Development/Tutorials/First program/KF5: Difference between revisions
Rough draft |
m Remove use of ECM_KDE_MODULE_DIR, part of ECM_MODULE_PATH |
||
| (11 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
<translate> | <translate> | ||
<!--T: | <!--T:35--> | ||
series=Beginner Tutorial| | series=Beginner Tutorial| | ||
<!--T: | <!--T:36--> | ||
name=Hello World| | name=Hello World| | ||
<!--T: | <!--T:37--> | ||
pre=[http://mindview.net/Books/TICPP/ThinkingInCPP2e.html C++], [http://qt.nokia.com Qt], [[Getting_Started/Build|Building KDE]]| | pre=[http://mindview.net/Books/TICPP/ThinkingInCPP2e.html C++], [http://qt.nokia.com Qt], [[Getting_Started/Build|Building KDE]]| | ||
<!--T: | <!--T:38--> | ||
next=[[Development/Tutorials/Using_KXmlGuiWindow|Tutorial 2 - KXmlGuiWindow]]| | next=[[Development/Tutorials/Using_KXmlGuiWindow/KF5|Tutorial 2 - KXmlGuiWindow]]| | ||
<!--T: | <!--T:39--> | ||
reading=[[Development/Tutorials/CMake|CMake]] | reading=[[Development/Tutorials/CMake|CMake]] | ||
}} | }} | ||
==Abstract== | ==Abstract== <!--T:6--> | ||
<!--T:7--> | |||
Your first program shall greet the world with a friendly "Hello World", what else? For that, we will use a {{class|KMessageBox}} and customise one of the buttons. | |||
<!--T:40--> | |||
[[image:Introtokdetutorial1-kf5.png|frame|center]] | [[image:Introtokdetutorial1-kf5.png|frame|center]] | ||
<!--T:8--> | |||
{{Tip|To get more information about any class you come across, you can use the ‘kde’ search engine. For example, to look for information about KMessageBox, just type "kde:kmessagebox" into Konqueror, Rekonq or KRunner, and you’ll be taken to the documentation.}} | |||
<!--T:9--> | |||
{{Tip| | |||
You might want to use [[KDevelop|KDevelop]] or [[qtcreator|QtCreator]] as IDE for your projects. | |||
}} | |||
==The Code== <!--T:10--> | |||
<!--T:11--> | |||
All the code we need will be in one file, <tt>main.cpp</tt>. Create that file with the code below: | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="cpp-qt"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="cpp-qt"> | ||
#include <cstdlib> | #include <cstdlib> | ||
<!--T:14--> | |||
#include <QApplication> | #include <QApplication> | ||
#include <QCommandLineParser> | #include <QCommandLineParser> | ||
#include <KAboutData> | #include <KAboutData> | ||
#include <KLocalizedString> | #include <KLocalizedString> | ||
#include <KMessageBox> | #include <KMessageBox> | ||
<!--T:13--> | |||
int main (int argc, char *argv[]) | int main (int argc, char *argv[]) | ||
{ | { | ||
QApplication app(argc, argv); | QApplication app(argc, argv); | ||
KLocalizedString::setApplicationDomain("tutorial1"); | KLocalizedString::setApplicationDomain("tutorial1"); | ||
KAboutData aboutData( | KAboutData aboutData( | ||
// The program name used internally. (componentName) | // The program name used internally. (componentName) | ||
QStringLiteral("tutorial1"), | QStringLiteral("tutorial1"), | ||
// A displayable program name string. (displayName) | // A displayable program name string. (displayName) | ||
i18n("Tutorial 1"), | i18n("Tutorial 1"), | ||
// The program version string. (version) | // The program version string. (version) | ||
| Line 59: | Line 68: | ||
i18n("Displays a KMessageBox popup"), | i18n("Displays a KMessageBox popup"), | ||
// The license this code is released under | // The license this code is released under | ||
KAboutLicense::GPL, | KAboutLicense::GPL, | ||
// Copyright Statement (copyrightStatement = QString()) | // Copyright Statement (copyrightStatement = QString()) | ||
| Line 68: | Line 76: | ||
// The program homepage string. (homePageAddress = QString()) | // The program homepage string. (homePageAddress = QString()) | ||
QStringLiteral("http://example.com/"), | QStringLiteral("http://example.com/"), | ||
// The bug report email address (bugsEmailAddress = QLatin1String("[email protected]") | // The bug report email address | ||
