Development/Tutorials/Plasma4/GettingStarted: Difference between revisions
the K_Export should be in the .cpp file, not in the header |
→Plasma/Svg: fixed Plasma Theme link |
||
| (31 intermediate revisions by 15 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{TutorialBrowser| | {{TutorialBrowser| | ||
series=Plasma Tutorial| | series=[[Development/Tutorials/Plasma|Plasma Tutorial]]| | ||
name=Creating your first Plasmoid| | name=Creating your first Plasmoid| | ||
pre=[http:// | pre=[http://stackoverflow.com/questions/388242/the-definitive-c-book-guide-and-list C++], [http://www.trolltech.com/products/qt/ Qt], [[Getting_Started/Build|KDE4 development environment]]| | ||
next=| | next=[[Development/Tutorials/Plasma/GettingStarted..Some_More]]| | ||
reading=[[Development/Tutorials/CMake|CMake]] | reading=[[Development/Tutorials/CMake|CMake]] | ||
}} | }} | ||
==Abstract== | ==Abstract== | ||
This tutorial needs KDE 4.2 ( | This tutorial needs KDE 4.2 (or newer) to build. | ||
We are going to create a simple plasmoid in this tutorial. To keep things simple, we will only create a static plasmoid which will contain the following items: | We are going to create a simple plasmoid in this tutorial. To keep things simple, we will only create a static plasmoid which will contain the following items: | ||
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
'''plasma-applet-tutorial1.desktop''' | '''plasma-applet-tutorial1.desktop''' | ||
< | <syntaxhighlight lang="ini"> | ||
[Desktop Entry] | [Desktop Entry] | ||
Name=Tutorial 1 | Name=Tutorial 1 | ||
| Line 36: | Line 36: | ||
X-KDE-Library=plasma_applet_tutorial1 | X-KDE-Library=plasma_applet_tutorial1 | ||
X-KDE-PluginInfo-Name=tutorial1 | |||
X-KDE-PluginInfo-Category=Examples | |||
X-KDE-PluginInfo-Author=Bas Grolleman | X-KDE-PluginInfo-Author=Bas Grolleman | ||
X-KDE-PluginInfo-Version=0.1 | X-KDE-PluginInfo-Version=0.1 | ||
X-KDE-PluginInfo-Website=http://plasma.kde.org/ | X-KDE-PluginInfo-Website=http://plasma.kde.org/ | ||
X-KDE-PluginInfo-Depends= | X-KDE-PluginInfo-Depends= | ||
X-KDE-PluginInfo-License=GPL | X-KDE-PluginInfo-License=GPL | ||
X-KDE-PluginInfo-EnabledByDefault=true | X-KDE-PluginInfo-EnabledByDefault=true | ||
</ | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
The most important bits are the '''X-KDE-Library''' and '''X-KDE-PluginInfo-Name''', they are the "glue" between your class and plasma, without it, nothing will start. For '''X-KDE-PluginInfo-Category''', refer to the [[Projects/Plasma/PIG | PIG]]. | The most important bits are the '''X-KDE-Library''' and '''X-KDE-PluginInfo-Name''', they are the "glue" between your class and plasma, without it, nothing will start. For '''X-KDE-PluginInfo-Category''', refer to the [[Projects/Plasma/PIG | PIG]]. | ||
| Line 53: | Line 53: | ||
'''plasma-tutorial1.h''' | '''plasma-tutorial1.h''' | ||
< | <syntaxhighlight lang="cpp-qt"> | ||
// Here we avoid loading the header multiple times | // Here we avoid loading the header multiple times | ||
#ifndef Tutorial1_HEADER | #ifndef Tutorial1_HEADER | ||
| Line 75: | Line 75: | ||
// The paintInterface procedure paints the applet to screen | // The paintInterface procedure paints the applet to screen | ||
void paintInterface(QPainter * | void paintInterface(QPainter *p, | ||
const QStyleOptionGraphicsItem *option, | const QStyleOptionGraphicsItem *option, | ||
const QRect& contentsRect); | const QRect& contentsRect); | ||
| Line 84: | Line 84: | ||
KIcon m_icon; | KIcon m_icon; | ||
}; | }; | ||
#endif | #endif | ||
</ | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
==== void paintInterface(QRectF contentsRect) ==== | ==== void paintInterface(QRectF contentsRect) ==== | ||
This can be considered the main function since it paints the plasmoid on to the screen. Here, you define how you want your plasmoid to look. | This can be considered the main function since it paints the plasmoid on to the screen. Here, you define how you want your plasmoid to look. | ||
