Development/Tutorials/Qt4 Ruby Tutorial/Chapter 10: Difference between revisions
Created page with '{{Template:I18n/Language Navigation Bar|Development/Tutorials/Qt4 Ruby Tutorial/Chapter 10}} {{TutorialBrowser| series=[[Development/Tutorials/Qt4_Ruby_Tutorial|Qt4 Ruby Tutori...' |
No edit summary |
||
| (6 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<languages /> | |||
series=[[Development/Tutorials/Qt4_Ruby_Tutorial|Qt4 Ruby Tutorial]]| | {{<translate><!--T:1--> | ||
TutorialBrowser</translate>| | |||
name=Smooth as Silk| | series=[[Special:myLanguage/Development/Tutorials/Qt4_Ruby_Tutorial|<translate><!--T:2--> | ||
Qt4 Ruby Tutorial</translate>]]| | |||
pre=[[Development/Tutorials/Qt4_Ruby_Tutorial/Chapter_09|Tutorial 9 - With Cannon You Can]]| | name=<translate><!--T:3--> | ||
Smooth as Silk</translate>| | |||
next=[[Development/Tutorials/Qt4_Ruby_Tutorial/Chapter_11|Tutorial 11 - Giving It a Shot]] | pre=[[Special:myLanguage/Development/Tutorials/Qt4_Ruby_Tutorial/Chapter_09|<translate><!--T:4--> | ||
Tutorial 9 - With Cannon You Can</translate>]]| | |||
next=[[Special:myLanguage/Development/Tutorials/Qt4_Ruby_Tutorial/Chapter_11|<translate><!--T:5--> | |||
Tutorial 11 - Giving It a Shot</translate>]] | |||
}} | }} | ||
== Smooth as Silk == | <translate> | ||
== Smooth as Silk == <!--T:6--> | |||
</translate> | |||
<translate> | |||
<!--T:7--> | |||
[[Image:Qt4_Ruby_Tutorial_Screenshot_10.png|center]] | [[Image:Qt4_Ruby_Tutorial_Screenshot_10.png|center]] | ||
</translate> | |||
<translate> | |||
<!--T:8--> | |||
Files: | Files: | ||
</translate> | |||
* [http://www.darshancomputing.com/qt4-qtruby-tutorial/tutorial/t10/lcdrange.rb lcdrange.rb] | * [http://www.darshancomputing.com/qt4-qtruby-tutorial/tutorial/t10/lcdrange.rb lcdrange.rb] | ||
* [http://www.darshancomputing.com/qt4-qtruby-tutorial/tutorial/t10/t10.rb t10.rb] | * [http://www.darshancomputing.com/qt4-qtruby-tutorial/tutorial/t10/t10.rb t10.rb] | ||
* [http://www.darshancomputing.com/qt4-qtruby-tutorial/tutorial/t10/cannon.rb cannon.rb] | * [http://www.darshancomputing.com/qt4-qtruby-tutorial/tutorial/t10/cannon.rb cannon.rb] | ||
=== Overview === | <translate> | ||
=== Overview === <!--T:9--> | |||
<!--T:10--> | |||
In this example, we add a force control. | In this example, we add a force control. | ||
=== Line by Line Walkthrough === | === Line by Line Walkthrough === <!--T:11--> | ||
</translate> | |||
'''[http://www.darshancomputing.com/qt4-qtruby-tutorial/tutorial/t10/cannon.rb cannon.rb]''' | '''[http://www.darshancomputing.com/qt4-qtruby-tutorial/tutorial/t10/cannon.rb cannon.rb]''' | ||
The CannonField now has a force value in addition to the angle. | <translate> | ||
<!--T:12--> | |||
The '''<tt>CannonField</tt>''' now has a force value in addition to the angle. | |||
</translate> | |||
< | <syntaxhighlight lang="ruby"> | ||
signals 'angleChanged(int)', 'forceChanged(int)' | signals 'angleChanged(int)', 'forceChanged(int)' | ||
slots 'setAngle(int)', 'setForce(int)' | slots 'setAngle(int)', 'setForce(int)' | ||
</ | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
<translate> | |||
<!--T:13--> | |||
The interface to the force follows the same practice as for the angle. | The interface to the force follows the same practice as for the angle. | ||
</translate> | |||
< | <syntaxhighlight lang="ruby"> | ||
def initialize(parent = nil) | def initialize(parent = nil) | ||
super() | super() | ||
| Line 43: | Line 63: | ||
setAutoFillBackground(true) | setAutoFillBackground(true) | ||
end | end | ||
</ | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
The force @currentForce is initialized to zero. | <translate> | ||