// (bugsEmailAddress = QLatin1String("[email protected]") | |||
QStringLiteral("[email protected]")); | QStringLiteral("[email protected]")); | ||
aboutData.addAuthor(i18n("Name"), i18n("Task"), QStringLiteral("[email protected]"), | |||
aboutData.addAuthor(i18n("Name"), i18n("Task"), QStringLiteral("[email protected]"), QStringLiteral("http://your.website.com"), QStringLiteral("OSC Username")); | QStringLiteral("http://your.website.com"), QStringLiteral("OSC Username")); | ||
KAboutData::setApplicationData(aboutData); | KAboutData::setApplicationData(aboutData); | ||
<!--T:41--> | |||
QCommandLineParser parser; | |||
parser.addHelpOption(); | parser.addHelpOption(); | ||
parser.addVersionOption(); | parser.addVersionOption(); | ||
| Line 88: | Line 95: | ||
i18n( "This is a WhatsThis help text." ) ); | i18n( "This is a WhatsThis help text." ) ); | ||
return | <!--T:42--> | ||
return | |||
KMessageBox::questionYesNo | KMessageBox::questionYesNo | ||
(0, i18n( "Hello World" ), i18n( "Hello" ), yesButton ) | (0, i18n( "Hello World" ), i18n( "Hello" ), yesButton ) | ||
| Line 94: | Line 102: | ||
} | } | ||
<!--T:43--> | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
First we need to create a [http://doc.qt.io/qt-5/qapplication.html QApplication] object. This needs to be done exactly once in each program since it is needed for things such as [[Development/Tutorials/Localization/i18n|i18n]]. It also should be created before any other KDE or Qt object. A call to {{class|KLocalizedString}}::setApplicationDomain() is required to properly set the translation catalog and must be done before the next step happens. | |||
<!--T:15--> | |||
The first KDE specific object we create in this program is {{class|KAboutData}}. This is the class used to store information about the program such as a short description, authors or license information. Pretty much every KDE application should use this class. We then call {{class|KAboutData}}::setApplicationData() to initialize the properties of the [http://doc.qt.io/qt-5/qapplication.html QApplication] object. | |||
<!--T:16--> | |||
Then we come to [http://doc.qt.io/qt-5/qcommandlineparser.html QCommandLineParser]. This is the class one would use to specify command line switches to, for example, open the program with a specific file. However, in this tutorial, we simply initialise it with the {{class|KAboutData}} object we created so we can use the <tt>--version</tt> or <tt>--author</tt> switches. | |||
<!--T:17--> | |||
Now we've done all the necessary KDE setup, we can move on to doing interesting things with our application. We're going to create a popup box but we're going to customise one of the buttons. To do this customisation, we need to use a {{class|KGuiItem}} object. The first argument in the {{class|KGuiItem}} constructor is the text that will appear on the item (in our case, a button). Then we have an option of setting an icon for the button but we don't want one so we just give it <tt>QString()</tt>. We then set the tooltip (what appears when you hover over an item) and finally the "What's This?" (accessed through right-clicking or Shift-F1) text. | |||
<!--T:18--> | |||
Now we have our item, we can create our popup. We call the <tt>{{class|KMessageBox}}::questionYesNo()</tt> function which, by default, creates a message box with a "Yes" and a "No" button. The second argument is the text that will appear in the message box above the buttons. The third is the caption the window will have and finally we set the KGuiItem for (what would normally be) the "Yes" button to the <tt>KGuiItem yesButton</tt> we created. | |||
<!--T:19--> | |||
Note that all user-visible text is passed through the i18n() function; this is necessary for the UI to be translatable. More information on localization can be found in the [[Development/Tutorials/Localization/i18n|localization tutorial]]. | |||
<!--T:20--> | |||
We're all done as far as the code is concerned. Now to build it and try it out. | |||
