
If that doesn't work you will have to restart your KDE session by logging out and back in.