You should only paint in the boundaries defined by contentsRect and avoid using geometry(). When a plasmoid does not have a standard background, e.g. when it's disabled with a setBackgroundHints() call or it's in the panel, geometry() and boundingRect() behave the same; however, when the standard background is enabled (the usual case), the | You should only paint in the boundaries defined by contentsRect and avoid using geometry(). When a plasmoid does not have a standard background, e.g. when it's disabled with a setBackgroundHints() call or it's in the panel, geometry() and boundingRect() behave the same; however, when the standard background is enabled (the usual case), the applet will have a margin where it should not be painted | ||
| Line 103: | Line 99: | ||
'''plasma-tutorial1.cpp''' | '''plasma-tutorial1.cpp''' | ||
< | <syntaxhighlight lang="cpp-qt"> | ||
#include "plasma-tutorial1.h" | #include "plasma-tutorial1.h" | ||
#include <QPainter> | #include <QPainter> | ||
| Line 111: | Line 107: | ||
#include <plasma/svg.h> | #include <plasma/svg.h> | ||
#include <plasma/theme.h> | #include <plasma/theme.h> | ||
| Line 166: | Line 159: | ||
p->restore(); | p->restore(); | ||
} | } | ||
// This is the command that links your applet to the .desktop file | |||
K_EXPORT_PLASMA_APPLET(tutorial1, PlasmaTutorial1) | |||
#include "plasma-tutorial1.moc" | #include "plasma-tutorial1.moc" | ||
</ | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
==== K_EXPORT_PLASMA_APPLET ( <name>, <class> ) ==== | ==== K_EXPORT_PLASMA_APPLET ( <name>, <class> ) ==== | ||
| Line 180: | Line 176: | ||
As you can see in the example code we are using the {{class|Plasma::Svg}} object, there are some important things to note here. | As you can see in the example code we are using the {{class|Plasma::Svg}} object, there are some important things to note here. | ||
First we're using a relative path '''widgets/background''' which causes {{class|Plasma::Svg}} to use {{class|Plasma::Theme}} to locate the SVG data. While {{class|Plasma::Svg}} does support loading arbitrary files when passed an absolute path, use relative paths from the theme as often as possible as it makes Plasma skinable and the individual plasmoids look like a combined whole instead of a group of separate unrelated applications. You can see a list of available image components on the [[ | First we're using a relative path '''widgets/background''' which causes {{class|Plasma::Svg}} to use {{class|Plasma::Theme}} to locate the SVG data. While {{class|Plasma::Svg}} does support loading arbitrary files when passed an absolute path, use relative paths from the theme as often as possible as it makes Plasma skinable and the individual plasmoids look like a combined whole instead of a group of separate unrelated applications. You can see a list of available image components on the [[Development/Tutorials/Plasma4/ThemeDetails|Plasma Theme page]]. | ||
In either mode, {{class|Plasma::Svg}} can be used to draw a subset of the SVG file by passing it an element id that appears in the SVG document. As a good example, if you open the clock.svg file that ships with the default theme, you will see that it has a background, 3 | In either mode, {{class|Plasma::Svg}} can be used to draw a subset of the SVG file by passing it an element id that appears in the SVG document. As a good example, if you open the clock.svg file that ships with the default theme, you will see that it has a background, 3 needles (hour, minute and seconds) and a foreground (the glass). Due to the ability to put all the elements in one file the SVG file shows a clock. This is much nicer for artists compared to editing 5 separate files that they have to imagine on top of each other, and much nicer for performance as only one SVG renderer and one file read from disk is necessary. | ||