== Build == <!--T:21--> | |||
<!--T:22--> | |||
You want to [[Development/Tutorials/CMake|use CMake]] for your build environment. You provide a file CMakeLists.txt, cmake uses this file to generate all Makefiles out of it. | |||
=== CMakeLists.txt === <!--T:23--> | |||
<!--T:24--> | |||
Create a file named CMakeLists.txt in the same directory as main.cpp with this content: | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="cmake"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="cmake"> | ||
project (tutorial1) | project (tutorial1) | ||
<!--T:44--> | |||
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 2.8.12 FATAL_ERROR) | cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 2.8.12 FATAL_ERROR) | ||
set(QT_MIN_VERSION "5.3.0") | set(QT_MIN_VERSION "5.3.0") | ||
set(KF5_MIN_VERSION "5.2.0") | set(KF5_MIN_VERSION "5.2.0") | ||
<!--T:45--> | |||
find_package(ECM 1.0.0 REQUIRED NO_MODULE) | find_package(ECM 1.0.0 REQUIRED NO_MODULE) | ||
set(CMAKE_MODULE_PATH ${ECM_MODULE_PATH | set(CMAKE_MODULE_PATH ${ECM_MODULE_PATH} ${CMAKE_CURRENT_SOURCE_DIR}/cmake) | ||
<!--T:46--> | |||
include(KDEInstallDirs) | include(KDEInstallDirs) | ||
include(KDECMakeSettings) | include(KDECMakeSettings) | ||
| Line 125: | Line 151: | ||
include(FeatureSummary) | include(FeatureSummary) | ||
<!--T:47--> | |||
# Find Qt modules | # Find Qt modules | ||
find_package(Qt5 ${QT_MIN_VERSION} CONFIG REQUIRED COMPONENTS | find_package(Qt5 ${QT_MIN_VERSION} CONFIG REQUIRED COMPONENTS | ||
| Line 131: | Line 158: | ||
) | ) | ||
<!--T:48--> | |||
# Find KDE modules | # Find KDE modules | ||
find_package(KF5 ${KF5_MIN_VERSION} REQUIRED COMPONENTS | find_package(KF5 ${KF5_MIN_VERSION} REQUIRED COMPONENTS | ||
| Line 138: | Line 166: | ||
) | ) | ||
<!--T:49--> | |||
feature_summary(WHAT ALL INCLUDE_QUIET_PACKAGES FATAL_ON_MISSING_REQUIRED_PACKAGES) | feature_summary(WHAT ALL INCLUDE_QUIET_PACKAGES FATAL_ON_MISSING_REQUIRED_PACKAGES) | ||
set(tutorial1_SRCS main.cpp) | set(tutorial1_SRCS main.cpp) | ||
<!--T:50--> | |||
add_executable(tutorial1 ${tutorial1_SRCS}) | add_executable(tutorial1 ${tutorial1_SRCS}) | ||
<!--T:51--> | |||
target_link_libraries(tutorial1 | target_link_libraries(tutorial1 | ||
Qt5::Widgets | Qt5::Widgets | ||
| Line 153: | Line 182: | ||
) | ) | ||
<!--T:52--> | |||
install(TARGETS tutorial1 ${INSTALL_TARGETS_DEFAULT_ARGS}) | install(TARGETS tutorial1 ${INSTALL_TARGETS_DEFAULT_ARGS}) | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
The <tt>find_package()</tt> function locates the package that you ask it for (in this case ECM, Qt5, or KF5) and sets some variables describing the location of the package's headers and libraries. ECM, or Extra CMake Modules, is required to import special CMake files and functions for building KDE applications. | |||
<!--T:25--> | |||
Here we try to find the modules for Qt 5 and KDE Frameworks 5 required to build our tutorial. The necessary files are included by CMake so that the compiler can see them at build time. Minimum version numbers are set at the very top of CMakeLists.txt file for easier reference. | |||
<!--T:26--> | |||
Next we create a variable called <tt>tutorial1_SRCS</tt> using the <tt>set()</tt> function. In this case we simply set it to the name of our only source file. | |||
<!--T:27--> | |||
Then we use <tt>add_executable()</tt> to create an executable called <tt>tutorial1</tt> from the source files listed in our <tt>tutorial1_SRCS</tt> variable. Afterwards, we link our executable to the necessary libraries using <tt>target_link_libraries()</tt> function. The line starting with <tt>install</tt> writes a default "install" target into the Makefile. | |||
=== Make And Run === <!--T:28--> | |||
<!--T:29--> | |||
To compile, link and install your program, you must have several software installed, e.g. cmake, make and gcc-c++, and the Qt 5 and KDE Frameworks development files. To be sure you have everything, best follow [[Getting_Started/Build/Environment|this install guide]]. | |||