<!--T:14--> | |||
The force '''<tt>@currentForce</tt>''' is initialized to zero. | |||
</translate> | |||
< | <syntaxhighlight lang="ruby"> | ||
def setAngle(angle) | |||
if angle < 5 | |||
angle = 5 | |||
elsif angle > 70 | |||
angle = 70 | |||
end | |||
if @currentAngle == angle | |||
return | |||
end | end | ||
@currentAngle = angle | |||
update(cannonRect()) | |||
emit angleChanged(@currentAngle) | |||
end | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
< | <translate> | ||
<!--T:15--> | |||
We have made a slight change in the '''<tt>setAngle()</tt>''' function. It repaints only the portion of the widget that contains the cannon. | |||
</translate> | |||
@currentForce = force | <syntaxhighlight lang="ruby"> | ||
def setForce(force) | |||
if force < 0 | |||
force = 0 | |||
end | |||
if @currentForce == force | |||
return | |||
end | end | ||
The implementation of setForce() is quite similar to that of setAngle(). The only difference is that because we don't show the force value, we don't need to repaint the widget. | @currentForce = force | ||
emit forceChanged(@currentForce) | |||
end | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
<translate> | |||
<!--T:16--> | |||
The implementation of '''<tt>setForce()</tt>''' is quite similar to that of '''<tt>setAngle()</tt>'''. The only difference is that because we don't show the force value, we don't need to repaint the widget. | |||
</translate> | |||
< | <syntaxhighlight lang="ruby"> | ||
def paintEvent(event) | |||
painter = Qt::Painter.new(self) | |||
painter.setPen(Qt::NoPen) | |||
painter.setBrush(Qt::Brush.new(Qt::blue)) | |||
painter.translate(0, height()) | |||
painter.drawPie(Qt::Rect.new(-35, -35, 70, 70), 0, 90 * 16) | |||
painter.rotate(-@currentAngle) | |||
painter.drawRect(Qt::Rect.new(30, -5, 20, 10)) | |||
painter.end() | |||
end | |||
</ | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
<translate> | |||
<!--T:17--> | |||
We paint as in Chapter 9. | We paint as in Chapter 9. | ||
</translate> | |||
< | <syntaxhighlight lang="ruby"> | ||
def cannonRect() | |||
result = Qt::Rect.new(0, 0, 50, 50) | |||
result.moveBottomLeft(rect().bottomLeft()) | |||
return result | |||
end | |||
</ | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
The cannonRect() function returns the rectangle enclosing the cannon in widget coordinates. First we create a rectangle with the size 50 x 50 and then move it so its bottom-left corner is equal to the widget's own bottom-left corner. | <translate> | ||
<!--T:18--> | |||
The '''<tt>cannonRect()</tt>''' function returns the rectangle enclosing the cannon in widget coordinates. First we create a rectangle with the size 50 x 50 and then move it so its bottom-left corner is equal to the widget's own bottom-left corner. | |||
The Qt::Widget::rect() function returns the widget's enclosing rectangle in the widget's own coordinates. The top-left corner of the rectangle is always (0, 0). | <!--T:19--> | ||
The [http://doc.qt.nokia.com/latest/qwidget.html#rect-prop Qt::Widget::rect()] function returns the widget's enclosing rectangle in the widget's own coordinates. The top-left corner of the rectangle is always (0, 0). | |||
</translate> | |||
'''[http://www.darshancomputing.com/qt4-qtruby-tutorial/tutorial/t10/t10.rb t10.rb]''' | '''[http://www.darshancomputing.com/qt4-qtruby-tutorial/tutorial/t10/t10.rb t10.rb]''' | ||
<translate> | |||
<!--T:20--> | |||
The constructor is mostly the same, but some new bits have been added. | The constructor is mostly the same, but some new bits have been added. | ||
</translate> | |||
< | <syntaxhighlight lang="ruby"> | ||