==== setBackgroundHints(DefaultBackground) ==== | ==== setBackgroundHints(DefaultBackground) ==== | ||
Since drawing a background is a common function there is fast and easier way of doing it. By adding <tt>setBackgroundHints(DefaultBackground)</tt> to the code, the default Plasma background gets drawn behind your plasmoid. This not only saves you time and code, but creates a more consistent presentation for the user. | Since drawing a background is a common function there is a fast and easier way of doing it. By adding <tt>setBackgroundHints(DefaultBackground)</tt> to the code, the default Plasma background gets drawn behind your plasmoid. This not only saves you time and code, but creates a more consistent presentation for the user. | ||
==== The init() method ==== | ==== The init() method ==== | ||
In the constructor you only tell plasma about the background and configuration file if any. You also set the start size in the constructor. After that, plasma will take care of any resizing and you never have to worry about size. In the <tt>init()</tt> method you initialize everything that needs to be | In the constructor you only tell plasma about the background and configuration file if any. You also set the start size in the constructor. After that, plasma will take care of any resizing and you never have to worry about size. In the <tt>init()</tt> method you initialize everything that needs to be initialized such as reading config data for example. | ||
==== hasFailedToLaunch() ==== | ==== hasFailedToLaunch() ==== | ||
| Line 196: | Line 192: | ||
When your application is unable to start, this function allows you to inform Plasma and give an optional reason why. Plasma will then draw a standardized error interface to inform the user of the situation and your applet will not be called upon to do any drawing on its own from that point forward. If your plasmoid becomes more complex and depends on multiple factors this is the nicest way to cleanup. | When your application is unable to start, this function allows you to inform Plasma and give an optional reason why. Plasma will then draw a standardized error interface to inform the user of the situation and your applet will not be called upon to do any drawing on its own from that point forward. If your plasmoid becomes more complex and depends on multiple factors this is the nicest way to cleanup. | ||
==== dataUpdated ==== | ==== dataUpdated(const QString &source, const Plasma::DataEngine::Data &data) ==== | ||
If you would connect to any of | If you would like to connect to any of Plasma's DataEngines, you can implement the dataUpdated method in your Plasmoid. When a DataEngine is connected directly to your Applet subclass, dataUpdated will be called when the DataEngine sends you updated data. | ||
==== Determine the applet size and geometry: geometry() and contentsRect() ==== | ==== Determine the applet size and geometry: geometry() and contentsRect() ==== | ||
| Line 208: | Line 204: | ||
For more details on CMake please read [[Development/Tutorials/CMake]] | For more details on CMake please read [[Development/Tutorials/CMake]] | ||
< | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
# Project Needs a name ofcourse | # Project Needs a name ofcourse | ||
project(plasma-tutorial1) | project(plasma-tutorial1) | ||
| Line 236: | Line 232: | ||
install(FILES plasma-applet-tutorial1.desktop | install(FILES plasma-applet-tutorial1.desktop | ||
DESTINATION ${SERVICES_INSTALL_DIR}) | DESTINATION ${SERVICES_INSTALL_DIR}) | ||
</ | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
== Testing the Applet == | == Testing the Applet == | ||
If your current Development Environment differs from the Test Installation, you have to run cmake with -DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX= | If your current Development Environment differs from the Test Installation, you have to run cmake with -DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=`kde4-config --prefix`. Then run make. If succesfull the applet can be installed by running sudo make install | ||
