Archive:Development/Tutorials/Qt4 Ruby Tutorial/Chapter 3 (zh TW): Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
m AnneW moved page Development/Tutorials/Qt4 Ruby Tutorial/Chapter 3 (zh TW) to Archive:Development/Tutorials/Qt4 Ruby Tutorial/Chapter 3 (zh TW) without leaving a redirect: Obsolete |
||
| (4 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
pre=[[Development/Tutorials/Qt4_Ruby_Tutorial/Chapter_2_(zh_TW)|教學 2 -Calling it Quits]]| | pre=[[Development/Tutorials/Qt4_Ruby_Tutorial/Chapter_2_(zh_TW)|教學 2 -Calling it Quits]]| | ||
next=[[Development/Tutorials/Qt4_Ruby_Tutorial/ | next=[[Development/Tutorials/Qt4_Ruby_Tutorial/Chapter_04_(zh_TW)|教學 4 - Let There Be Widgets]] | ||
}} | }} | ||
== Family Values == | == Family Values == | ||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
我們將保持簡單性,只採用單一父 widget 和一個單獨的子 widget。 | 我們將保持簡單性,只採用單一父 widget 和一個單獨的子 widget。 | ||
< | <syntaxhighlight lang="ruby"> | ||
require 'Qt4' | require 'Qt4' | ||
| Line 36: | Line 36: | ||
window.show() | window.show() | ||
app.exec() | app.exec() | ||
</ | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
===一行一行的瀏覽=== | ===一行一行的瀏覽=== | ||
< | <syntaxhighlight lang="ruby"> | ||
window = Qt::Widget.new() | window = Qt::Widget.new() | ||
</ | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
在這裡,我們簡單地建立一個空白的 widget 物件。[http://doc.qt.nokia.com/latest/qwidget.html Qt::Widget] 類別是所有使用者界面物件的基礎類別。widget 是使用者界面物件的原子:它接收滑鼠、鍵盤和其他來自視窗系統的事件,並在螢幕上描繪自身代表。widget 會被其父 widget 和在它前面的 widget 修剪。 | 在這裡,我們簡單地建立一個空白的 widget 物件。[http://doc.qt.nokia.com/latest/qwidget.html Qt::Widget] 類別是所有使用者界面物件的基礎類別。widget 是使用者界面物件的原子:它接收滑鼠、鍵盤和其他來自視窗系統的事件,並在螢幕上描繪自身代表。widget 會被其父 widget 和在它前面的 widget 修剪。 | ||
| Line 47: | Line 47: | ||
一個沒有嵌入在父 widget 的 widget,像這樣的特殊 widget,被稱為視窗(window)。通常視窗會有視窗系統提供的外框和工作列(taskbar)項目。沒有父 widget 的 widget 就是一個獨立的視窗。其在螢幕上的初始位置是視窗系統所控制。 | 一個沒有嵌入在父 widget 的 widget,像這樣的特殊 widget,被稱為視窗(window)。通常視窗會有視窗系統提供的外框和工作列(taskbar)項目。沒有父 widget 的 widget 就是一個獨立的視窗。其在螢幕上的初始位置是視窗系統所控制。 | ||
< | <syntaxhighlight lang="ruby"> | ||
window.resize(200, 120) | window.resize(200, 120) | ||
</ | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
我們設定視窗的寬為200像素,高為120像素。 | 我們設定視窗的寬為200像素,高為120像素。 | ||
< | <syntaxhighlight lang="ruby"> | ||
quit = Qt::PushButton.new('Quit', window) | quit = Qt::PushButton.new('Quit', window) | ||
</ | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
子 widget 誕生。[http://doc.qt.nokia.com/latest/qpushbutton.html Qt::PushButton] 建立並指定父 widget('''<tt>window</tt>''')。子 widget 總是顯示在其父的區域裡面。當顯示時,它會被其父 widget 的邊界裁剪。預設情況下,它會被放置在其父 widget 的左上角,在(0,0)的位置。 | |||