<!--T:30--> | |||
While you can run cmake directly inside the source code directory itself, it is a best practice, and actually enforced in some KDE software, to use a separate build directory and run cmake from there: | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | |||
mkdir build && cd build | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
You can invoke CMake and make manually: | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | |||
cmake .. && make | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
<!--T:31--> | |||
And launch it with: | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | |||
./tutorial1 | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
== | ==Moving On== <!--T:32--> | ||
<!--T:33--> | |||
Now you can move on to [[Development/Tutorials/Using_KXmlGuiWindow/KF5|using KXmlGuiWindow]]. | |||
<!--T:34--> | |||
[[Category:C++]] | [[Category:C++]] | ||
</translate> | </translate> | ||
Latest revision as of 18:00, 18 April 2020
| Tutorial Series | Beginner Tutorial |
| Previous | C++, Qt, Building KDE |
| What's Next | Tutorial 2 - KXmlGuiWindow |
| Further Reading | CMake |
Abstract
Your first program shall greet the world with a friendly "Hello World", what else? For that, we will use a KMessageBox and customise one of the buttons.
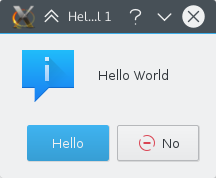

The Code
All the code we need will be in one file, main.cpp. Create that file with the code below:
#include <cstdlib>
#include <QApplication>
#include <QCommandLineParser>
#include <KAboutData>
#include <KLocalizedString>
#include <KMessageBox>
int main (int argc, char *argv[])
{
QApplication app(argc, argv);
KLocalizedString::setApplicationDomain("tutorial1");
KAboutData aboutData(
// The program name used internally. (componentName)
QStringLiteral("tutorial1"),
// A displayable program name string. (displayName)
i18n("Tutorial 1"),
// The program version string. (version)
QStringLiteral("1.0"),
// Short description of what the app does. (shortDescription)
i18n("Displays a KMessageBox popup"),
// The license this code is released under
KAboutLicense::GPL,
// Copyright Statement (copyrightStatement = QString())
i18n("(c) 2015"),
// Optional text shown in the About box.
// Can contain any information desired. (otherText)
i18n("Some text..."),
// The program homepage string. (homePageAddress = QString())
QStringLiteral("http://example.com/"),
// The bug report email address
// (bugsEmailAddress = QLatin1String("[email protected]")
QStringLiteral("[email protected]"));
aboutData.addAuthor(i18n("Name"), i18n("Task"), QStringLiteral("[email protected]"),
QStringLiteral("http://your.website.com"), QStringLiteral("OSC Username"));
KAboutData::setApplicationData(aboutData);
QCommandLineParser parser;
parser.addHelpOption();
parser.addVersionOption();
aboutData.setupCommandLine(&parser);
parser.process(app);
aboutData.processCommandLine(&parser);
KGuiItem yesButton( i18n( "Hello" ), QString(),
i18n( "This is a tooltip" ),
i18n( "This is a WhatsThis help text." ) );
return
KMessageBox::questionYesNo
(0, i18n( "Hello World" ), i18n( "Hello" ), yesButton )
== KMessageBox::Yes? EXIT_SUCCESS: EXIT_FAILURE;
}
First we need to create a QApplication object. This needs to be done exactly once in each program since it is needed for things such as i18n. It also should be created before any other KDE or Qt object. A call to KLocalizedString::setApplicationDomain() is required to properly set the translation catalog and must be done before the next step happens.
The first KDE specific object we create in this program is KAboutData. This is the class used to store information about the program such as a short description, authors or license information. Pretty much every KDE application should use this class. We then call KAboutData::setApplicationData() to initialize the properties of the QApplication object.