or | or | ||
* cp ./lib/plasma_applet_tutorial1.so $KDEDIR/lib | * cp ./lib/plasma_applet_tutorial1.so $KDEDIR/lib/kde4 | ||
* cp ./plasma-applet-tutorial1.desktop $KDEDIR/share/kde4/services/ | * cp ./plasma-applet-tutorial1.desktop $KDEDIR/share/kde4/services/ | ||
and run kbuildsycoca4 (so that KDE apps will know about the new desktop files). | and run kbuildsycoca4 (so that KDE apps will know about the new desktop files). | ||
In order to test your Applet you can use the '''plasmoidviewer''' program: | In order to test your Applet you can use the '''plasmoidviewer''' program: | ||
< | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
kbuildsycoca4 #Needed once to let KDE know there is a new plugin | |||
plasmoidviewer applet_name | plasmoidviewer applet_name | ||
</ | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
You can even view your Applet in a small desktop using plasmoidviewer: | You can even view your Applet in a small desktop using plasmoidviewer: | ||
< | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
plasmoidviewer -c desktop applet_name | plasmoidviewer -c desktop applet_name | ||
</ | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
Where '''applet_name''' is the value specified into .desktop for the '''X-KDE-PluginInfo-Name''' key. | Where '''applet_name''' is the value specified into .desktop for the '''X-KDE-PluginInfo-Name''' key. | ||
Otherwise you can restart plasma, so the Applet will be displayed in the Applet Browser: | Otherwise you can restart plasma, so the Applet will be displayed in the Applet Browser: | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | |||
kbuildsycoca4 | |||
kquitapp plasma-desktop | |||
plasma-desktop | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
If that doesn't work you will have to restart your KDE session by logging out and back in. Or try to set export KDEDIRS=/usr/local:'kde4-config --prefix' and run kbuildsycoca4 again | If that doesn't work you will have to restart your KDE session by logging out and back in. Or try to set export KDEDIRS=/usr/local:'kde4-config --prefix' and run kbuildsycoca4 again | ||
== Wow that was fun! == | |||
Now that you made your first C++ Plasmoid, if you would like to continue down the path of enlightenment, check out: [[Development/Tutorials/Plasma/GettingStarted..Some_More]] | |||
Latest revision as of 10:12, 22 December 2014
| Tutorial Series | Plasma Tutorial |
| Previous | C++, Qt, KDE4 development environment |
| What's Next | Development/Tutorials/Plasma/GettingStarted..Some_More |
| Further Reading | CMake |
Abstract
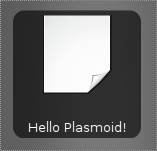
This tutorial needs KDE 4.2 (or newer) to build. We are going to create a simple plasmoid in this tutorial. To keep things simple, we will only create a static plasmoid which will contain the following items:
- An SVG Image
- Icon
- Some nice text
The Code
The .desktop file
Every Plasmoid needs a .desktop file to tell plasma how it should be started and what name it carries.
plasma-applet-tutorial1.desktop
[Desktop Entry]
Name=Tutorial 1
Comment=Plasma Tutorial 1
Type=Service
ServiceTypes=Plasma/Applet
X-KDE-Library=plasma_applet_tutorial1
X-KDE-PluginInfo-Name=tutorial1
X-KDE-PluginInfo-Category=Examples
X-KDE-PluginInfo-Author=Bas Grolleman
X-KDE-PluginInfo-Email=[email protected]
X-KDE-PluginInfo-Version=0.1
X-KDE-PluginInfo-Website=http://plasma.kde.org/
X-KDE-PluginInfo-Depends=
X-KDE-PluginInfo-License=GPL
X-KDE-PluginInfo-EnabledByDefault=true
The most important bits are the X-KDE-Library and X-KDE-PluginInfo-Name, they are the "glue" between your class and plasma, without it, nothing will start. For X-KDE-PluginInfo-Category, refer to the PIG.
The header file
This is the example header file. Comments have been added in the code for clarity.