force = LCDRange.new() | force = LCDRange.new() | ||
force.setRange(10, 50) | force.setRange(10, 50) | ||
</ | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
We add a second LCDRange, which will be used to set the force. | <translate> | ||
<!--T:21--> | |||
We add a second '''<tt>LCDRange</tt>''', which will be used to set the force. | |||
</translate> | |||
< | <syntaxhighlight lang="ruby"> | ||
connect(force, SIGNAL('valueChanged(int)'), | |||
cannonField, SLOT('setForce(int)')) | |||
connect(cannonField, SIGNAL('forceChanged(int)'), | |||
force, SLOT('setValue(int)')) | |||
</ | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
We connect the force widget and the cannonField widget, just like we did for the angle widget. | <translate> | ||
<!--T:22--> | |||
We connect the '''<tt>force</tt>''' widget and the '''<tt>cannonField</tt>''' widget, just like we did for the '''<tt>angle</tt>''' widget. | |||
</translate> | |||
< | <syntaxhighlight lang="ruby"> | ||
leftLayout = Qt::VBoxLayout.new() | leftLayout = Qt::VBoxLayout.new() | ||
leftLayout.addWidget(angle) | leftLayout.addWidget(angle) | ||
| Line 142: | Line 187: | ||
gridLayout.addWidget(cannonField, 1, 1, 2, 1) | gridLayout.addWidget(cannonField, 1, 1, 2, 1) | ||
gridLayout.setColumnStretch(1, 10) | gridLayout.setColumnStretch(1, 10) | ||
</ | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
In Chapter 9, we put angle in the lower-left cell of the layout. Now we want to have two widgets in that cell, so we make a vertical box, put the vertical box in the grid cell, and put each of angle and range in the vertical box. | <translate> | ||
<!--T:23--> | |||
In Chapter 9, we put '''<tt>angle</tt>''' in the lower-left cell of the layout. Now we want to have two widgets in that cell, so we make a vertical box, put the vertical box in the grid cell, and put each of '''<tt>angle</tt>''' and '''<tt>range</tt>''' in the vertical box. | |||
</translate> | |||
< | <syntaxhighlight lang="ruby"> | ||
force.setValue(25) | |||
</ | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
<translate> | |||
<!--T:24--> | |||
We initialize the force value to 25. | We initialize the force value to 25. | ||
</translate> | |||
=== Running the Application === | <translate> | ||
=== Running the Application === <!--T:25--> | |||
<!--T:26--> | |||
We now have a force control. | We now have a force control. | ||
=== Exercises === | === Exercises === <!--T:27--> | ||
Make the size of the cannon barrel be dependent on the force. | Make the size of the cannon barrel be dependent on the force. | ||
<!--T:28--> | |||
Put the cannon in the bottom-right corner. | Put the cannon in the bottom-right corner. | ||
Try adding a better keyboard interface. For example, make + and - increase and decrease the force and enter shoot. If you're bothered by the way the Left and Right keys work, change that too. [Hint: Reimplement Qt::Widget::keyPressEvent().] | <!--T:29--> | ||
Try adding a better keyboard interface. For example, make + and - increase and decrease the force and enter shoot. If you're bothered by the way the '''<tt>Left</tt>''' and '''<tt>Right</tt>''' keys work, change that too. [Hint: Reimplement [http://doc.qt.nokia.com/latest/qwidget.html#keyPressEvent Qt::Widget::keyPressEvent()].] | |||
<!--T:30--> | |||
[[Category:Ruby]] | |||
</translate> | |||
Latest revision as of 14:21, 18 July 2012
| Tutorial Series | Qt4 Ruby Tutorial |
| Previous | Tutorial 9 - With Cannon You Can |
| What's Next | Tutorial 11 - Giving It a Shot |
| Further Reading | n/a |
Smooth as Silk
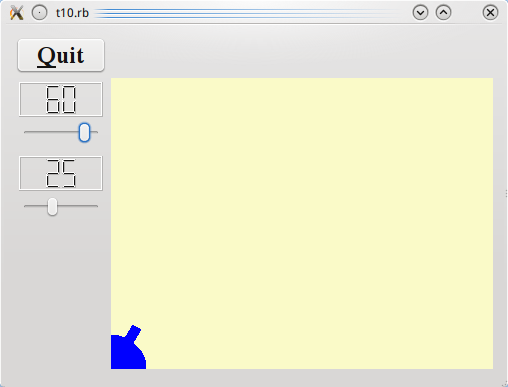
Files:
Overview
In this example, we add a force control.