< | <syntaxhighlight lang="ruby"> | ||
quit.setGeometry(10, 40, 180, 40) | quit.setGeometry(10, 40, 180, 40) | ||
</ | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
[http://doc.qt.nokia.com/latest/qwidget.html#setgeometry Qt::Widget::setGeometry()] 函式有四個參數:前兩個參數是按鈕左上角的x和y坐標。坐標是相對於父 widget。而後兩個參數是按鈕的寬度和高度。結果是按鈕的範圍從(10,40)到(190,80)。 | |||
< | <syntaxhighlight lang="ruby"> | ||
window.show() | window.show() | ||
</ | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
當父 widget 顯示時,它會呼叫顯示其所有的子 widget(除了那些已明確使用[http://doc.qt.nokia.com/latest/qwidget.html#hide Qt::Widget::hide()] 隱藏的)。 | |||
===執行應用程式=== | ===執行應用程式=== | ||
該按鈕不再填滿整個視窗。相反地,因為 [http://doc.qt.nokia.com/latest/qwidget.html#geometry-prop Qt::Widget::setGeometry()] 呼叫,它留在視窗(10,40)的位置和以及(180,40)的大小。 | |||
===練習=== | ===練習=== | ||
嘗試調整視窗的大小。按鈕有什麼改變?如果你使用更大的字體執行該程式,按鈕的高度會發生什麼改變?如果你試圖使視窗變得非常小,會發生什麼事? | |||
[[Category:Ruby]] | |||
Latest revision as of 15:37, 23 June 2013
Template:I18n/Language Navigation Bar (zh TW)
Template:TutorialBrowser (zh TW)
Family Values
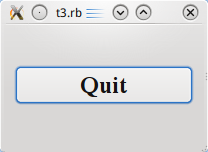
檔案:
概覽
這個範例說明如何建立父(parent)widget 和子(child) widget。
我們將保持簡單性,只採用單一父 widget 和一個單獨的子 widget。
require 'Qt4'
app = Qt::Application.new(ARGV)
window = Qt::Widget.new()
window.resize(200, 120)
quit = Qt::PushButton.new('Quit', window)
quit.font = Qt::Font.new('Times', 18, Qt::Font::Bold)
quit.setGeometry(10, 40, 180, 40)
Qt::Object.connect(quit, SIGNAL('clicked()'), app, SLOT('quit()'))
window.show()
app.exec()
一行一行的瀏覽
window = Qt::Widget.new()
在這裡,我們簡單地建立一個空白的 widget 物件。Qt::Widget 類別是所有使用者界面物件的基礎類別。widget 是使用者界面物件的原子:它接收滑鼠、鍵盤和其他來自視窗系統的事件,並在螢幕上描繪自身代表。widget 會被其父 widget 和在它前面的 widget 修剪。
一個沒有嵌入在父 widget 的 widget,像這樣的特殊 widget,被稱為視窗(window)。通常視窗會有視窗系統提供的外框和工作列(taskbar)項目。沒有父 widget 的 widget 就是一個獨立的視窗。其在螢幕上的初始位置是視窗系統所控制。
window.resize(200, 120)
我們設定視窗的寬為200像素,高為120像素。
quit = Qt::PushButton.new('Quit', window)
子 widget 誕生。Qt::PushButton 建立並指定父 widget(window)。子 widget 總是顯示在其父的區域裡面。當顯示時,它會被其父 widget 的邊界裁剪。預設情況下,它會被放置在其父 widget 的左上角,在(0,0)的位置。
quit.setGeometry(10, 40, 180, 40)
Qt::Widget::setGeometry() 函式有四個參數:前兩個參數是按鈕左上角的x和y坐標。坐標是相對於父 widget。而後兩個參數是按鈕的寬度和高度。結果是按鈕的範圍從(10,40)到(190,80)。
window.show()
當父 widget 顯示時,它會呼叫顯示其所有的子 widget(除了那些已明確使用Qt::Widget::hide() 隱藏的)。
執行應用程式
該按鈕不再填滿整個視窗。相反地,因為 Qt::Widget::setGeometry() 呼叫,它留在視窗(10,40)的位置和以及(180,40)的大小。
練習
嘗試調整視窗的大小。按鈕有什麼改變?如果你使用更大的字體執行該程式,按鈕的高度會發生什麼改變?如果你試圖使視窗變得非常小,會發生什麼事?