plasma-tutorial1.h
// Here we avoid loading the header multiple times
#ifndef Tutorial1_HEADER
#define Tutorial1_HEADER
// We need the Plasma Applet headers
#include <KIcon>
#include <Plasma/Applet>
#include <Plasma/Svg>
class QSizeF;
// Define our plasma Applet
class PlasmaTutorial1 : public Plasma::Applet
{
Q_OBJECT
public:
// Basic Create/Destroy
PlasmaTutorial1(QObject *parent, const QVariantList &args);
~PlasmaTutorial1();
// The paintInterface procedure paints the applet to screen
void paintInterface(QPainter *p,
const QStyleOptionGraphicsItem *option,
const QRect& contentsRect);
void init();
private:
Plasma::Svg m_svg;
KIcon m_icon;
};
#endif
void paintInterface(QRectF contentsRect)
This can be considered the main function since it paints the plasmoid on to the screen. Here, you define how you want your plasmoid to look. You should only paint in the boundaries defined by contentsRect and avoid using geometry(). When a plasmoid does not have a standard background, e.g. when it's disabled with a setBackgroundHints() call or it's in the panel, geometry() and boundingRect() behave the same; however, when the standard background is enabled (the usual case), the applet will have a margin where it should not be painted
The actual work file
Here is the body of the function, again with a lot of comments in between.
plasma-tutorial1.cpp
#include "plasma-tutorial1.h"
#include <QPainter>
#include <QFontMetrics>
#include <QSizeF>
#include <plasma/svg.h>
#include <plasma/theme.h>
PlasmaTutorial1::PlasmaTutorial1(QObject *parent, const QVariantList &args)
: Plasma::Applet(parent, args),
m_svg(this),
m_icon("document")
{
m_svg.setImagePath("widgets/background");
// this will get us the standard applet background, for free!
setBackgroundHints(DefaultBackground);
resize(200, 200);
}
PlasmaTutorial1::~PlasmaTutorial1()
{
if (hasFailedToLaunch()) {
// Do some cleanup here
} else {
// Save settings
}
}
void PlasmaTutorial1::init()
{
// A small demonstration of the setFailedToLaunch function
if (m_icon.isNull()) {
setFailedToLaunch(true, "No world to say hello");
}
}
void PlasmaTutorial1::paintInterface(QPainter *p,
const QStyleOptionGraphicsItem *option, const QRect &contentsRect)
{
p->setRenderHint(QPainter::SmoothPixmapTransform);
p->setRenderHint(QPainter::Antialiasing);
// Now we draw the applet, starting with our svg
m_svg.resize((int)contentsRect.width(), (int)contentsRect.height());
m_svg.paint(p, (int)contentsRect.left(), (int)contentsRect.top());
// We place the icon and text
p->drawPixmap(7, 0, m_icon.pixmap((int)contentsRect.width(),(int)contentsRect.width()-14));
p->save();
p->setPen(Qt::white);
p->drawText(contentsRect,
Qt::AlignBottom | Qt::AlignHCenter,
"Hello Plasmoid!");
p->restore();
}
// This is the command that links your applet to the .desktop file
K_EXPORT_PLASMA_APPLET(tutorial1, PlasmaTutorial1)
#include "plasma-tutorial1.moc"
K_EXPORT_PLASMA_APPLET ( <name>, <class> )
This is a small but very important part that links your classname to the applet name in the .desktop file. If your applet doesn't seem to get loaded, there may be a difference between this declaration and your .desktop file

Plasma/Svg
As you can see in the example code we are using the Plasma::Svg object, there are some important things to note here.
First we're using a relative path widgets/background which causes Plasma::Svg to use Plasma::Theme to locate the SVG data. While Plasma::Svg does support loading arbitrary files when passed an absolute path, use relative paths from the theme as often as possible as it makes Plasma skinable and the individual plasmoids look like a combined whole instead of a group of separate unrelated applications. You can see a list of available image components on the Plasma Theme page.
In either mode, Plasma::Svg can be used to draw a subset of the SVG file by passing it an element id that appears in the SVG document. As a good example, if you open the clock.svg file that ships with the default theme, you will see that it has a background, 3 needles (hour, minute and seconds) and a foreground (the glass). Due to the ability to put all the elements in one file the SVG file shows a clock. This is much nicer for artists compared to editing 5 separate files that they have to imagine on top of each other, and much nicer for performance as only one SVG renderer and one file read from disk is necessary.
setBackgroundHints(DefaultBackground)
Since drawing a background is a common function there is a fast and easier way of doing it. By adding setBackgroundHints(DefaultBackground) to the code, the default Plasma background gets drawn behind your plasmoid. This not only saves you time and code, but creates a more consistent presentation for the user.
