Projects/Usability/HIG/Toggle Buttons: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| (11 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== | ==Purpose== | ||
A toggle button is a button which stays down when clicked once and goes up when clicked a second time. | A toggle button is a button which stays down when clicked once and goes up when clicked a second time. | ||
==When to Use== | ==Guidelines== | ||
===When to Use=== | |||
Use a toggle button to indicate a '''state'''. | Use a toggle button to indicate a '''state'''. | ||
| Line 9: | Line 10: | ||
Example: A word processor should use toggle buttons to indicate the state of "Bold", "Italic" or "Underline" formatting. | Example: A word processor should use toggle buttons to indicate the state of "Bold", "Italic" or "Underline" formatting. | ||
==When not to Use== | [[File:Toggle-button-formatting.png]] | ||
(Toggle buttons used in a rich text editor) | |||
===When not to Use=== | |||
Do not use a toggle button to indicate an '''action'''. | Do not use a toggle button to indicate an '''action'''. | ||
| Line 15: | Line 19: | ||
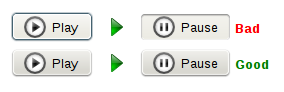
Example: A music player should not use a toggle button to implement a combined Play/Pause button. It should use a normal button and adjust the icon and label to represent the action which would be performed when clicked. | Example: A music player should not use a toggle button to implement a combined Play/Pause button. It should use a normal button and adjust the icon and label to represent the action which would be performed when clicked. | ||
[[File:Toggle-button-media-player.png]] | |||
==Icon and Label== | |||
There are two ways to label a toggle button | There are two ways to label a toggle button. You can either describe the state reached when the button is down or describe the current state. | ||
===First option: Describe the state reached when the button is down=== | |||
In this case the icon and label should not change when the button is down. | In this case the icon and label should not change when the button is down. | ||
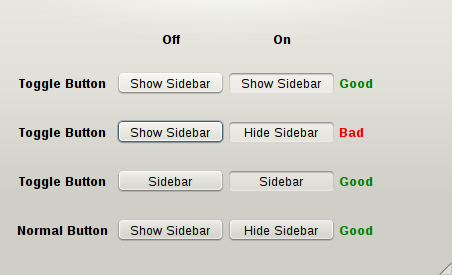
Example: We create a toggle button to toggle the visibility of a sidebar. The label of this button is "Show Sidebar". When the button is toggled down, it should still say "Show Sidebar": it should not be changed to "Hide Sidebar". | |||
If | Think of the button as a check box: when you click a check box you do not expect its label to change. If it makes more sense to change the button text to "Hide Sidebar" when the sidebar is shown then you should use a normal button, not a toggle button. | ||
It is worth noting that unlike normal buttons, the label of a toggle button does not need to contain a verb, as long as there is no ambiguity. In this example the label can be reduced to "Sidebar". | |||
[[File:Toggle-button-summary.png]] | [[File:Toggle-button-summary.png]] | ||
===Second option: Describe the current state=== | |||
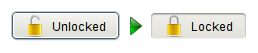
In this case the label will often include a passive verb. For example a button to lock or unlock an element would say "Unlocked" when it is up and "Locked" when it is down. The icon should also change to match the label. | |||
[[File:Toggle-button-unlocked-locked.png]] | |||
===Which option to use=== | |||
There is no strict rule to decide which option is the best, it depends on the context of your application. Note however that the second option has one drawback: since the label change, the button width will change as well. This can be annoying if the button is in the middle of a toolbar as it will cause all buttons after it to shift horizontally. | |||
== Implementation == | |||
* [http://api.kde.org/4.10-api/kdelibs-apidocs/kdeui/html/classKPushButton.html KPushButton] for generic buttons. | |||
* [http://api.kde.org/4.10-api/kdelibs-apidocs/kdeui/html/classKAction.html KAction] is used to generate buttons in toolbars. | |||
Both classes have a <code>checkable</code> property which must be set to <code>true</code> to turn them into toggle buttons. You can then use the <code>checked</code> property to get and set the state of the button. | |||
Revision as of 15:53, 27 June 2013
Purpose
A toggle button is a button which stays down when clicked once and goes up when clicked a second time.
Guidelines
When to Use
Use a toggle button to indicate a state.
Example: A word processor should use toggle buttons to indicate the state of "Bold", "Italic" or "Underline" formatting.
![]() (Toggle buttons used in a rich text editor)
(Toggle buttons used in a rich text editor)
When not to Use
Do not use a toggle button to indicate an action.
Example: A music player should not use a toggle button to implement a combined Play/Pause button. It should use a normal button and adjust the icon and label to represent the action which would be performed when clicked.
Icon and Label
There are two ways to label a toggle button. You can either describe the state reached when the button is down or describe the current state.
First option: Describe the state reached when the button is down
In this case the icon and label should not change when the button is down.
Example: We create a toggle button to toggle the visibility of a sidebar. The label of this button is "Show Sidebar". When the button is toggled down, it should still say "Show Sidebar": it should not be changed to "Hide Sidebar".
Think of the button as a check box: when you click a check box you do not expect its label to change. If it makes more sense to change the button text to "Hide Sidebar" when the sidebar is shown then you should use a normal button, not a toggle button.
It is worth noting that unlike normal buttons, the label of a toggle button does not need to contain a verb, as long as there is no ambiguity. In this example the label can be reduced to "Sidebar".
Second option: Describe the current state
In this case the label will often include a passive verb. For example a button to lock or unlock an element would say "Unlocked" when it is up and "Locked" when it is down. The icon should also change to match the label.
Which option to use
There is no strict rule to decide which option is the best, it depends on the context of your application. Note however that the second option has one drawback: since the label change, the button width will change as well. This can be annoying if the button is in the middle of a toolbar as it will cause all buttons after it to shift horizontally.
Implementation
- KPushButton for generic buttons.
- KAction is used to generate buttons in toolbars.
Both classes have a checkable property which must be set to true to turn them into toggle buttons. You can then use the checked property to get and set the state of the button.