Then we come to QCommandLineParser. This is the class one would use to specify command line switches to, for example, open the program with a specific file. However, in this tutorial, we simply initialise it with the KAboutData object we created so we can use the --version or --author switches.
Now we've done all the necessary KDE setup, we can move on to doing interesting things with our application. We're going to create a popup box but we're going to customise one of the buttons. To do this customisation, we need to use a KGuiItem object. The first argument in the KGuiItem constructor is the text that will appear on the item (in our case, a button). Then we have an option of setting an icon for the button but we don't want one so we just give it QString(). We then set the tooltip (what appears when you hover over an item) and finally the "What's This?" (accessed through right-clicking or Shift-F1) text.
Now we have our item, we can create our popup. We call the KMessageBox::questionYesNo() function which, by default, creates a message box with a "Yes" and a "No" button. The second argument is the text that will appear in the message box above the buttons. The third is the caption the window will have and finally we set the KGuiItem for (what would normally be) the "Yes" button to the KGuiItem yesButton we created.
Note that all user-visible text is passed through the i18n() function; this is necessary for the UI to be translatable. More information on localization can be found in the localization tutorial.
We're all done as far as the code is concerned. Now to build it and try it out.
Build
You want to use CMake for your build environment. You provide a file CMakeLists.txt, cmake uses this file to generate all Makefiles out of it.
CMakeLists.txt
Create a file named CMakeLists.txt in the same directory as main.cpp with this content:
project (tutorial1)
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 2.8.12 FATAL_ERROR)
set(QT_MIN_VERSION "5.3.0")
set(KF5_MIN_VERSION "5.2.0")
find_package(ECM 1.0.0 REQUIRED NO_MODULE)
set(CMAKE_MODULE_PATH ${ECM_MODULE_PATH} ${CMAKE_CURRENT_SOURCE_DIR}/cmake)
include(KDEInstallDirs)
include(KDECMakeSettings)
include(KDECompilerSettings)
include(FeatureSummary)
# Find Qt modules
find_package(Qt5 ${QT_MIN_VERSION} CONFIG REQUIRED COMPONENTS
Core # QCommandLineParser, QStringLiteral
Widgets # QApplication
)
# Find KDE modules
find_package(KF5 ${KF5_MIN_VERSION} REQUIRED COMPONENTS
CoreAddons # KAboutData
I18n # KLocalizedString
WidgetsAddons # KMessageBox
)
feature_summary(WHAT ALL INCLUDE_QUIET_PACKAGES FATAL_ON_MISSING_REQUIRED_PACKAGES)
set(tutorial1_SRCS main.cpp)
add_executable(tutorial1 ${tutorial1_SRCS})
target_link_libraries(tutorial1
Qt5::Widgets
KF5::CoreAddons
KF5::I18n
KF5::WidgetsAddons
)
install(TARGETS tutorial1 ${INSTALL_TARGETS_DEFAULT_ARGS})
The find_package() function locates the package that you ask it for (in this case ECM, Qt5, or KF5) and sets some variables describing the location of the package's headers and libraries. ECM, or Extra CMake Modules, is required to import special CMake files and functions for building KDE applications.
Here we try to find the modules for Qt 5 and KDE Frameworks 5 required to build our tutorial. The necessary files are included by CMake so that the compiler can see them at build time. Minimum version numbers are set at the very top of CMakeLists.txt file for easier reference.
Next we create a variable called tutorial1_SRCS using the set() function. In this case we simply set it to the name of our only source file.
Then we use add_executable() to create an executable called tutorial1 from the source files listed in our tutorial1_SRCS variable. Afterwards, we link our executable to the necessary libraries using target_link_libraries() function. The line starting with install writes a default "install" target into the Makefile.
Make And Run
To compile, link and install your program, you must have several software installed, e.g. cmake, make and gcc-c++, and the Qt 5 and KDE Frameworks development files. To be sure you have everything, best follow this install guide.
While you can run cmake directly inside the source code directory itself, it is a best practice, and actually enforced in some KDE software, to use a separate build directory and run cmake from there:
mkdir build && cd build
You can invoke CMake and make manually:
cmake .. && make
And launch it with:
./tutorial1
Moving On
Now you can move on to using KXmlGuiWindow.