The init() method
In the constructor you only tell plasma about the background and configuration file if any. You also set the start size in the constructor. After that, plasma will take care of any resizing and you never have to worry about size. In the init() method you initialize everything that needs to be initialized such as reading config data for example.
hasFailedToLaunch()
If for some reason, the applet fails to get up on its feet (the library couldn't be loaded, necessary hardware support wasn't found, etc..) this method returns true. Using this function gives your application a chance to cleanup before quiting.
setFailedToLaunch(bool, QString)
When your application is unable to start, this function allows you to inform Plasma and give an optional reason why. Plasma will then draw a standardized error interface to inform the user of the situation and your applet will not be called upon to do any drawing on its own from that point forward. If your plasmoid becomes more complex and depends on multiple factors this is the nicest way to cleanup.
dataUpdated(const QString &source, const Plasma::DataEngine::Data &data)
If you would like to connect to any of Plasma's DataEngines, you can implement the dataUpdated method in your Plasmoid. When a DataEngine is connected directly to your Applet subclass, dataUpdated will be called when the DataEngine sends you updated data.
Determine the applet size and geometry: geometry() and contentsRect()
If you need to know, in your applet code, what the applet size and geometry is, call contentsRect() and contentsRect().size(). Avoid calling geometry() and size() because they don't take into account the margin's size set by the applets default background. Also avoid using absolute numbers to position items in the applet like QPoint(0, 0) to indicate the top-left point of your applet, instead use contentsRect().topLeft().
Building it all, the CMakeLists.txt
Finally, to put everything together you need to build everything. To tell cmake what needs to go where there is the CMakeLists.txt file.
For more details on CMake please read Development/Tutorials/CMake
# Project Needs a name ofcourse
project(plasma-tutorial1)
# Find the required Libaries
find_package(KDE4 REQUIRED)
include(KDE4Defaults)
add_definitions (${QT_DEFINITIONS} ${KDE4_DEFINITIONS})
include_directories(
${CMAKE_SOURCE_DIR}
${CMAKE_BINARY_DIR}
${KDE4_INCLUDES}
)
# We add our source code here
set(tutorial1_SRCS plasma-tutorial1.cpp)
# Now make sure all files get to the right place
kde4_add_plugin(plasma_applet_tutorial1 ${tutorial1_SRCS})
target_link_libraries(plasma_applet_tutorial1
${KDE4_PLASMA_LIBS} ${KDE4_KDEUI_LIBS})
install(TARGETS plasma_applet_tutorial1
DESTINATION ${PLUGIN_INSTALL_DIR})
install(FILES plasma-applet-tutorial1.desktop
DESTINATION ${SERVICES_INSTALL_DIR})
Testing the Applet
If your current Development Environment differs from the Test Installation, you have to run cmake with -DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=`kde4-config --prefix`. Then run make. If succesfull the applet can be installed by running sudo make install or
- cp ./lib/plasma_applet_tutorial1.so $KDEDIR/lib/kde4
- cp ./plasma-applet-tutorial1.desktop $KDEDIR/share/kde4/services/
and run kbuildsycoca4 (so that KDE apps will know about the new desktop files). In order to test your Applet you can use the plasmoidviewer program:
kbuildsycoca4 #Needed once to let KDE know there is a new plugin
plasmoidviewer applet_name
You can even view your Applet in a small desktop using plasmoidviewer:
plasmoidviewer -c desktop applet_name
Where applet_name is the value specified into .desktop for the X-KDE-PluginInfo-Name key.
Otherwise you can restart plasma, so the Applet will be displayed in the Applet Browser:
kbuildsycoca4
kquitapp plasma-desktop
plasma-desktop
If that doesn't work you will have to restart your KDE session by logging out and back in. Or try to set export KDEDIRS=/usr/local:'kde4-config --prefix' and run kbuildsycoca4 again
Wow that was fun!
Now that you made your first C++ Plasmoid, if you would like to continue down the path of enlightenment, check out: Development/Tutorials/Plasma/GettingStarted..Some_More
