Marble/Routing/MarblePythonGeoPainter: Difference between revisions
Created page with " {{TutorialBrowser| series=Marble Python Tutorial| name=GeoPainter: Painting onto the map| pre=[[Projects/Marble/Runners/MarblePythonParse|Tutorial 12 - Opening .kml, .gpx...." |
m Ochurlaud moved page Projects/Marble/Routing/MarblePythonGeoPainter to Marble/Routing/MarblePythonGeoPainter |
||
| (One intermediate revision by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
name=GeoPainter: Painting onto the map| | name=GeoPainter: Painting onto the map| | ||
pre=[[Projects/Marble/Runners/ | pre=[[Projects/Marble/Runners/MarblePythonVehicleTracking|Tutorial 7 - Vehicle Tracking]]| | ||
next=[[Projects/Marble/MarblePythonLayerInterface|Tutorial 14 - Drawing in Custom Layers]]| | next=[[Projects/Marble/MarblePythonLayerInterface|Tutorial 14 - Drawing in Custom Layers]]| | ||
Latest revision as of 21:01, 10 March 2016
| Tutorial Series | Marble Python Tutorial |
| Previous | Tutorial 7 - Vehicle Tracking |
| What's Next | Tutorial 14 - Drawing in Custom Layers |
| Further Reading | n/a |

In the previous tutorial you've seen how easy it is to embed a MarbleWidget into a Qt application: Just create a MarbleWidget, set a map theme on it and ... you're done already.
Next we'll extend that example a bit and write our own little paint method to add some extra content to the globe. To facilitate this, Marble provides a painting hook called MarbleWidget.customPaint(). It is called in between of the normal paint operations: After the background and tiles are painted, but before the top layers like float items (info boxes).
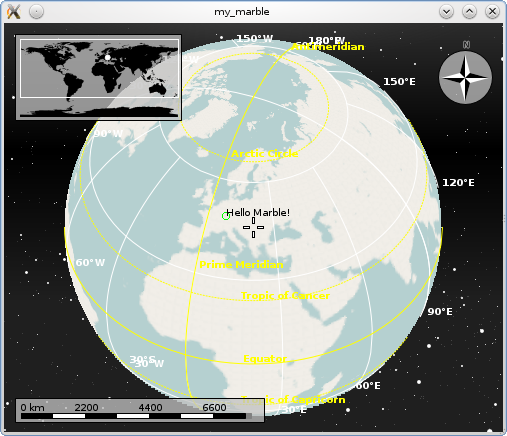
The customPaint operation is called with a GeoPainter: An extended QPainter which not only is able to paint at certain screen (pixel) positions, but also at certain geo (lat,lon) positions. We'll make use of that feature now. To keep things simple again, we just add a little 'Hello World' message indicated by a green circle.
#!/usr/bin/env python
from PyQt4.QtCore import *
from PyQt4.QtGui import *
from PyKDE4.marble import *
import sys
class MyMarbleWidget(Marble.MarbleWidget):
def __init__(self):
Marble.MarbleWidget.__init__(self)
def customPaint(self, painter):
home = Marble.GeoDataCoordinates(8.4, 49.0, 0.0, Marble.GeoDataCoordinates.Degree)
painter.setPen(Qt.green)
painter.drawEllipse(home, 7, 7)
painter.setPen(Qt.black)
painter.drawText(home, "Hello Marble!")
def main():
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
# create the marble widget
marble = MyMarbleWidget()
# resize the widget and add a window title
marble.resize(500, 500)
marble.setWindowTitle("my_marble")
# Load the OpenStreetMap map
marble.setMapThemeId("earth/openstreetmap/openstreetmap.dgml")
marble.setZoom(1100)
marble.centerOn(Marble.GeoDataCoordinates(8.4, 49.0, 0.0, Marble.GeoDataCoordinates.Degree))
# show the marble widget
marble.show()
# run the app
app.exec_()
main()
Save the code above as painting.py and execute python painting.py and you end up with a globe view similar to this:
There may be situations where MarbleWidget::customPaint() does not suit your needs. This can be the case when you don't want to paint at the very top position (above all other items), or when subclassing MarbleWidget is not possible for some reason. In that case, have a look at the next chapter Drawing in Custom Layers