Line by Line Walkthrough
The CannonField now has a force value in addition to the angle.
signals 'angleChanged(int)', 'forceChanged(int)'
slots 'setAngle(int)', 'setForce(int)'
The interface to the force follows the same practice as for the angle.
def initialize(parent = nil)
super()
@currentAngle = 45
@currentForce = 0
setPalette(Qt::Palette.new(Qt::Color.new(250, 250, 200)))
setAutoFillBackground(true)
end
The force @currentForce is initialized to zero.
def setAngle(angle)
if angle < 5
angle = 5
elsif angle > 70
angle = 70
end
if @currentAngle == angle
return
end
@currentAngle = angle
update(cannonRect())
emit angleChanged(@currentAngle)
end
We have made a slight change in the setAngle() function. It repaints only the portion of the widget that contains the cannon.
def setForce(force)
if force < 0
force = 0
end
if @currentForce == force
return
end
@currentForce = force
emit forceChanged(@currentForce)
end
The implementation of setForce() is quite similar to that of setAngle(). The only difference is that because we don't show the force value, we don't need to repaint the widget.
def paintEvent(event)
painter = Qt::Painter.new(self)
painter.setPen(Qt::NoPen)
painter.setBrush(Qt::Brush.new(Qt::blue))
painter.translate(0, height())
painter.drawPie(Qt::Rect.new(-35, -35, 70, 70), 0, 90 * 16)
painter.rotate(-@currentAngle)
painter.drawRect(Qt::Rect.new(30, -5, 20, 10))
painter.end()
end
We paint as in Chapter 9.
def cannonRect()
result = Qt::Rect.new(0, 0, 50, 50)
result.moveBottomLeft(rect().bottomLeft())
return result
end
The cannonRect() function returns the rectangle enclosing the cannon in widget coordinates. First we create a rectangle with the size 50 x 50 and then move it so its bottom-left corner is equal to the widget's own bottom-left corner.
The Qt::Widget::rect() function returns the widget's enclosing rectangle in the widget's own coordinates. The top-left corner of the rectangle is always (0, 0).
The constructor is mostly the same, but some new bits have been added.
force = LCDRange.new()
force.setRange(10, 50)
We add a second LCDRange, which will be used to set the force.
connect(force, SIGNAL('valueChanged(int)'),
cannonField, SLOT('setForce(int)'))
connect(cannonField, SIGNAL('forceChanged(int)'),
force, SLOT('setValue(int)'))
We connect the force widget and the cannonField widget, just like we did for the angle widget.
leftLayout = Qt::VBoxLayout.new()
leftLayout.addWidget(angle)
leftLayout.addWidget(force)
gridLayout = Qt::GridLayout.new()
gridLayout.addWidget(quit, 0, 0)
gridLayout.addLayout(leftLayout, 1, 0)
gridLayout.addWidget(cannonField, 1, 1, 2, 1)
gridLayout.setColumnStretch(1, 10)
In Chapter 9, we put angle in the lower-left cell of the layout. Now we want to have two widgets in that cell, so we make a vertical box, put the vertical box in the grid cell, and put each of angle and range in the vertical box.
force.setValue(25)
We initialize the force value to 25.
Running the Application
We now have a force control.
Exercises
Make the size of the cannon barrel be dependent on the force.
Put the cannon in the bottom-right corner.
Try adding a better keyboard interface. For example, make + and - increase and decrease the force and enter shoot. If you're bothered by the way the Left and Right keys work, change that too. [Hint: Reimplement Qt::Widget::keyPressEvent().]
